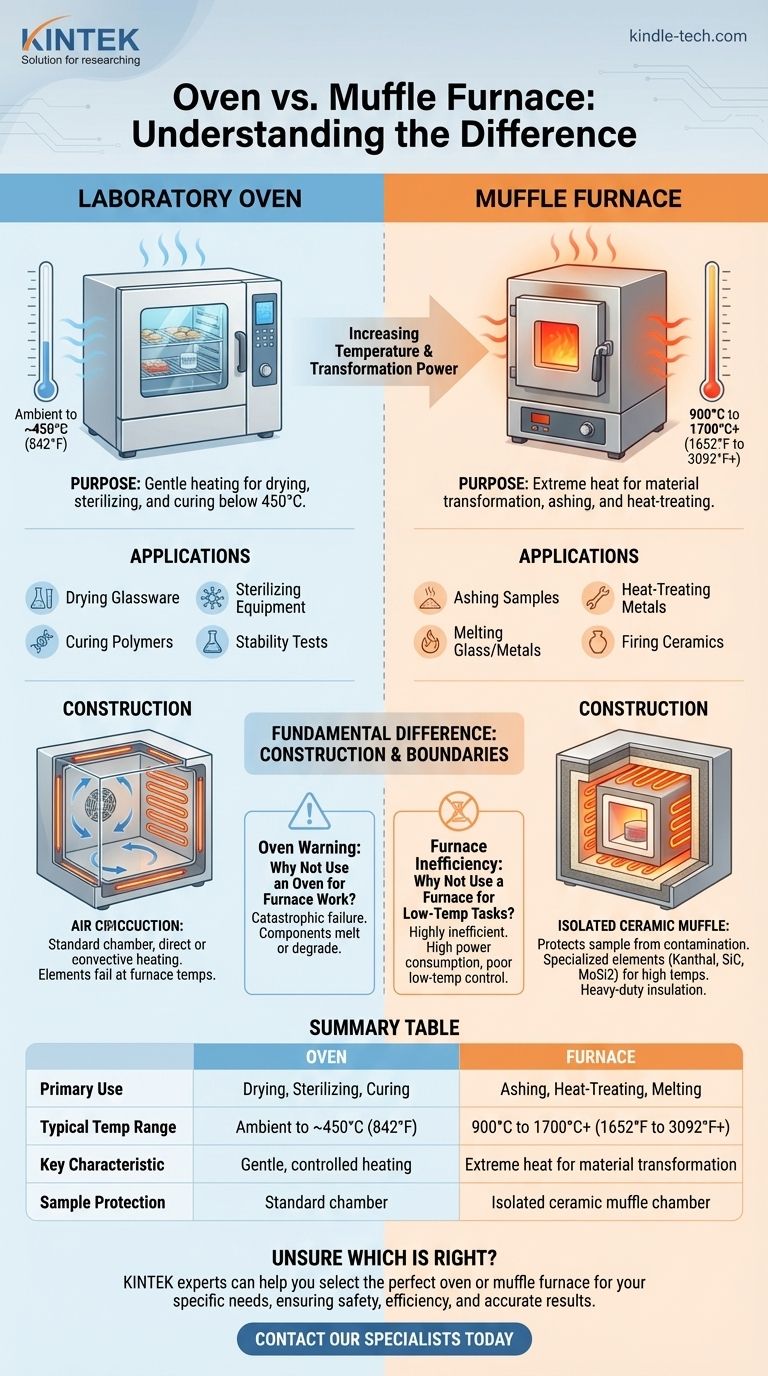
In essence, the primary difference between an oven and a muffle furnace is their operational temperature range and the underlying construction that enables it. A laboratory oven is designed for lower-temperature applications like drying and sterilizing, typically operating up to 450°C. A muffle furnace, by contrast, is built for high-temperature material transformation, reaching temperatures of 900°C to well over 1400°C.
The choice between an oven and a muffle furnace is not about which is superior, but which is engineered for the specific thermal process. Ovens provide controlled, gentle heating, while muffle furnaces create extreme heat environments necessary for altering the fundamental properties of a material.

The Fundamental Difference: Temperature and Purpose
The function of each device is directly tied to its achievable temperature. This dictates the types of applications for which each is suitable.
Laboratory Ovens: Precision at Lower Temperatures
A laboratory oven is the workhorse for processes that do not require extreme heat. Its purpose is often to remove moisture or induce a simple chemical reaction.
Common applications include drying glassware, sterilizing equipment, curing polymers, and performing stability tests on materials. Their temperature range generally spans from slightly above ambient to a maximum of around 450°C (842°F).
Muffle Furnaces: Extreme Heat for Material Transformation
A muffle furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed to fundamentally change a material's state. It is used for processes that require intense, sustained heat far beyond an oven's capability.
Typical applications include ashing samples to determine inorganic content, heat-treating metals to alter their hardness, melting glass or metals, and firing ceramics. These processes require temperatures starting around 900°C (1652°F) and can extend to 1700°C (3092°F) or more.
How Their Construction Dictates Function
The vast difference in temperature capability stems from fundamentally different designs in heating elements, insulation, and chamber construction.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The key feature of a muffle furnace is its namesake: the muffle. This is a high-temperature chamber, typically made of a refractory ceramic material, that contains the sample being heated.
The heating elements are positioned on the outside of this chamber. This design isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, preventing contamination and ensuring highly uniform radiant heat.
Specialized Heating Elements for High Temperatures
A standard oven's heating elements would quickly fail at furnace temperatures. Muffle furnaces use specialized components designed to withstand extreme heat.
The material used for the heating element determines the furnace's maximum temperature:
- Up to 1200°C: Electric heating wires (e.g., Kanthal) are common.
- Up to 1400°C: Silicon-carbon (SiC) rods are required.
- Up to 1700°C: Silicon molybdenum (MoSi2) rods are used for the most demanding applications.
Heavy-Duty Insulation and Control
To safely contain such high temperatures and achieve stability, muffle furnaces are built with multiple layers of high-density refractory insulation. This makes them significantly heavier and more robust than ovens.
Understanding the Application Boundaries
Using the wrong instrument is not just inefficient; it can be dangerous and destructive to both the sample and the equipment.
Why You Can't Use an Oven for Furnace Work
Attempting to push a laboratory oven to furnace-level temperatures would cause catastrophic failure. The heating elements, temperature sensors, door gaskets, and internal wiring are not designed to withstand such heat and would quickly melt or degrade.
The Inefficiency of Using a Furnace for Low-Temp Tasks
While a furnace can be set to a lower temperature, it is highly inefficient. It consumes significantly more power to operate and often lacks the fine temperature control and uniformity needed for delicate drying or curing processes below 300°C.
Selecting the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
Your choice must be guided by the requirements of your specific application to ensure accuracy, safety, and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing below 450°C: A laboratory oven is the correct tool, providing the necessary temperature control and energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is ashing, melting, or heat-treating materials above 900°C: A muffle furnace is the only suitable and safe choice due to its high-temperature construction.
- If you need to protect a sample from contamination during heating: The isolated "muffle" chamber is a critical design feature that makes a muffle furnace the superior option.
Choosing the right thermal processing equipment ensures your results are repeatable and your lab operates safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laboratory Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Drying, Sterilizing, Curing | Ashing, Heat-Treating, Melting |
| Typical Temp Range | Ambient to ~450°C (842°F) | 900°C to 1700°C+ (1652°F to 3092°F+) |
| Key Characteristic | Gentle, controlled heating | Extreme heat for material transformation |
| Sample Protection | Standard chamber | Isolated ceramic muffle chamber |
Unsure which thermal processing equipment is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect oven or muffle furnace for your specific needs, ensuring safety, efficiency, and accurate results.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of muffle furnace? Achieving Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace in the food industry? A Key Tool for Accurate Nutritional Analysis
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the design and construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Isolated Heating Chamber
- What is the importance of muffle furnace? Ensuring Contaminant-Free Heating for Accurate Results



















