Brazing is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, used to create high-strength, reliable joints in everything from jet engine turbines and automotive fuel injectors to medical implants and electronic components. Its unique ability to join different types of metals with minimal heat distortion makes it indispensable in industries where precision and material integrity are paramount.
The core reason brazing is so widely adopted is its capacity to produce strong, clean, and leak-proof joints in complex assemblies—especially with dissimilar or thin materials—where conventional welding would be impractical or destructive.
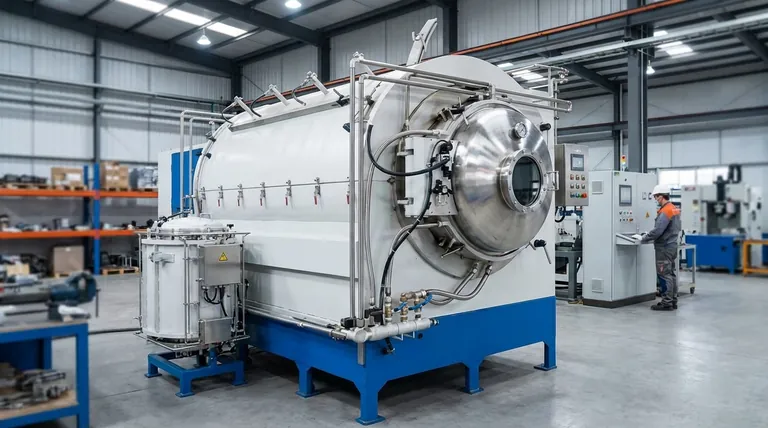

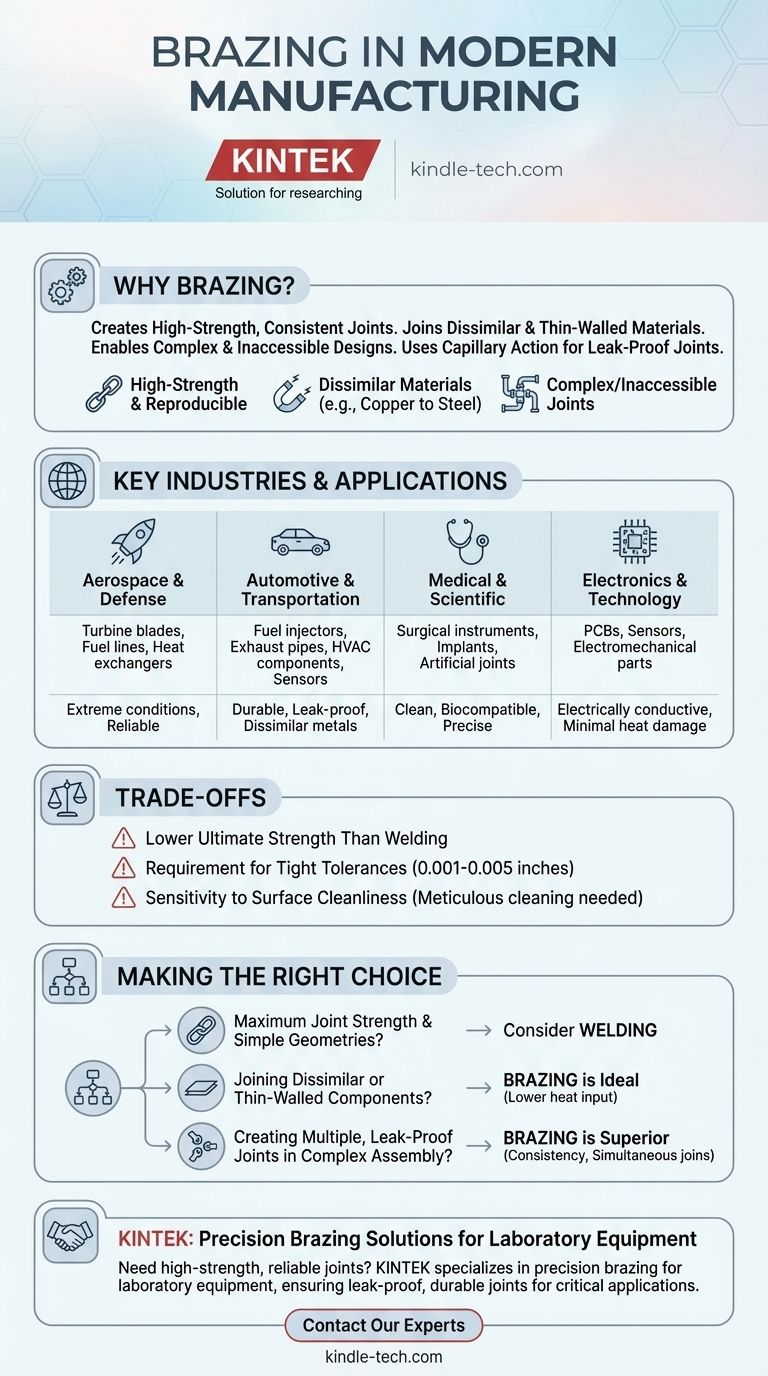
Why Brazing Is Used in Critical Industries
Brazing isn't just another way to join metal; its specific characteristics solve fundamental engineering challenges that other methods cannot. This is why it's trusted for applications where failure is not an option.
Creating High-Strength, Consistent Joints
Brazing creates a metallurgical bond between the filler metal and the base materials. This results in a connection that is exceptionally strong and often stronger than the filler metal itself.
Processes like vacuum furnace brazing offer outstanding reproducibility, ensuring that every joint in a large batch meets the same high-quality standard.
Joining Dissimilar and Thin-Walled Materials
A key advantage of brazing is its ability to join completely different metals, such as copper to steel or aluminum to ceramic. This is extremely difficult or impossible with traditional welding.
Because brazing uses lower temperatures than welding, it minimizes the risk of melting, warping, or distorting the base materials. This makes it ideal for joining delicate or thin-walled components.
Enabling Complex and Inaccessible Designs
Brazing relies on capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting space between components.
This allows engineers to design assemblies with joints that are hidden, located deep within a part, or too intricate for a welding torch to reach. It's also highly effective for creating multiple joints on a single assembly in one heating cycle.
Key Application Examples by Industry
The principles of strength, precision, and versatility make brazing a critical process across a vast range of high-performance sectors.
Aerospace and Defense
In this sector, components must withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and vibrations. Brazing is used for critical parts where reliability is non-negotiable.
Examples include turbine blades, fuel lines and piping, and high-performance heat exchangers.
Automotive and Transportation
Brazing is essential for manufacturing components that manage fluids, heat, and exhaust gases with long-term durability.
Common applications are exhaust pipes, sensors, fuel injectors, and components for HVAC systems and heat exchangers. It is also used in high-performance motorsport, including Formula 1.
Medical and Scientific Instruments
The need for clean, strong, and biocompatible joints makes brazing a preferred method for medical devices.
Typical uses include manufacturing surgical instruments, artificial joints, and other medical implants where joint integrity is crucial for patient safety.
Electronics and Technology
In electronics, brazing provides strong, electrically conductive joints without damaging sensitive components.
It is used to assemble printed circuit boards (PCBs), sensors, and other electromechanical components where precision is key.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is not the universal solution for every joining task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Lower Ultimate Strength Than Welding
A properly executed weld, which fuses the parent metals, will typically be stronger than a brazed joint. Brazing strength is limited by the shear strength of the filler alloy.
Requirement for Tight Tolerances
Brazing depends on capillary action, which only works if the gap between the two parts is very small and precisely controlled (typically 0.001 to 0.005 inches). This often requires more precise machining than welding.
Sensitivity to Surface Cleanliness
The base metal surfaces must be meticulously cleaned before brazing. Any oxides, oils, or contaminants will prevent the filler metal from wetting the surface and creating a strong bond, causing the joint to fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength with simple geometries: You should consider welding, as it fuses the parent metals for a potentially stronger bond.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or thin-walled components: Brazing is an ideal candidate due to its lower heat input, which prevents material damage.
- If your primary focus is creating multiple, leak-proof joints in a complex assembly: Brazing is the superior choice for its consistency and ability to join inaccessible areas simultaneously.
Ultimately, brazing is the engineering solution for creating robust, precise connections where other methods would compromise the integrity of the design.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Benefits of Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Turbine blades, heat exchangers, fuel lines | High strength, withstands extreme temperatures & pressures |
| Automotive & Transportation | Fuel injectors, exhaust pipes, HVAC components | Joins dissimilar metals, leak-proof, durable |
| Medical & Scientific Instruments | Surgical tools, implants, artificial joints | Clean, biocompatible, precise joints |
| Electronics & Technology | PCBs, sensors, electromechanical parts | Electrically conductive, minimal heat damage |
Need high-strength, reliable joints for your lab equipment or components? KINTEK specializes in precision brazing solutions for laboratory equipment and consumables, ensuring leak-proof, durable joints for your most critical applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how our brazing expertise can enhance your product performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining



















