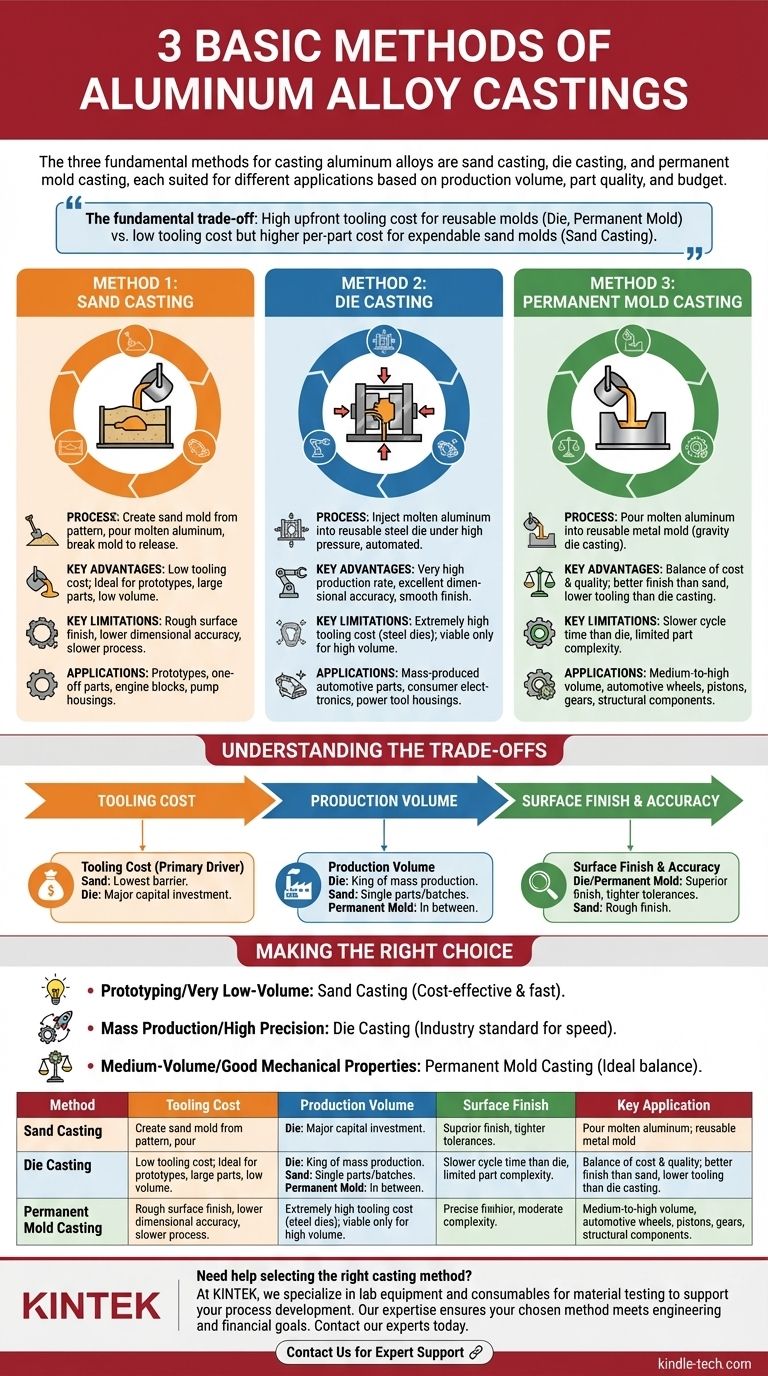
At its core, the three fundamental methods for casting aluminum alloys are sand casting, die casting, and permanent mold casting. Each method uses a different type of mold and filling process, making them suitable for vastly different applications. The choice between them is a critical engineering decision driven by factors like production volume, required part quality, and budget.
The fundamental trade-off in aluminum casting is between the high, upfront tooling cost of reusable metal molds (die and permanent mold casting) for high-volume production and the low tooling cost but higher per-part cost and lower precision of expendable sand molds (sand casting) for prototypes and low-volume runs.
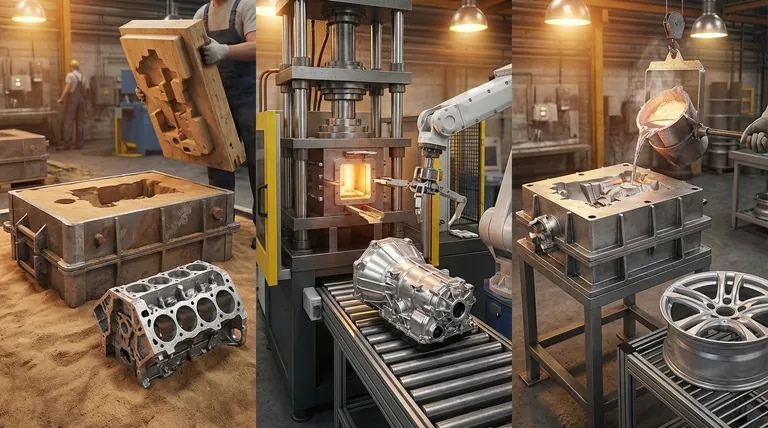

Method 1: Sand Casting
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most versatile metal casting processes. It involves creating a mold out of a sand mixture and then pouring molten aluminum into the cavity to form the part.
The Process: How It Works
A pattern, which is a replica of the final part, is pressed into a tightly packed sand mixture to create a mold cavity. The pattern is removed, and molten aluminum is poured into the cavity. Once the metal solidifies, the sand mold is broken away to release the casting.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage of sand casting is its low tooling cost. Since the patterns are often made of wood or plastic and the sand molds are temporary, the initial investment is minimal compared to other methods. This makes it ideal for producing very large parts or for projects with low production volumes.
Key Limitations
Sand casting produces parts with a rough surface finish and lower dimensional accuracy. The process is also relatively slow, making the per-part cost higher in mass production. More secondary machining is often required to achieve final specifications.
Common Applications
This method is the go-to for prototypes, one-off parts, and low-volume production runs. It's commonly used for large, complex components like automotive engine blocks, cylinder heads, and industrial pump housings.
Method 2: Die Casting
Die casting is a manufacturing process that forces molten aluminum into a reusable steel mold, known as a die, under high pressure. It is a highly automated process designed for speed and precision.
The Process: How It Works
Two hardened tool steel dies are machined into a precise mold cavity. These dies are clamped together tightly as molten aluminum is injected under immense pressure. The pressure is maintained until the casting solidifies, after which the die is opened and the part is ejected.
Key Advantages
Die casting excels at producing parts at a very high rate with excellent dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface finish. It can create complex shapes with thin walls, often eliminating the need for subsequent machining operations.
Key Limitations
The most significant drawback is the extremely high cost of the steel dies. This massive initial investment means die casting is only financially viable for high-volume production where the cost can be amortized over hundreds of thousands of parts.
Common Applications
This is the dominant method for mass-produced aluminum parts requiring high precision. Examples include automotive components (transmission cases, engine components), consumer electronics enclosures (laptop bodies, phone frames), and power tool housings.
Method 3: Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting, also known as gravity die casting, occupies a middle ground between sand and die casting. It uses a reusable metal mold, but the molten aluminum is poured using gravity rather than high pressure.
The Process: How It Works
Similar to die casting, a reusable mold is created, typically from iron or steel. However, instead of injecting the metal, molten aluminum is simply poured into a gating system at the top of the mold, filling the cavity under its own weight.
Key Advantages
This method offers a balance of cost and quality. It produces parts with a better surface finish and tighter dimensional tolerances than sand casting, but its tooling costs are significantly lower than high-pressure die casting. The resulting castings often have superior mechanical properties due to a more controlled cooling rate.
Key Limitations
Permanent mold casting has a slower cycle time than die casting, making it less suitable for the highest production volumes. The complexity of parts is also somewhat more limited compared to high-pressure die casting.
Common Applications
It is ideal for medium-to-high volume production where quality and mechanical performance are more critical than in sand casting. Common applications include automotive wheels, pistons, gears, and other high-integrity structural components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right casting method requires a clear understanding of the direct trade-offs between cost, volume, and quality. No single method is universally superior; they are tools designed for different jobs.
Tooling Cost
This is often the primary decision driver. Sand casting has the lowest barrier to entry, while the steel dies for die casting represent a major capital investment.
Production Volume
Die casting is built for speed and automation, making it the king of mass production. Sand casting is best suited for single parts or small batches. Permanent mold casting fits comfortably in between.
Surface Finish & Accuracy
The quality of the mold directly impacts the quality of the part. The reusable, precisely machined steel molds of die casting and permanent mold casting produce far superior surface finishes and tighter tolerances than single-use sand molds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first define your project's most critical priority.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or very low-volume production: Sand casting is almost always the most cost-effective and fastest way to get a functional part.
- If your primary focus is mass production with high precision: Die casting is the industry standard, provided you can justify the significant initial tooling investment.
- If your primary focus is medium-volume production with good mechanical properties: Permanent mold casting offers the ideal balance between part quality and overall cost.
Understanding these core methods empowers you to align your manufacturing process with your project's specific financial and engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Method | Tooling Cost | Production Volume | Surface Finish | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Low | Low (Prototypes, Large Parts) | Rough | Engine Blocks, Prototypes |
| Die Casting | Very High | High (Mass Production) | Excellent | Automotive Parts, Electronics |
| Permanent Mold Casting | Moderate | Medium to High | Good | Wheels, Pistons, Gears |
Need help selecting the right casting method for your aluminum components? The choice between sand, die, and permanent mold casting directly impacts your project's cost, timeline, and final part quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for material testing and analysis to support your casting process development. Our expertise helps ensure your chosen method meets your engineering and financial goals. Contact our experts today via the form below to discuss your specific application and how we can support your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
People Also Ask
- How do you prepare a maintenance list for Mould maintenance? Implement a Proactive Tiered System
- What is the compression method of processing plastic? A Guide to Strong, Cost-Effective Molding
- What is the importance of injection moulding machine? Unlocking High-Volume, Precision Manufacturing
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of injection molding machine? Maximize Efficiency for Mass Production
- What is the significance of compression molding? Achieve Superior Strength in Large Composite Parts



















