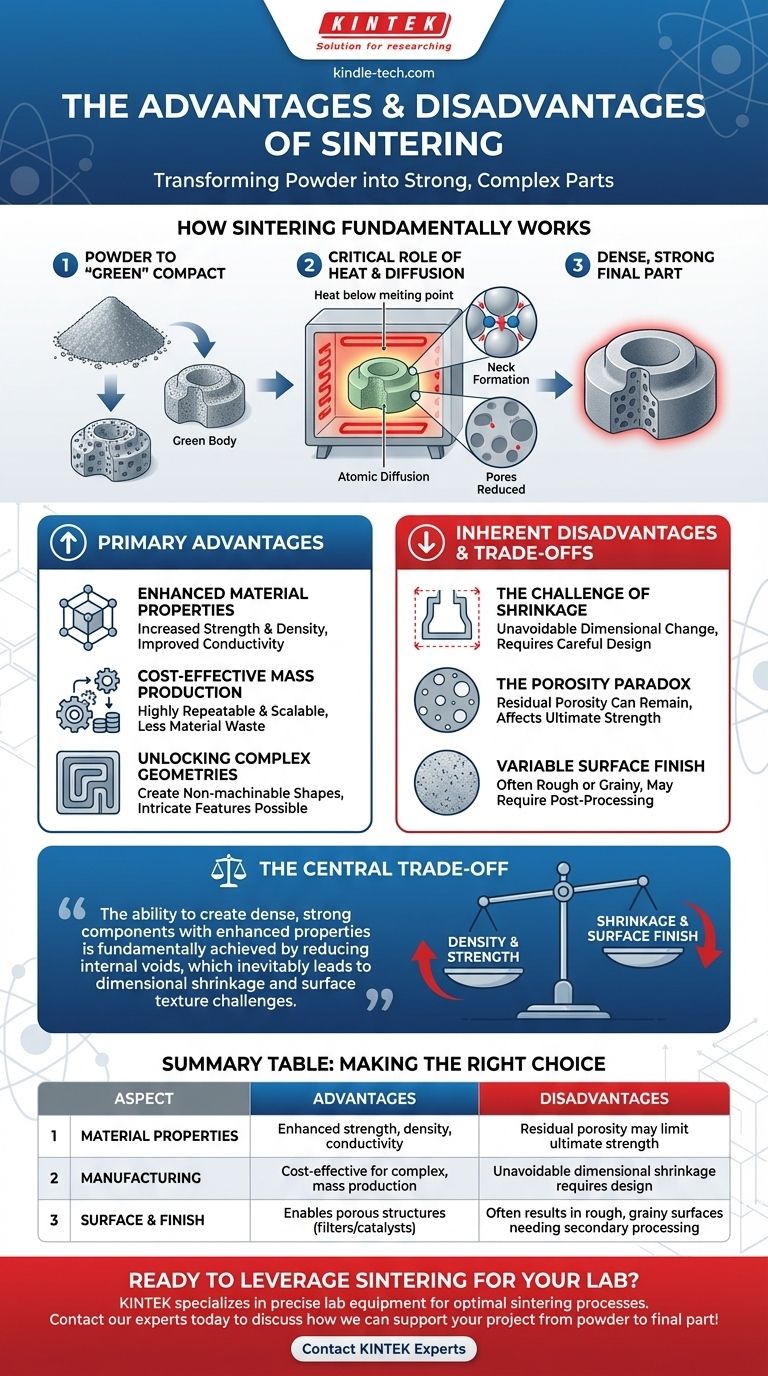
At its core, sintering is a powerful manufacturing process that transforms powdered materials into a strong, solid mass using heat below the material's melting point. Its primary advantages lie in creating strong, complex parts from materials with high melting points and achieving this cost-effectively at scale. The main disadvantages are the inherent part shrinkage during cooling and a potentially rough or porous surface finish that may require secondary processing.
The central trade-off of sintering is clear: it grants the ability to create dense, strong components with enhanced properties, but this transformation is fundamentally achieved by reducing internal voids, which inevitably leads to dimensional shrinkage and surface texture challenges that must be engineered for.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
To understand the advantages and disadvantages, you must first understand the mechanism. Sintering is not melting; it is a solid-state process of atomic diffusion.
From Powder to "Green" Compact
The process begins with a fine powder, which is compacted into a desired shape. This initial, fragile part is known as a "green" compact or "green body."
The Critical Role of Heat
This green compact is then heated in a furnace to a high temperature, but crucially, this temperature remains below the material's melting point. This is why sintering is ideal for materials with extremely high melting points, like ceramics or tungsten.
The Magic of Diffusion Bonding
At these elevated temperatures, the atoms at the contact points of the powder particles become mobile. They diffuse across the particle boundaries, forming "necks" that gradually grow.
This atomic transport pulls the particles closer together, systematically eliminating the pores between them. The result is a denser, stronger, and more cohesive final part.
The Primary Advantages of Sintering
The unique mechanism of sintering delivers several key engineering and economic benefits.
Enhanced Material Properties
This is the most common reason to use sintering. By reducing porosity and creating a strong atomic bond between particles, the process significantly improves strength, density, and overall integrity.
It also enhances functional properties like thermal and electrical conductivity. In certain ceramics, it can even increase translucency.
Cost-Effective Mass Production
For large production volumes, sintering is highly repeatable and cost-effective. Once the tooling and process parameters are set, it can produce thousands of identical parts with high accuracy, often with less material waste than subtractive methods like machining.
Unlocking Complex Geometries
Sintering enables the mass production of parts with non-machinable geometries. Intricate internal channels, undercuts, and complex curves can be molded into the green compact and retained in the final part, a feat impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional methods.
Understanding the Inherent Disadvantages and Trade-offs
The benefits of sintering do not come without engineering challenges. These are not so much flaws as they are physical consequences of the process that must be anticipated and managed.
The Challenge of Shrinkage
As the pores between particles are eliminated, the overall volume of the part must decrease. This shrinkage is an unavoidable aspect of sintering.
Predicting and controlling this dimensional change is critical for achieving tight tolerances. Designs must be created with a specific "shrink factor" in mind.
The Porosity Paradox
While the goal is to reduce porosity, achieving 100% density is often difficult or impractical. Some residual porosity can remain, which may affect the ultimate mechanical strength of the part.
However, in some applications like filters or catalysts, this porosity is intentionally controlled and preserved to create a functional feature.
Variable Surface Finish
The final surface texture depends heavily on the initial powder size and the specific sintering technique. Processes like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) can leave a rough, grainy surface.
Achieving a smooth, cosmetic finish often requires secondary operations like polishing, grinding, or coating, which adds time and cost to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to decide if sintering is the correct approach for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Sintering is an excellent choice for converting powders into robust parts, but you must design your tooling and component to account for shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes at scale: The process offers significant geometric freedom and is far more cost-effective than machining for high-volume production of intricate components.
- If your primary focus is a perfect surface finish: Be prepared to include post-processing steps in your manufacturing plan, as the as-sintered surface may not meet high cosmetic standards.
By leveraging its benefits while actively mitigating its inherent trade-offs, you can effectively utilize sintering to manufacture superior components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | Enhanced strength, density, and thermal/electrical conductivity | Residual porosity may limit ultimate strength |
| Manufacturing | Cost-effective mass production of complex, non-machinable geometries | Unavoidable dimensional shrinkage requires careful design |
| Surface & Finish | Enables creation of porous structures for filters/catalysts | Often results in rough, grainy surfaces needing secondary processing |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's manufacturing needs? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables required for optimal sintering processes. Whether you're developing complex components or scaling production, our expertise ensures you achieve the desired material properties and geometric accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project from powder to final part!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Expert Guide for Ti-22Al-25Nb Fabrication



















