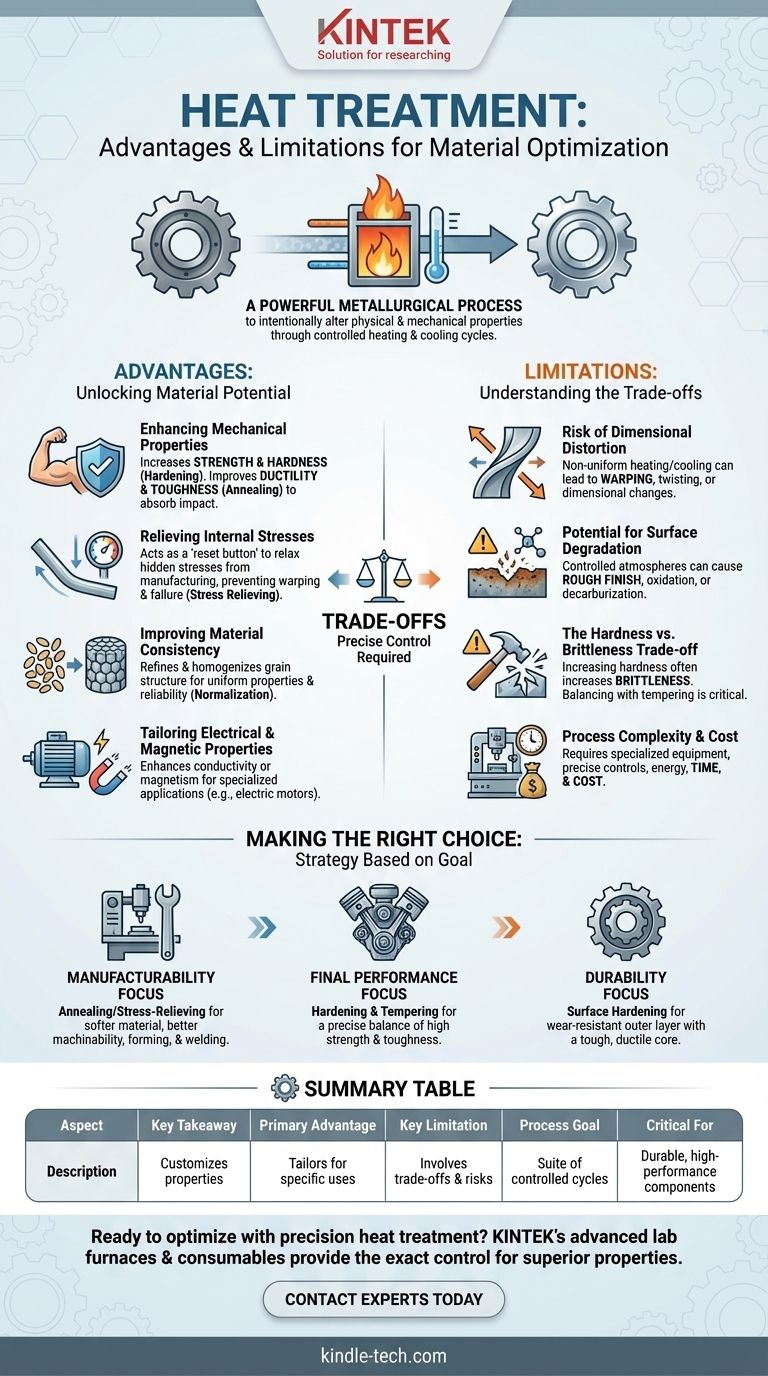
In essence, heat treatment is a powerful metallurgical process used to intentionally alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. It is widely employed to increase a material's strength, relieve internal stresses for easier manufacturing, improve wear resistance, and even refine its electrical or magnetic characteristics. This makes it a critical step in producing durable, high-performance components, especially from steel.
Heat treatment is not a single process, but a suite of controlled heating and cooling cycles. The primary advantage is the ability to customize a material's properties for a specific application, but its main limitation is that each benefit comes with a trade-off that must be carefully managed.
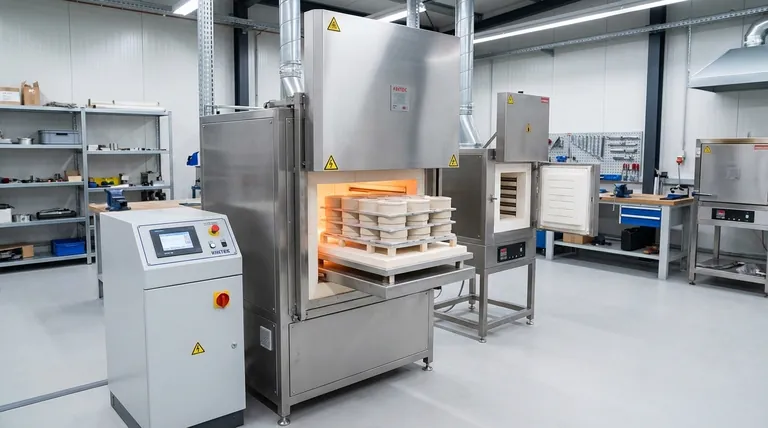

The Core Advantages of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment fundamentally changes a material's microstructure, unlocking properties that are not present in its as-produced state.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
The most common reason for heat treatment is to improve mechanical characteristics. Processes like hardening can dramatically increase a material's strength and hardness, making it more resistant to deformation and wear.
Other processes, like annealing, can increase ductility and toughness, making the material less brittle and more capable of absorbing impact without fracturing.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, or cold working can create significant internal stresses within a material. These hidden stresses can cause warping over time or lead to premature failure.
Heat treatment, specifically stress relieving, acts like a reset button. By heating the material below its transformation temperature and cooling it slowly, these internal stresses are relaxed, resulting in a more stable and predictable part that is easier to machine or weld.
Improving Material Consistency
After processes like hot forming, a component's metallic grain structure can be inconsistent. Heat treatment can refine and homogenize the grain structure throughout the part.
This normalization ensures that the mechanical properties are uniform, eliminating weak spots and improving the overall reliability of the component.
Tailoring Electrical and Magnetic Properties
For specialized applications, heat treatment can be used to enhance a material's electrical conductivity or magnetic properties. This is critical in the manufacturing of components for electric motors, transformers, and other electromagnetic devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly beneficial, heat treatment is a precise science where unintended consequences can arise if not properly controlled.
The Risk of Dimensional Distortion
The very act of heating and cooling a part causes it to expand and contract. If this is not done uniformly, or if the part has a complex geometry, it can lead to warping, twisting, or other dimensional changes.
Controlling these changes requires careful planning, proper support of the part in the furnace, and precisely managed cooling rates.
Potential for Surface Degradation
Certain heat treatment methods, particularly those involving a controlled atmosphere, can negatively affect the part's surface. This can result in a rough surface finish or oxidation.
In some cases, the process can also cause decarburization, where carbon is depleted from the surface of steel, making it softer and reducing its fatigue life.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Trade-off
One of the most fundamental trade-offs in metallurgy is that increasing a material's hardness often increases its brittleness.
A very hard part may be extremely wear-resistant, but it could also be prone to shattering under sudden impact. Achieving the right balance of hardness and toughness through processes like tempering is a critical skill.
Process Complexity and Cost
Heat treatment is not a simple step. It requires specialized furnaces, precise temperature and atmosphere controls, and significant energy consumption. This adds both time and cost to the manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct heat treatment strategy depends entirely on the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability: Use annealing or stress-relieving to soften the material, improve ductility, and make it easier to machine, form, or weld.
- If your primary focus is final performance: Use hardening and tempering to achieve a precise balance of high strength and adequate toughness for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is durability: Use surface hardening methods to create an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer layer while keeping the core of the material tough and ductile.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about understanding it not as a single action, but as a precise tool for engineering a material's final character.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Customizes material properties (strength, hardness, ductility) for specific applications. |
| Key Limitation | Involves trade-offs (e.g., hardness vs. brittleness) and risks (e.g., warping, surface degradation). |
| Process Goal | A suite of controlled heating and cooling cycles, not a single process. |
| Critical for | Manufacturing durable, high-performance metal components, especially from steel. |
Ready to optimize your materials with precision heat treatment?
KINTEK's advanced lab furnaces and consumables provide the exact control and consistency needed to achieve superior material properties—whether you're aiming for maximum strength, improved ductility, or enhanced wear resistance. Our equipment helps you mitigate common limitations like distortion and surface degradation.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heat treatment solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the operating temperature of a muffle furnace? From 200°C to 1800°C for Your Application
- How does a muffle oven work? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the main purpose of a furnace? A Guide to Heating, Comfort, and Material Transformation
- What should be considered when performing melting point determination? Ensure Accurate Compound Identification and Purity Assessment
- What is the operating range of a muffle furnace? Unlock the Key to Your High-Temperature Tasks



















