In short, the primary advantages of annealing are to relieve internal stresses, increase a material's ductility and workability, and reduce its hardness. This foundational heat treatment effectively "resets" a metal's internal structure after it has been hardened or stressed by manufacturing processes, making it easier to work with and more reliable in service.
The core purpose of annealing is not just to change a metal's properties, but to reverse the undesirable side effects of fabrication. It makes a material more uniform, stable, and predictable for subsequent processing or its final application.
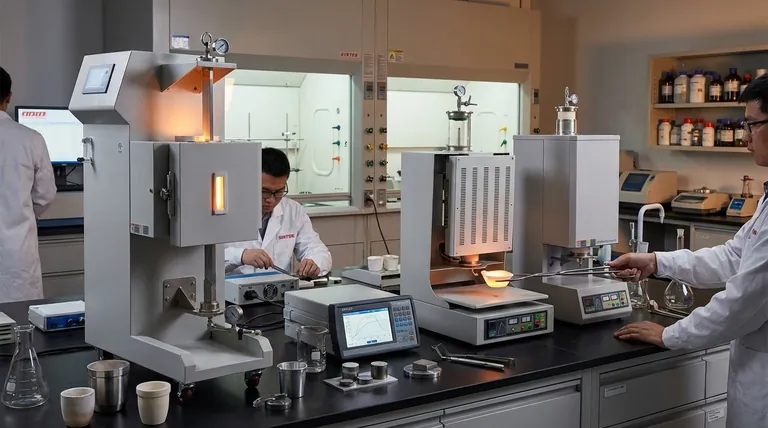

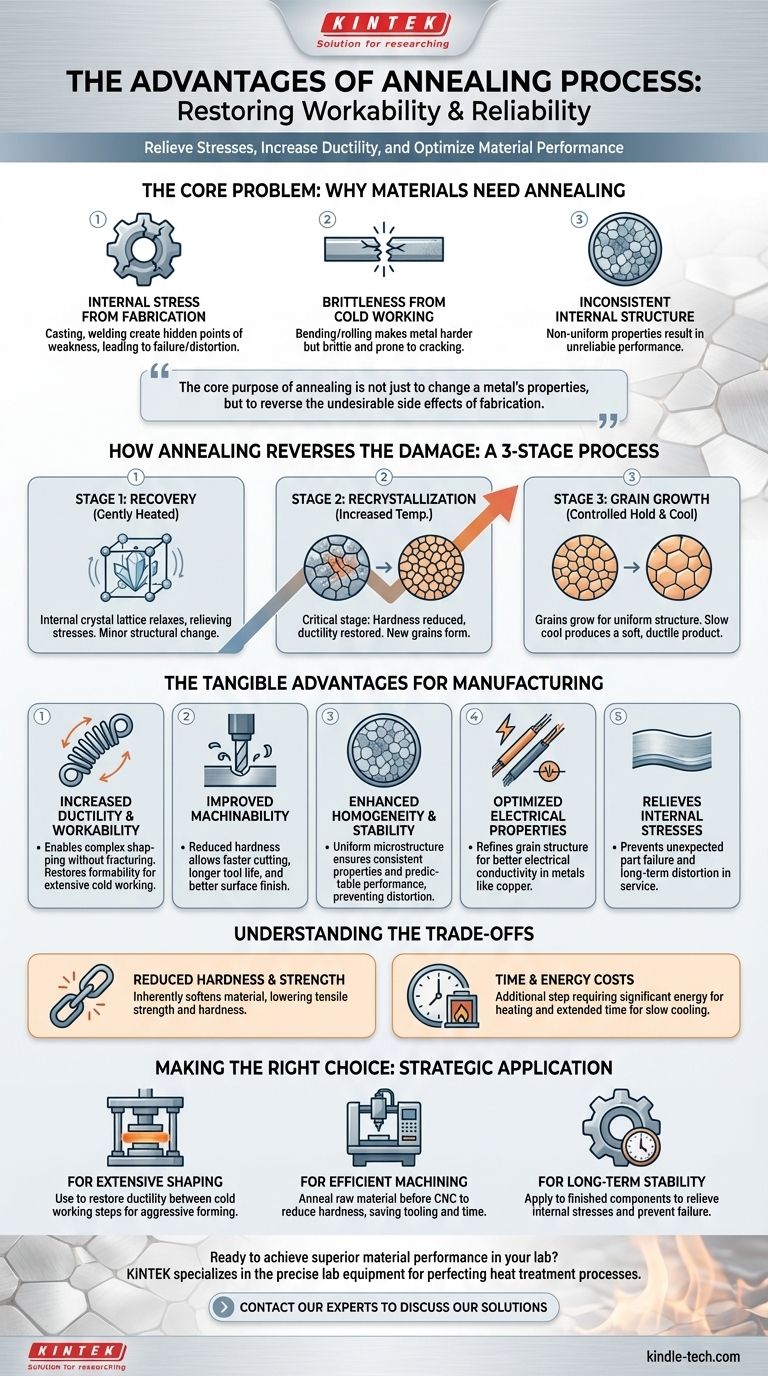
The Core Problem: Why Materials Need Annealing
Manufacturing processes like casting, machining, and cold working are essential for shaping metal, but they introduce significant internal problems. Annealing is the solution to these induced flaws.
Internal Stress from Fabrication
Processes like casting, grinding, or welding can create immense internal stresses within a material. These hidden stresses are points of weakness that can lead to unexpected part failure or distortion over time.
The Brittleness of Cold Working
Bending, rolling, or drawing a metal at room temperature (cold working) makes it harder and stronger. However, this comes at a cost: it significantly reduces the material's ductility, making it brittle and prone to cracking if further work is attempted.
Inconsistent Internal Structure
Fabrication can also result in a non-uniform or "inhomogeneous" internal structure. This lack of consistency means the material's properties can vary from one point to another, making its performance unreliable.
How Annealing Reverses the Damage
The annealing process is a controlled, three-stage heat treatment designed to systematically repair the metal's internal crystal structure.
Stage 1: Recovery
As the material is gently heated, the first stage allows the internal crystal lattice to relax. This relieves the internal stresses induced during fabrication without significantly changing the material's larger structure.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
As the temperature increases to a specific point, the old, deformed, and defect-ridden grains are replaced. New, strain-free grains begin to form, a process called recrystallization. This is the critical stage where hardness is reduced and ductility is restored.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
After recrystallization, holding the material at the annealing temperature allows the new grains to grow. By carefully controlling the heating time and subsequent cooling rate, engineers can influence the final grain size to achieve specific mechanical properties. A slow cool is essential for producing a soft, ductile final product.
The Tangible Advantages for Manufacturing
By repairing the internal structure, annealing provides clear, practical benefits that are critical for modern production.
Increased Ductility and Workability
The most significant advantage is the restoration of ductility. An annealed material can be bent, stretched, or formed into complex shapes without fracturing, enabling extensive cold working that would otherwise be impossible.
Improved Machinability
A material with reduced hardness and relieved internal stress is far easier to machine. This results in faster cutting speeds, longer tool life, and a better surface finish, which directly lowers manufacturing costs.
Enhanced Homogeneity and Stability
Annealing creates a more uniform, homogeneous microstructure. This ensures that the material's properties are consistent throughout the part, preventing distortion during subsequent heat treatments and guaranteeing predictable performance.
Optimized Electrical Properties
For certain metals, particularly copper, annealing can refine the grain structure in a way that improves electrical conductivity. This is a critical advantage for producing high-quality wiring and electrical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, annealing is not a universal solution and involves important considerations.
Reduced Hardness and Strength
The primary goal of annealing is to soften a material. This process inherently reduces the material's tensile strength and hardness, which may be undesirable for the final application if high strength is required.
Time and Energy Costs
Annealing is an additional manufacturing step. It requires significant energy to heat the material in a furnace and can take a long time, especially during the slow cooling phase, which adds to the overall production cost and lead time.
Process Control is Critical
The effectiveness of annealing depends entirely on precise control over temperature and cooling rates. Improper execution can lead to undesirable outcomes, such as excessive grain growth, which can harm the material's properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying annealing effectively requires aligning the process with your specific manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is extensive shaping: Use annealing to restore ductility between cold working steps, allowing for more aggressive forming without the risk of cracking.
- If your primary focus is efficient machining: Anneal the raw material before it reaches the CNC machine to reduce hardness, which will save on tooling costs and production time.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability: Apply an annealing process to relieve internal stresses in finished components to prevent distortion or premature failure in service.
Ultimately, annealing is a powerful tool for turning a stressed, brittle, and unworkable material into a stable, ductile, and predictable manufacturing asset.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Relieves Internal Stresses | Prevents part failure and distortion. |
| Increases Ductility & Workability | Enables further cold working without cracking. |
| Improves Machinability | Extends tool life and lowers production costs. |
| Enhances Homogeneity | Creates uniform, predictable material properties. |
| Optimizes Electrical Properties | Improves conductivity in metals like copper. |
Ready to achieve superior material performance in your lab?
The annealing process is critical for ensuring material reliability, but it requires precise temperature control to be effective. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your heat treatment processes.
We provide the reliable tools that help you restore workability, improve machinability, and guarantee the long-term stability of your materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















