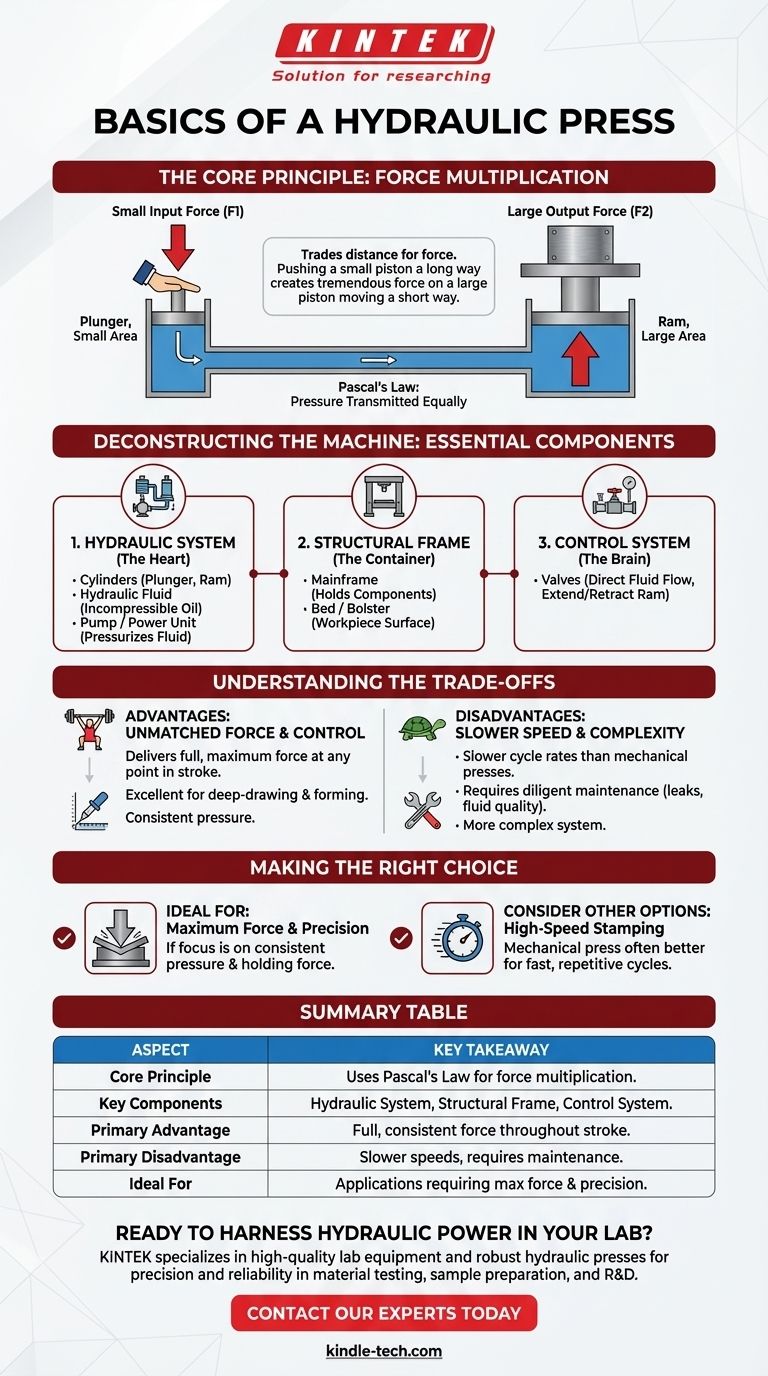
At its core, a hydraulic press is a machine that uses a confined liquid to multiply force. It operates on Pascal's law, which dictates that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally throughout. This allows a small force applied to a small piston to generate a significantly larger force on a bigger piston, enabling tasks like stamping, forging, and forming metal with immense power.
A hydraulic press doesn't create energy; it trades distance for force. By pushing a small piston a long way, you can make a large piston move a short way with tremendous force, all thanks to the incompressibility of a fluid.
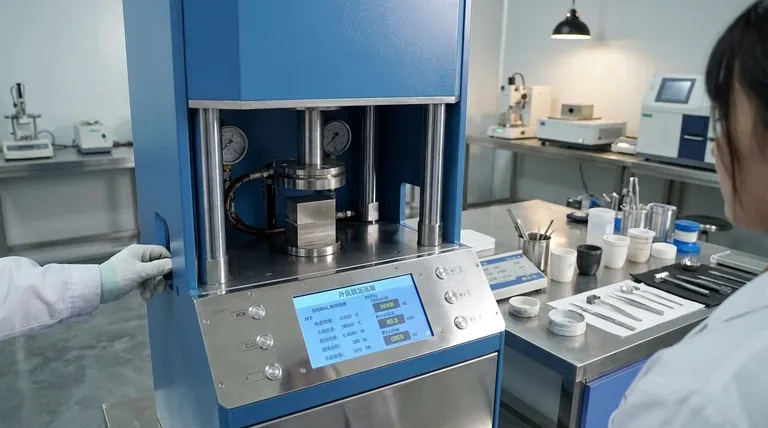

The Core Principle: Force Multiplication
The entire function of a hydraulic press is built on a single, elegant piece of physics discovered in the 17th century. Understanding this principle is key to understanding the machine.
The Foundation: Pascal's Law
Pascal's law states that when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined, incompressible fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container.
In simple terms, if you push on a sealed container of water, the pressure increases everywhere inside that container at the same time.
The Mechanism: How Two Cylinders Create Force
A hydraulic press uses two interconnected cylinders, each with a piston. One cylinder is small (the plunger), and the other is large (the ram).
When you apply a small force to the plunger, it creates pressure in the hydraulic fluid (Pressure = Force ÷ Area). Because this pressure is transmitted equally throughout the fluid, the same pressure is exerted on the large ram.
However, because the ram has a much larger surface area, that same pressure results in a much larger output force (Force = Pressure x Area). This is the source of the press's power.
Deconstructing the Machine: The Essential Components
While the principle is simple, a functional press requires several key components working together. These can be grouped into three main systems.
1. The Hydraulic System
This is the heart of the press. It consists of the parts that move and transmit the force.
- Cylinders: The small plunger cylinder receives the initial force, and the large ram cylinder delivers the multiplied output force.
- Hydraulic Fluid: A non-compressible fluid, typically oil, that fills the cylinders and transmits the pressure.
- Pump / Power Unit: A motor-driven pump that applies the initial force to the hydraulic fluid, pressurizing the system to move the plunger.
2. The Structural Frame
The immense forces generated by the press must be contained.
- Mainframe: This is the heavy, rigid structure that holds all the components together and withstands the opposing forces of the pressing operation.
- Bed / Bolster: The flat, stable surface on which the workpiece is placed. It is part of the mainframe and must be strong enough to resist the force from the ram.
3. The Control System
A press needs to be controlled to be useful. This system manages the flow of hydraulic fluid.
- Valves: Directional control valves are used to guide the high-pressure fluid. They determine whether the ram extends (presses down) or retracts (moves up) by changing the path of the oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect. A hydraulic press offers incredible force but comes with specific operational characteristics you must understand.
Advantage: Unmatched Force and Control
A hydraulic press can deliver its full, maximum force at any point in the ram's stroke. This makes it exceptionally versatile for deep-drawing or forming operations where consistent pressure is critical.
Disadvantage: Slower Speed
Compared to mechanical presses, which operate with a crankshaft, hydraulic presses are generally slower. The time it takes for the pump to move the fluid and build pressure limits the cycle rate.
Disadvantage: Maintenance Complexity
Hydraulic systems require diligent maintenance. Hoses, seals, and fittings are all potential points for leaks, and the hydraulic fluid must be kept clean to prevent damage to the pump and valves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these fundamentals helps you evaluate whether a hydraulic press is the correct tool for your objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum force and precision: A hydraulic press is ideal due to its ability to deliver consistent pressure and hold it for extended periods.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive stamping: A mechanical press is often a more efficient choice due to its much faster cycle times.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: You must commit to a rigorous maintenance schedule that includes checking for leaks and monitoring fluid quality to ensure long-term performance.
By seeing the press as a system for converting pressure into massive force, you can move beyond its complexity and apply it effectively to your goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses Pascal's Law to multiply a small input force into a large output force. |
| Key Components | Hydraulic System (cylinders, fluid), Structural Frame, Control System (valves). |
| Primary Advantage | Delivers full, consistent force throughout the stroke; ideal for forming and deep-drawing. |
| Primary Disadvantage | Slower cycle speeds compared to mechanical presses; requires diligent maintenance. |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring maximum force and precision control over speed. |
Ready to harness the power of a hydraulic press in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including robust hydraulic presses designed for precision and reliability. Whether you're involved in material testing, sample preparation, or R&D, our presses deliver the consistent force and control you need.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect hydraulic press solution for your laboratory's specific challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- How much pressure can a hydraulic press make? From 1 Ton to 75,000+ Tons of Force
- What is the purpose of a laboratory hydraulic press in welding aerosol analysis? Create Clear Pellets for FTIR Success
- What are the advantages of pressed pellet technique? Enhance Precision & Accuracy in Sample Analysis
- What industry uses hydraulic press? Powering Manufacturing from Automotive to Aerospace
- How do I choose a hydraulic press machine? A Guide to Matching Tonnage, Size & Control
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in Diamond/Ti composite preparation? Ensuring Atomic Bonding
- Is a hydraulic press a hydraulic system? A Complete Guide to Its Core Principles
- Why is a high-pressure laboratory hydraulic press necessary for the Cold Sintering Process (CSP)? Key Benefits Explained



















