At its core, the term Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) refers to both a process and the family of instruments designed to execute it. The three main types of instruments are standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) systems, which use thermal energy, and more advanced systems like Plasma Enhanced CVD (PECVD) and Inductively Coupled Plasma CVD (ICPCVD), which use plasma to reduce the required temperature.
While different CVD instruments exist, they all share the same fundamental goal: reacting precursor gases on a substrate surface to grow a high-quality solid film. The key difference between instruments lies in how they supply the energy needed to drive this chemical reaction—be it high heat, plasma, or other sources.

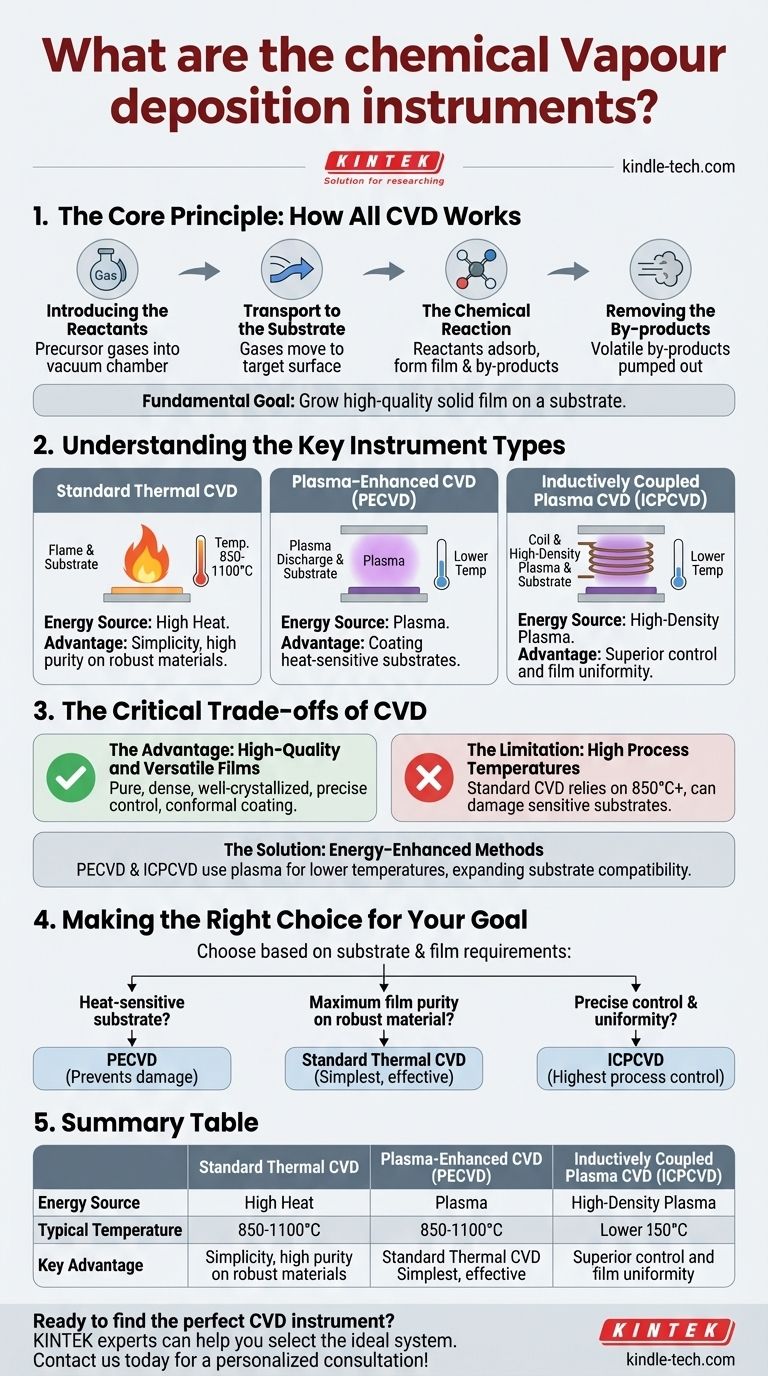
The Core Principle: How All CVD Works
Every CVD instrument, regardless of its specific type, facilitates a precise sequence of events to build a thin film layer by layer. This process is fundamentally about controlled chemical reactions on a surface.
Step 1: Introducing the Reactants
The process begins by introducing carefully measured precursor gases into a vacuum chamber. These gases contain the chemical elements that will eventually form the solid film.
Step 2: Transport to the Substrate
Once inside the chamber, these gases move—through diffusion and convection—towards the target material, known as the substrate. This is the surface where the film will be deposited.
Step 3: The Chemical Reaction
Reactant gases adsorb onto the substrate's surface. With sufficient energy, they undergo a chemical reaction that forms the desired solid material directly on the surface and produces gaseous by-products.
Step 4: Removing the By-products
These volatile by-products detach (desorb) from the surface and are pumped out of the reaction chamber, leaving behind only the pure, solid film.
Understanding the Key Instrument Types
The primary factor differentiating CVD instruments is the method used to provide energy for the surface reaction. This choice has significant implications for the process conditions and suitable substrate materials.
Standard Thermal CVD
This is the foundational method. It relies exclusively on high temperatures, typically between 850-1100°C, to give the precursor gases enough energy to react on the substrate. Its simplicity makes it robust for materials that can withstand the heat.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
This instrument uses an electric field to generate plasma, an ionized gas. The high-energy plasma transfers energy to the precursor gases, allowing the chemical reaction to occur at much lower temperatures than in standard thermal CVD.
Inductively Coupled Plasma CVD (ICPCVD)
ICPCVD is a more advanced type of PECVD. It uses electromagnetic induction to create a very high-density plasma without direct contact with electrodes. This offers even greater control over the film's properties and uniformity.
The Critical Trade-offs of CVD
Understanding the advantages and limitations of the CVD process is essential for determining its suitability for a specific application.
The Advantage: High-Quality and Versatile Films
CVD is renowned for producing films that are exceptionally pure, dense, and well-crystallized. It allows for precise control over the film's chemical composition, structure, and thickness. Furthermore, its "wrap-around" capability makes it excellent for uniformly coating complex, three-dimensional shapes.
The Limitation: High Process Temperatures
The primary drawback of standard thermal CVD is its reliance on extreme heat. Many potential substrate materials, such as polymers or certain electronic components, simply cannot withstand temperatures of 850°C or higher without being damaged or destroyed.
The Solution: Energy-Enhanced Methods
This temperature limitation is the driving force behind the development of instruments like PECVD and ICPCVD. By using plasma to supply the reaction energy, these systems achieve high-quality film deposition at significantly lower temperatures, expanding the range of compatible substrates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate CVD instrument depends entirely on the requirements of your substrate and the desired characteristics of the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing on a heat-sensitive substrate: An energy-enhanced method like PECVD is necessary to prevent damage to your material.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity on a robust material (like silicon): Standard thermal CVD is often the simplest and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is precise control and uniformity for advanced applications: A sophisticated system like ICPCVD provides the highest level of process control.
Ultimately, choosing the right instrument is about matching the energy source to the thermal limits of your substrate and the performance demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Instrument Type | Energy Source | Typical Temperature | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Thermal CVD | High Heat | 850-1100°C | Simplicity, high purity on robust materials |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Plasma | Lower Temperatures | Coating heat-sensitive substrates |
| Inductively Coupled Plasma CVD (ICPCVD) | High-Density Plasma | Lower Temperatures | Superior control and film uniformity |
Ready to find the perfect CVD instrument for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal system—whether it's a robust Thermal CVD for high-purity films or a advanced PECVD for delicate substrates—ensuring you achieve the film quality and performance your research demands.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can enhance your deposition processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures



















