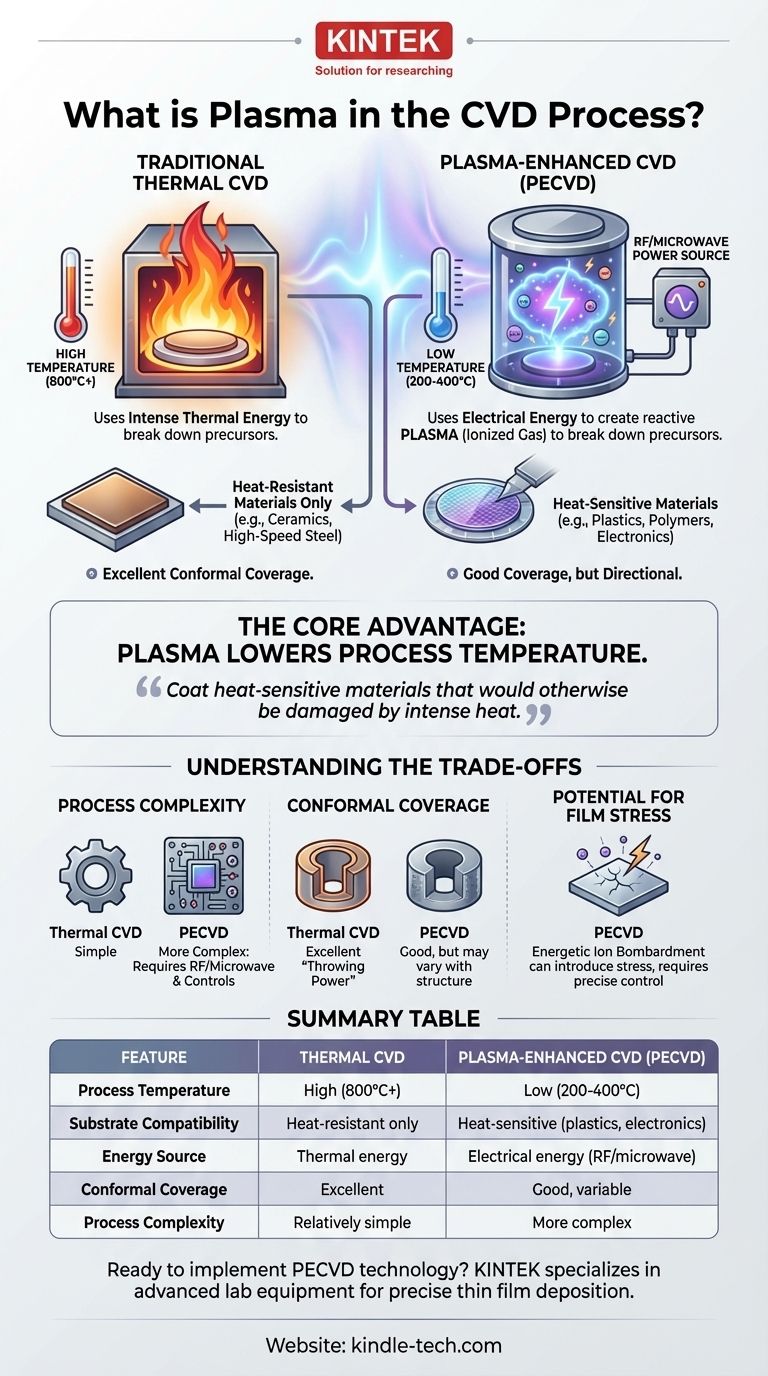
In the context of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), plasma is an energized, ionized gas that serves as an alternative to extreme heat. It is used to break down precursor gases and drive the chemical reactions necessary to deposit a thin film onto a substrate, enabling the process to occur at significantly lower temperatures than traditional thermal CVD.
The central purpose of using plasma in CVD is to lower the process temperature. This makes it possible to coat heat-sensitive materials that would otherwise be damaged or destroyed by the intense heat required for conventional thermal CVD.

How Plasma Transforms the Deposition Process
To understand the value of plasma, it's essential to first understand the role of energy in CVD. Both thermal and plasma-enhanced methods aim to create a high-quality, dense coating, but they use different energy sources to achieve it.
The Traditional Method: Thermal Energy
In conventional CVD, a substrate is heated to very high temperatures, often exceeding 800°C. Precursor gases are introduced into a chamber, and this intense heat provides the thermal energy needed to break their chemical bonds.
The resulting reactive molecules then deposit onto the hot substrate, gradually building a thin, uniform film.
The Plasma Method: Electrical Energy
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) replaces most of this thermal energy with electrical energy. An electric field, typically generated by a radio frequency (RF) or microwave source, is applied to a low-pressure gas in the chamber.
This energy strips electrons from the gas atoms, creating a highly reactive environment filled with ions, electrons, radicals, and other excited particles. This energized state is plasma.
This reactive "soup" of particles then bombards the precursor gases, breaking them down far more efficiently than heat alone. This allows the deposition reaction to proceed at much lower temperatures, often in the 200-400°C range.
Comparing PECVD to Traditional Thermal CVD
The decision to use plasma is a strategic one based on the substrate material and desired outcome. Each method has distinct characteristics.
Deposition Temperature
This is the most significant difference. Thermal CVD is a high-temperature process, which limits its use to materials that can withstand thermal stress, like certain ceramics and high-speed steels.
PECVD is a low-temperature process, opening up the possibility of coating plastics, polymers, and a wider range of metallic alloys without altering their fundamental properties.
Substrate Compatibility
Because of its high heat, thermal CVD is unsuitable for many modern electronic components and temperature-sensitive materials. Some tools, like high-speed steel, even require a secondary heat treatment after coating to restore their hardness.
PECVD's gentle, low-temperature nature makes it ideal for depositing films on delicate silicon wafers for microelectronics, growing carbon nanotubes, or coating medical implants.
Film Characteristics
Both methods are capable of producing high-purity, dense, and hard coatings that are typically only a few microns thick. The specific properties can be tuned by adjusting process parameters, but the fundamental quality is excellent in both cases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PECVD's low-temperature capability is a powerful advantage, it is not universally superior. There are important trade-offs to consider.
Process Complexity
PECVD systems are inherently more complex. They require sophisticated RF or microwave power generators, impedance matching networks, and advanced process controls to maintain a stable plasma. This can increase equipment and operational costs.
Conformal Coverage
Traditional thermal CVD is renowned for its excellent conformal coverage, or "throwing power." The process happens in a low-vacuum gaseous environment, allowing the reactive species to diffuse evenly over all surfaces, including deep holes and complex internal geometries.
While PECVD coverage is good, the directed nature of the plasma can sometimes make it more challenging to achieve perfectly uniform coatings on highly complex 3D structures.
Potential for Film Stress
The energetic ion bombardment inherent in a plasma process can, if not carefully controlled, introduce stress into the growing film or even cause minor damage to the substrate surface. Managing this requires precise control over the plasma chemistry and energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right CVD method depends entirely on your specific material and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: PECVD is the clear and necessary choice, as its low-temperature process prevents substrate damage.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely hard coating on a durable material (like a steel tool): High-temperature thermal CVD is often the industry standard, as the substrate can tolerate the heat and the process is robust.
- If your primary focus is achieving a perfectly uniform coating on a part with complex internal geometries: Thermal CVD often holds an advantage due to its superior ability to coat all surfaces evenly.
Understanding the function of plasma elevates your decision from a simple process choice to a strategic selection aligned with your material constraints and application goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal CVD | Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | High (800°C+) | Low (200-400°C) |
| Substrate Compatibility | Heat-resistant materials only | Heat-sensitive materials (plastics, electronics) |
| Energy Source | Thermal energy | Electrical energy (RF/microwave) |
| Conformal Coverage | Excellent for complex geometries | Good, but may vary with structure |
| Process Complexity | Relatively simple | More complex with plasma controls |
Ready to implement PECVD technology in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin film deposition. Whether you're working with heat-sensitive electronics, medical implants, or specialized coatings, our plasma-enhanced CVD solutions deliver the low-temperature performance you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your deposition process and expand your material capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















