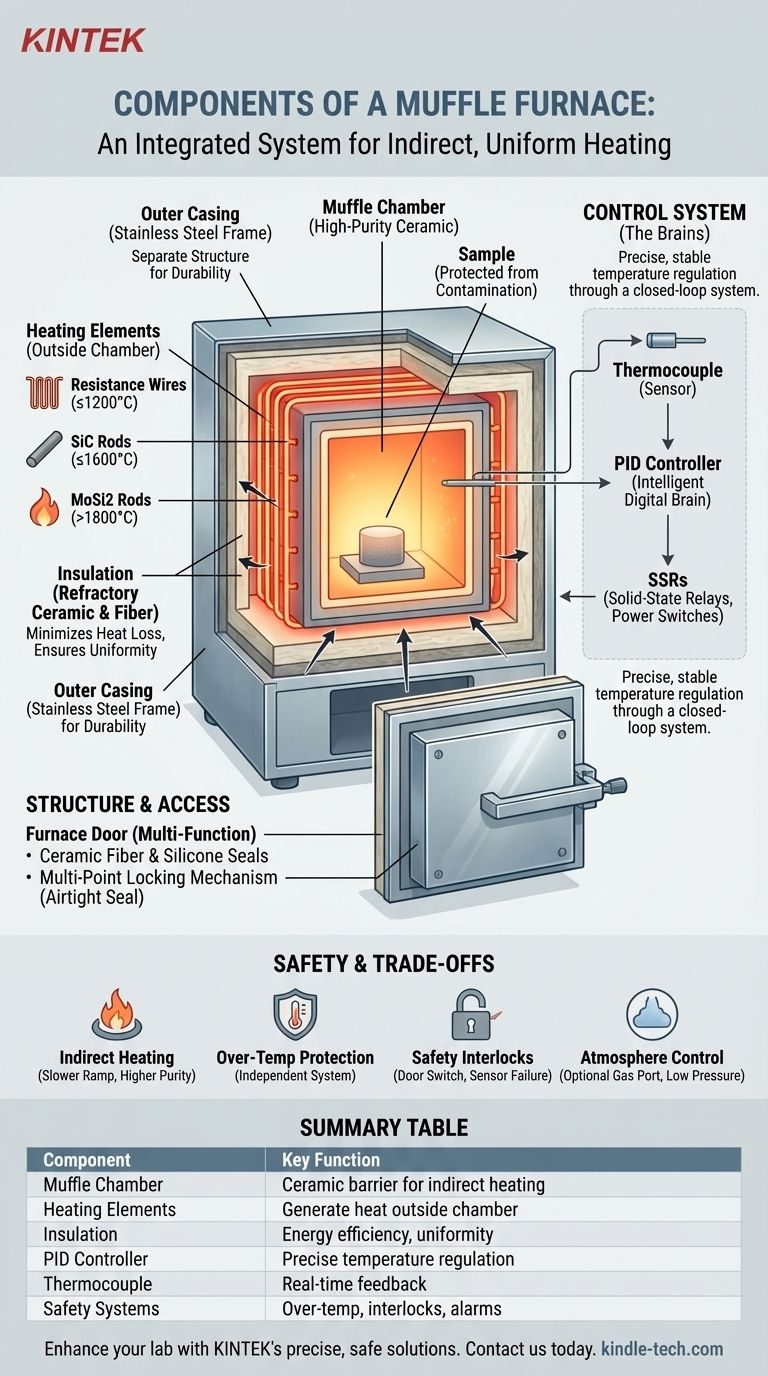
At its core, a muffle furnace consists of three primary systems: an insulated chamber known as the muffle, a set of heating elements, and a precision control system. These components work in unison to create a high-temperature environment that heats materials uniformly, without direct contact from the heat source or open flames. This principle of indirect heating is fundamental to its function.
A muffle furnace is more than just a hot box; it is an integrated system. Understanding its components reveals a design centered on indirect, uniform heating, where a sample is protected from contamination and subjected to precise thermal conditions managed by a sophisticated control loop for accuracy and safety.

The Core Heating System
The primary function of a muffle furnace—to generate and contain extreme heat—is handled by the interplay between the chamber, its insulation, and the heating elements.
The Muffle Chamber
The muffle is the inner chamber that holds the samples. It is made from high-purity refractory ceramic materials.
Its key purpose is to act as a barrier, separating the workload from the heating elements. This prevents contamination and ensures that heat is transferred radiantly and evenly to the sample.
The Heating Elements
These are the components that generate the heat. They are located outside the muffle chamber, which is a defining characteristic of this furnace type.
Different elements are used for different temperature ranges:
- Resistance Wires (e.g., Kanthal): Typically used for temperatures up to around 1200°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: Used for intermediate temperatures, often up to 1600°C.
- Silicon-Molybdenum (MoSi2) Rods: Required for the highest temperature applications, capable of exceeding 1800°C.
The Insulation
The insulation consists of the same refractory ceramic materials that form the muffle, often supplemented by layers of ceramic fiber.
Its role is critical for two reasons: it minimizes heat loss, making the furnace energy-efficient, and it helps maintain temperature uniformity throughout the chamber.
The Brains of the Operation: The Control System
A muffle furnace's value lies in its precision. This is achieved through a closed-loop control system where a sensor, a controller, and a power regulator work together continuously.
The Temperature Controller
This is the central processor of the furnace. Modern furnaces use a digital PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller.
Instead of simply turning the heat on and off, a PID controller intelligently anticipates heating needs, preventing overshooting the target temperature and maintaining it with exceptional stability.
The Thermocouple
The thermocouple is the temperature sensor. It is a probe placed inside the furnace chamber that measures the real-time temperature.
This data is fed back to the PID controller, closing the control loop and allowing the system to make constant, precise adjustments.
Solid-State Relays (SSRs)
These are the modern power switches that regulate the flow of electricity to the heating elements.
Directed by the PID controller, SSRs can switch on and off rapidly and silently. This allows for the fine-tuned pulsing of power needed for precise temperature regulation, unlike older mechanical relays.
The Physical Structure and Access
The furnace's external body and door are engineered to handle extreme temperatures, ensure a proper seal, and allow for safe operation.
The Outer Casing and Frame
The external body is typically made of stainless steel. In many designs, the inner furnace chamber is structurally separate from the outer frame.
This separation allows the inner chamber to expand and contract freely with temperature changes without stressing the outer casing, enhancing the furnace's durability.
The Furnace Door
The door is a multi-function component designed for access, sealing, and safety. High-quality furnaces often feature two layers of seals: an inner ceramic fiber rope to withstand heat and an outer silicone ring to ensure an airtight seal.
A multi-point locking mechanism, like a handwheel, applies even pressure to ensure the door seals tightly across its entire surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Features
A professional-grade muffle furnace is defined as much by its safety and operational limits as by its heating capabilities.
Indirect vs. Direct Heating
The core principle of a muffle furnace—indirect heating—ensures sample purity and temperature uniformity. The trade-off is that ramp rates (the speed of heating) can be slightly slower compared to direct-fired furnaces where the sample is exposed to the heat source.
Over-Temperature Protection
This is a critical, independent safety system. It uses a separate controller and thermocouple to monitor the furnace temperature.
If the primary controller fails and the temperature rises uncontrollably, this limiter will cut power to protect the furnace from damage and prevent a hazardous situation.
Atmosphere Control
Many furnaces include a gas port for purging the chamber with a non-flammable protective gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This creates an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation. However, a standard muffle furnace is not a vacuum furnace, and its seal is designed for low positive pressure, not high vacuum.
Critical Safety Interlocks
Modern furnaces include several non-negotiable safety interlocks. A switch automatically cuts power to the heating elements when the door is opened, and thermocouple failure detection shuts the system down if the sensor breaks, preventing a thermal runaway.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these components allows you to select a furnace that aligns perfectly with your application's demands.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature precision (above 1200°C): Look for furnaces with silicon carbide (SiC) or silicon-molybdenum (MoSi2) heating elements and a well-regarded PID controller.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and avoiding contamination: Ensure the furnace has a high-quality, non-reactive ceramic muffle and robust multi-layer door seals.
- If your primary focus is working with controlled atmospheres: Verify the furnace includes a gas inlet port for purging and a locking door mechanism that ensures a positive seal.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Prioritize models with an independent over-temperature limiter, a door safety interlock, and clear audio-visual alarm systems.
By viewing the furnace as an integrated system rather than a simple box, you can make a more informed decision that ensures reliable and safe results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Muffle Chamber | High-purity ceramic barrier for indirect, uniform heating and sample protection. |
| Heating Elements | Generate heat (up to 1800°C) located outside the chamber to prevent contamination. |
| Insulation | Refractory materials and ceramic fiber for energy efficiency and temperature uniformity. |
| PID Controller | Intelligent digital controller for precise, stable temperature regulation. |
| Thermocouple | Sensor providing real-time temperature feedback to the controller. |
| Safety Systems | Over-temperature protection, door interlocks, and alarms for safe operation. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a muffle furnace tailored to your specific needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for precise temperature control, sample purity, and operational safety. Whether your work requires high-temperature precision, contamination-free environments, or controlled atmospheres, our solutions are built to deliver reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect furnace for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the critical point of heat treatment? Master the Key to Steel Transformation
- What are the different types of ashing analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What is the capacity of a muffle furnace? Find the Right Size for Your Lab Needs
- What are the advantages and disadvantages to using a dry ashing technique? A Guide to High-Temperature Sample Prep
- What are the advantages of dry ashing over wet ashing? Streamline Your Lab's Sample Prep



















