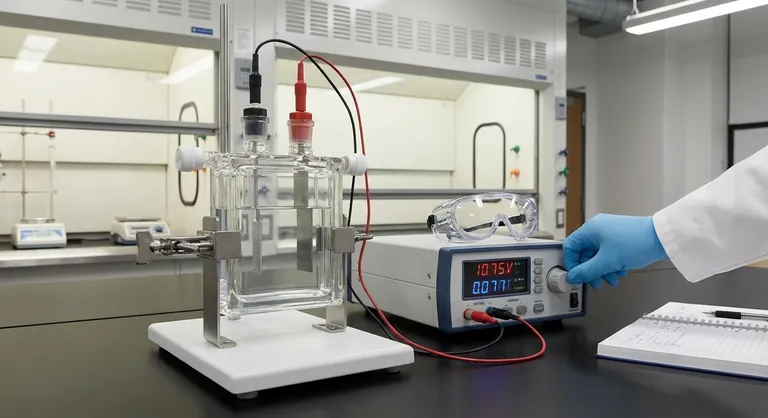
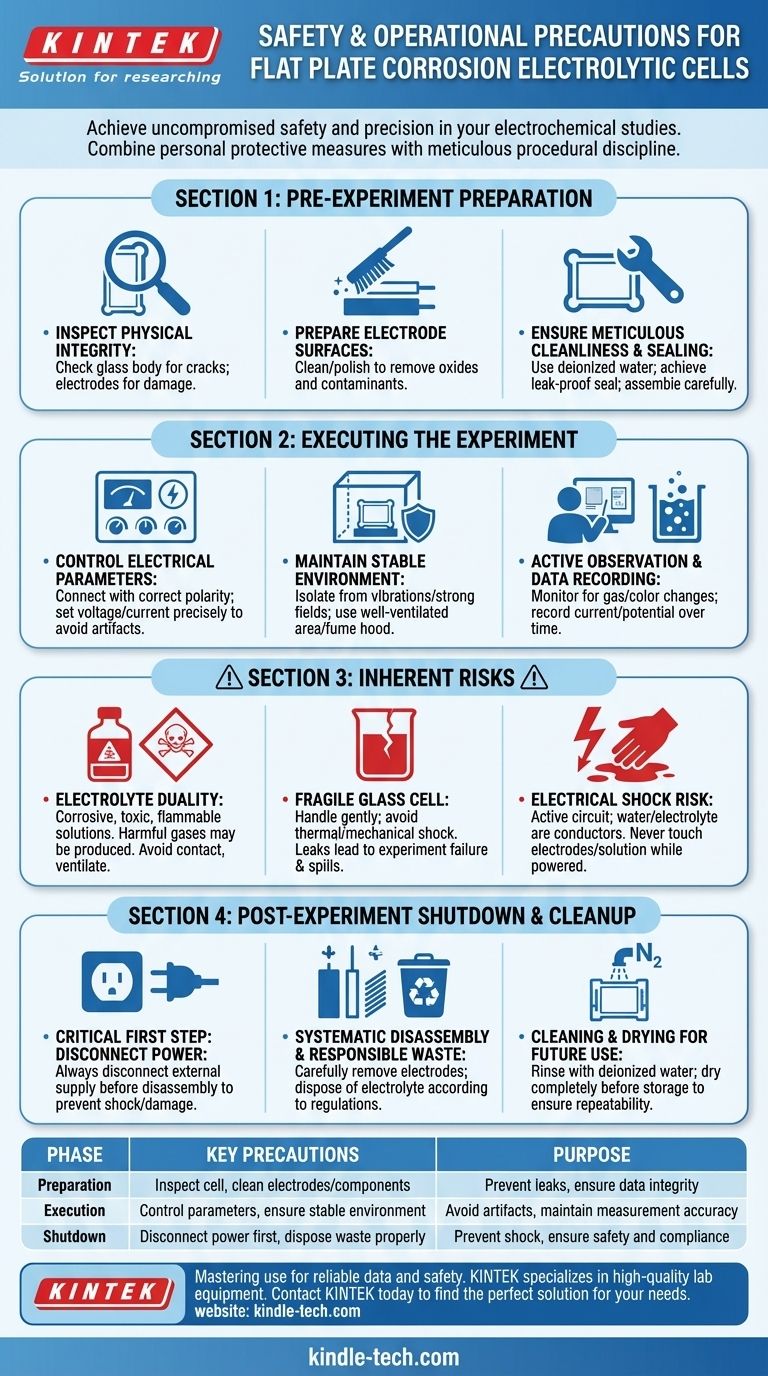
To use a flat plate corrosion cell safely and effectively, you must combine personal protective measures with meticulous procedural discipline. This involves wearing appropriate PPE to guard against electrical and chemical hazards, ensuring the cell is perfectly sealed to prevent leaks, controlling electrical parameters to avoid artifacts, and maintaining a stable environment free from external interference.
The core challenge is not merely avoiding accidents, but recognizing that your personal safety and the integrity of your experimental data are intrinsically linked. A failure in procedure, such as a leaky seal, simultaneously creates a physical hazard and invalidates your results.

The Foundation: Pre-Experiment Preparation
Proper setup is the most critical phase for ensuring a successful and safe experiment. Rushing these steps is a common source of error and risk.
Inspecting for Physical Integrity
Before beginning, thoroughly inspect the glass cell body for any cracks or chips. Because the material is fragile, even minor damage can lead to catastrophic failure and leakage under operational stress.
Also, examine the electrodes to confirm their surfaces are clean and structurally sound.
Preparing the Electrode Surfaces
The condition of your electrode surface directly impacts the results. Ensure it is free of oxides or contaminants from previous experiments by cleaning or polishing it according to your established protocol.
Ensuring Meticulous Cleanliness
All cell components must be thoroughly cleaned. Start with tap water to remove gross contaminants, followed by multiple rinses with deionized or distilled water to eliminate ionic impurities.
For new cells, an initial wash with a dilute acid or alkali solution may be necessary to remove manufacturing residues.
Assembling and Sealing the Cell
Carefully install the working, counter, and reference electrodes into their designated ports. The most critical part of this step is achieving a leak-proof seal. A poor seal compromises data, creates a chemical hazard, and can damage your equipment.
Pour in the prepared electrolyte solution, ensuring it immerses the electrodes adequately without overfilling.
Executing the Experiment with Precision
During the experiment, your focus shifts to control, observation, and data collection.
Controlling Electrical Parameters
Connect the cell to the potentiostat or power source, ensuring the polarity is correct. Set your voltage, current, and scan rate parameters based on the specific requirements of your experiment and materials.
Incorrect parameters can cause excessive electrode polarization, damage the cell, or generate meaningless data.
Maintaining a Stable Environment
Electrochemical measurements are highly sensitive. Isolate the cell from vibrations and strong electromagnetic fields (e.g., from other lab equipment) that can introduce noise and interfere with your measurements.
If the reaction is expected to produce hazardous fumes, ensure the entire setup is in a well-ventilated area or a fume hood.
Active Observation and Data Recording
Pay close attention to the experiment as it runs. Visual cues like gas bubbles on an electrode or color changes in the solution provide valuable qualitative information about the reactions occurring.
Simultaneously, ensure you are recording all quantitative data, such as current and potential over time, as this forms the basis of your analysis.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
True expertise involves understanding not just the procedure, but also the inherent risks and trade-offs.
The Duality of the Electrolyte
The electrolyte is essential for the experiment but is often the primary hazard. These solutions can be corrosive, toxic, or flammable. Avoid direct contact at all times.
Be aware that the electrochemical reaction itself can produce harmful gases, necessitating good ventilation.
The Fragility of the Glass Cell
The glass construction allows for visual inspection but makes the cell inherently fragile. Always handle it gently and avoid thermal or mechanical shock. A simple slip can result in a complete loss of the experiment and a chemical spill.
The Risk of Electrical Shock
While often using low voltages, the system is still an active electrical circuit. Never touch the electrodes or electrolyte with bare hands while the power is connected. Water and ionic solutions are excellent conductors.
Post-Experiment Shutdown and Cleanup
A disciplined shutdown procedure prevents accidents and preserves the equipment for future use.
The Critical First Step: Disconnect Power
Before any disassembly, always disconnect the external power supply. This is the single most important step to prevent electric shock or damage to the cell components.
Systematic Disassembly
Once the power is off, you can carefully remove the electrodes. If you need to analyze the corrosion products on the electrode surface, handle them with extreme care to keep them intact.
Responsible Waste Management
Dispose of the used electrolyte according to your institution's safety and environmental regulations. Never pour hazardous chemicals down the drain.
Cleaning and Drying for Future Use
Rinse the cell body and all components thoroughly with deionized water. A soft brush can be used for stubborn residue. Once clean, allow all parts to dry completely—either by air-drying or with a gentle stream of nitrogen—before storing them.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Integrate these precautions into a standardized workflow for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize wearing correct PPE, ensuring excellent ventilation, and always disconnecting power before handling any components.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Concentrate on meticulous electrode preparation, achieving a perfect cell seal, and shielding the experiment from all external interference.
- If you are establishing a new lab procedure: Document every step from pre-inspection to post-cleaning to ensure consistency and repeatability across all experiments.
By integrating these precautions into a routine, you transform them from a list of rules into a professional methodology that ensures both personal safety and scientific rigor.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Precautions | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Inspect cell for cracks; clean electrodes & components. | Prevent leaks, ensure data integrity. |
| Execution | Control electrical parameters; ensure stable environment. | Avoid artifacts, maintain measurement accuracy. |
| Shutdown | Disconnect power first; dispose of waste properly. | Prevent shock, ensure safety and compliance. |
| Inherent Risks | Handle fragile glass; beware of corrosive electrolytes. | Mitigate physical and chemical hazards. |
Achieve Uncompromised Safety and Precision in Your Corrosion Studies
Mastering the use of a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell is essential for reliable electrochemical data and lab safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the durable cells and reliable components you need to perform these tests with confidence.
Our products are designed to support meticulous procedures—from leak-proof seals to stable electrode materials—helping you protect your team and ensure the integrity of your results.
Ready to enhance your lab's electrochemical testing workflow? Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect equipment solution for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How does an electrochemical cell system ensure measurement precision during DL-EPR? | Expert Testing Guide
- What role does a water-jacketed electrolytic cell play in variable-temperature electrochemical corrosion measurements?
- What is the operating principle of a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? A Guide to Controlled Materials Testing
- How is a high-precision electrolytic cell used to evaluate metal corrosion resistance? Validate DCT Results Accurately
- What type of electrode system is the coating evaluation electrolytic cell designed for? Unlock Precise Coating Analysis



















