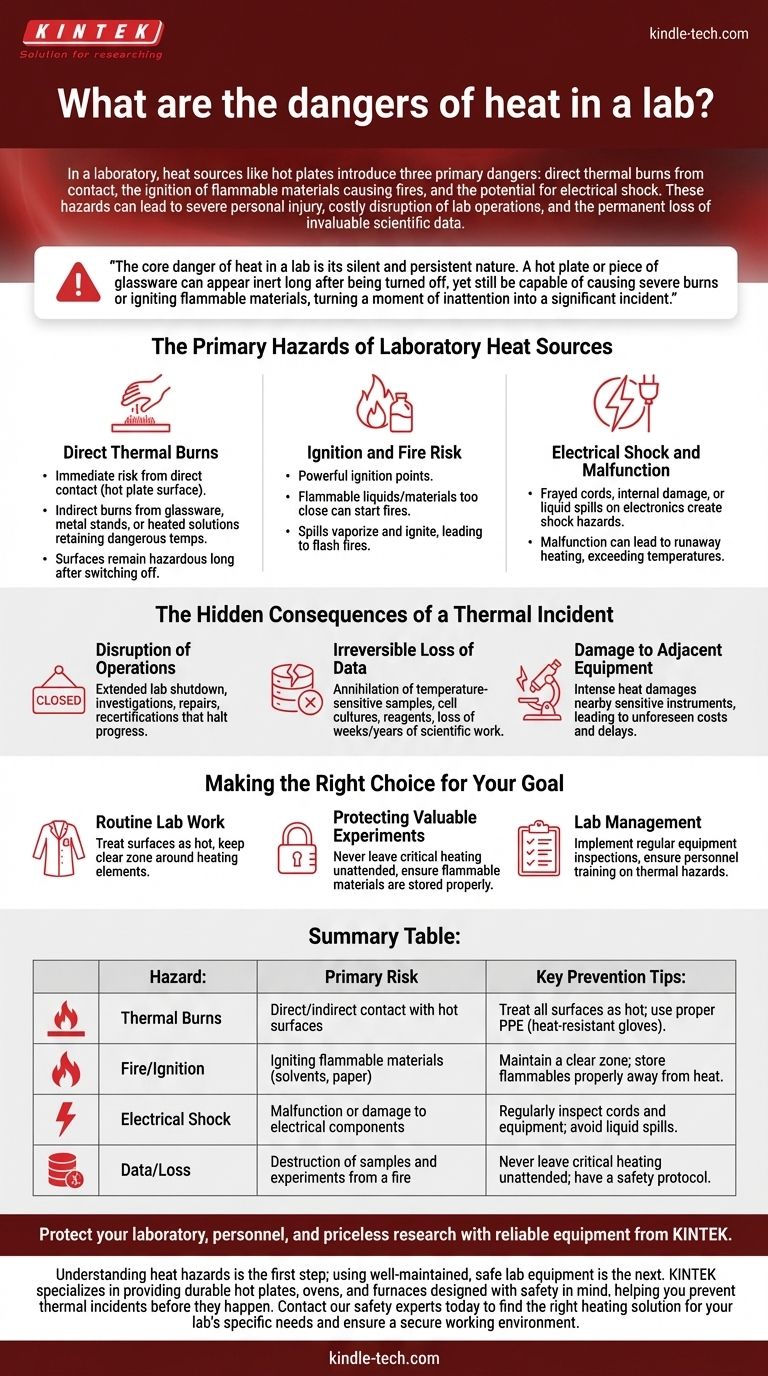
In a laboratory, heat sources like hot plates introduce three primary dangers: direct thermal burns from contact, the ignition of flammable materials causing fires, and the potential for electrical shock. These hazards can lead to severe personal injury, costly disruption of lab operations, and the permanent loss of invaluable scientific data.
The core danger of heat in a lab is its silent and persistent nature. A hot plate or piece of glassware can appear inert long after being turned off, yet still be capable of causing severe burns or igniting flammable materials, turning a moment of inattention into a significant incident.

The Primary Hazards of Laboratory Heat Sources
Understanding the specific risks associated with common heating equipment is the first step toward mitigating them. The dangers extend beyond the obvious and require constant vigilance.
Direct Thermal Burns
The most immediate risk is a thermal burn. This can occur from direct contact with a heating element, such as the surface of a hot plate.
Burns also happen indirectly. Glassware, metal stands, or solutions heated by the device will retain dangerous temperatures, often with no visual warning.
Crucially, these surfaces remain a burn hazard for a significant time even after the equipment has been switched off.
Ignition and Fire Risk
Laboratory heat sources are powerful ignition points. Placing flammable liquids, paper, or other combustibles too close to a hot plate can easily start a fire.
Spills are particularly dangerous. If a flammable solvent is spilled onto or near an active heating element, it can vaporize and ignite, leading to a flash fire.
Electrical Shock and Malfunction
Most modern heating devices, including hot plates, are electrical. Frayed cords, internal damage, or liquid spills onto the electronics can create a severe electrical shock hazard.
A malfunction can also lead to runaway heating, where the device exceeds its set temperature, dramatically increasing the risk of fire or damage to the experiment.
The Hidden Consequences of a Thermal Incident
The impact of a heat-related accident goes far beyond the immediate physical danger. The secondary consequences can be just as devastating to a research program.
Disruption of Operations
A fire or serious injury can shut down a lab for an extended period. This leads to investigations, repairs, and recertifications that halt all progress.
Irreversible Loss of Data
An uncontrolled heating event or resulting fire can destroy more than just equipment. It can annihilate temperature-sensitive samples, cell cultures, and unique reagents, representing the loss of weeks, months, or even years of scientific work.
Damage to Adjacent Equipment
The intense heat from a fire can damage nearby sensitive instruments that were not directly involved, leading to unforeseen costs and further operational delays.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting a proactive safety mindset is essential for preventing heat-related incidents and protecting your work.
- If your primary focus is routine lab work: Always treat surfaces as hot until proven otherwise and keep a clear, uncluttered zone around all heating elements.
- If your primary focus is protecting valuable experiments: Never leave a critical heating step unattended and ensure all flammable materials are stored properly and far from the work area.
- If your primary focus is lab management: Implement regular equipment inspections and ensure all personnel are trained on the specific thermal hazards present in the lab.
Ultimately, consistent awareness is the most effective safeguard against the silent threat of heat in the laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Hazard | Primary Risk | Key Prevention Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Burns | Direct or indirect contact with hot surfaces | Treat all surfaces as hot; use proper PPE (heat-resistant gloves). |
| Fire/Ignition | Igniting flammable materials (solvents, paper) | Maintain a clear zone; store flammables properly away from heat. |
| Electrical Shock | Malfunction or damage to electrical components | Regularly inspect cords and equipment; avoid liquid spills. |
| Data/Loss | Destruction of samples and experiments from a fire | Never leave critical heating unattended; have a safety protocol. |
Protect your laboratory, personnel, and priceless research with reliable equipment from KINTEK.
Understanding heat hazards is the first step; using well-maintained, safe lab equipment is the next. KINTEK specializes in providing durable hot plates, ovens, and furnaces designed with safety in mind, helping you prevent thermal incidents before they happen.
Contact our safety experts today to find the right heating solution for your lab's specific needs and ensure a secure working environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a magnetic stirring system contribute to the chemical synthesis of chlorine dioxide? Ensure Safety and Purity
- What are alternatives to lab-grown diamonds? Compare Natural Diamonds, Moissanite & More
- How do you make THC isolate from distillate? Master the Advanced Lab Purification Process
- Why is an industrial ultrasonic homogenizer used when processing bioproducts? Master PHA Extraction & Fluid Viscosity
- Why is a high-frequency ultrasonic cleaner necessary for steel substrate preparation? Achieve 100% Coating Adhesion
- What metals can be sintered? A Guide to Materials and Processes for Stronger Parts
- What is the difference between pyrolysis and incineration of plastic? Choose the Right Waste-to-Resource Path
- Why is deposition technology good? Unlock Atomic-Level Control for Superior Materials



















