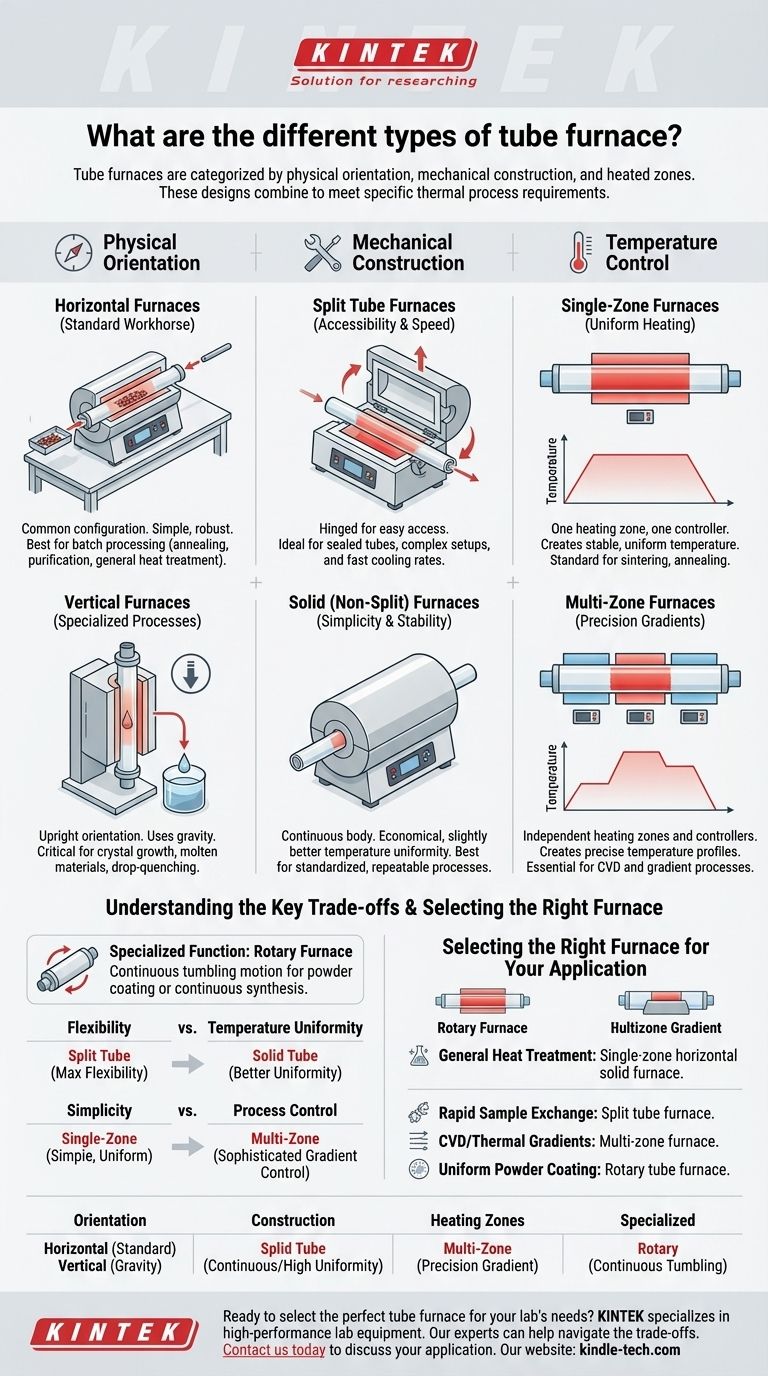
Tube furnaces are primarily categorized by their physical orientation, mechanical construction, and the number of heated zones. While many specific names exist, these designs boil down to a few core types: horizontal or vertical, split-tube or solid-tube, and single-zone or multi-zone. Specialized models, like rotary furnaces, are designed for highly specific continuous processing tasks.
The various "types" of tube furnaces are not mutually exclusive categories. Instead, they are combinations of design features—orientation, construction, and heating profile—that must be matched to the specific requirements of your thermal process.

The First Axis: Physical Orientation
The orientation of the furnace dictates how a sample is loaded and how forces like gravity can be used within the process.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Standard Workhorse
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration. Samples are typically placed in ceramic or metal "boats" and pushed into the central hot zone with a long rod.
This design is simple, robust, and well-suited for a wide range of batch processing applications, such as annealing, purification, and general heat treatment.
Vertical Furnaces: For Specialized Processes
Vertical furnaces orient the process tube upright. This allows gravity to be used for tasks like drop-quenching a sample into a liquid bath below the furnace.
This orientation is critical for certain crystal growth methods and for processes where the sample must not touch the sides of the process tube, such as when processing materials that become molten.
The Second Axis: Mechanical Construction
The construction determines how you access the process tube, which directly impacts setup time and cooling speed.
Split Tube Furnaces: Accessibility and Speed
Split tube furnaces are hinged, allowing them to open into two halves. This provides direct, easy access to the process tube.
This design is essential when working with sealed tubes or complex reactor setups that cannot be easily slid into the furnace from one end. It also allows for much faster cooling rates by simply opening the furnace body.
Solid (or Non-Split) Furnaces: Simplicity and Stability
Solid tube furnaces feature a single, continuous insulation body. The process tube must be inserted from one end.
These furnaces are often more economical and can offer slightly better temperature uniformity due to their uninterrupted insulation. They are ideal for standardized, repeatable processes where rapid cooling or complex tube setups are not required.
The Third Axis: Temperature Control
The heating element configuration determines whether you create a single uniform hot zone or a precise temperature gradient.
Single-Zone Furnaces: Uniform Heating
A single-zone furnace has one set of heating elements and a single controller. The goal is to create one stable, uniform temperature area in the center of the furnace.
This is the standard for most heat treatment applications, including calcination, sintering, and annealing, where the entire sample needs to be held at a specific temperature.
Multi-Zone Furnaces: Precision Gradients
Multi-zone furnaces (most commonly two or three zones) have independent heating elements and controllers for different sections of the tube.
This allows you to create a precise temperature profile along the length of the tube. This capability is non-negotiable for advanced processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where different temperature zones are required to vaporize precursors and deposit films.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance, flexibility, and cost. Each design feature comes with inherent compromises.
Flexibility vs. Temperature Uniformity
A split tube furnace offers maximum flexibility for sample loading but can introduce a minor point of heat loss along its seam, potentially creating a small dip in temperature uniformity compared to a solid furnace.
Simplicity vs. Process Control
A single-zone furnace is simple and excels at creating one uniform hot zone. A multi-zone furnace offers sophisticated gradient control but adds significant complexity and cost to the system's setup and programming.
Specialized Function: The Rotary Furnace
A rotary furnace is a highly specialized horizontal furnace that slowly rotates the process tube. This continuous tumbling motion is designed for applications like powder coating or continuous synthesis, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat and atmosphere. It is not a general-purpose tool.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be driven entirely by the demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment (annealing, calcination): A single-zone horizontal solid furnace offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample exchange or fast cooling cycles: A split tube furnace is essential for its accessibility.
- If your primary focus is chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or creating thermal gradients: A multi-zone furnace is non-negotiable for precise temperature profile control.
- If your primary focus is uniform powder coating or continuous processing: A rotary tube furnace is the specialized tool designed for this exact task.
Understanding these core design principles transforms your choice from a guess into a strategic decision aligned with your scientific or industrial goals.
Summary Table:
| Design Axis | Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Horizontal | Sample loaded on a boat | Standard annealing, calcination |
| Vertical | Uses gravity for quenching | Crystal growth, molten materials | |
| Construction | Split Tube | Hinged for easy access | Fast cooling, sealed tube setups |
| Solid Tube | Continuous insulation body | High uniformity, repeatable processes | |
| Heating Zones | Single-Zone | One uniform hot zone | Sintering, general heat treatment |
| Multi-Zone | Independent temperature control | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | |
| Specialized | Rotary | Rotates tube for tumbling | Continuous powder coating, synthesis |
Ready to select the perfect tube furnace for your lab's needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including a full range of tube furnaces tailored for applications like CVD, annealing, and materials synthesis. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between horizontal/vertical orientation, split/solid construction, and single/multi-zone control to match your specific thermal processing requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation—let KINTEK be your partner in achieving precise and reliable heat treatment results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















