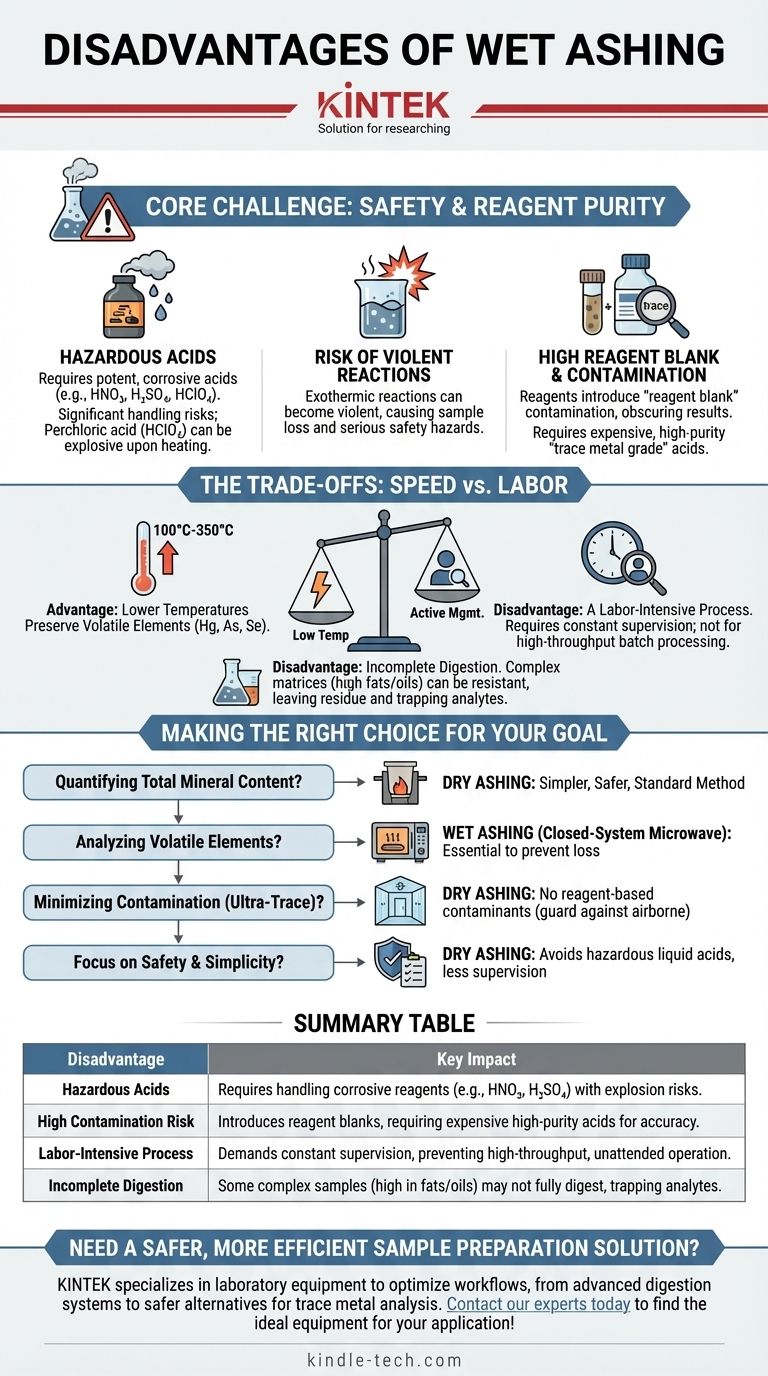
The primary disadvantages of wet ashing center on significant safety hazards from corrosive acids, the high risk of introducing sample contamination, and the labor-intensive nature of the process. While it is often faster than dry ashing and operates at lower temperatures, it requires constant supervision, specialized equipment like fume hoods, and the use of expensive, high-purity reagents to ensure accurate results.
Wet ashing trades the high-temperature simplicity of dry ashing for a lower-temperature, liquid-phase digestion. This exchange introduces considerable risks related to reagent handling and purity that are not present in dry ashing.

The Core Challenge: Safety and Reagent Purity
The defining characteristic of wet ashing, also known as wet digestion, is the use of strong liquid reagents to destroy a sample's organic matrix. This approach creates distinct disadvantages.
The Use of Hazardous Acids
Wet ashing requires potent, concentrated acids such as nitric acid (HNO₃), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and sometimes perchloric acid (HClO₄).
These chemicals are extremely corrosive and present significant handling risks. Perchloric acid, in particular, can become explosive upon heating, requiring a specialized fume hood with a dedicated wash-down system to prevent the buildup of explosive perchlorate salts.
The Risk of Violent Reactions
The reaction between concentrated acids and an organic sample is exothermic. If not managed carefully, the reaction can become violent, causing the sample to boil over and resulting in sample loss and a serious safety hazard.
This means the process is not "set and forget." It demands the constant attention of a skilled analyst to control the heating rate and add reagents carefully.
High Reagent Blank and Contamination
The acids and deionized water used in the process are a major source of potential contamination. Even "reagent grade" acids contain trace amounts of various metals.
This introduces a "reagent blank"—a background level of contamination that can obscure the true concentration of elements in your sample, especially when performing trace metal analysis. To mitigate this, labs must use expensive, high-purity "trace metal grade" acids, which significantly increases the cost per sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Labor
While wet ashing has clear drawbacks, it is employed because it solves specific problems that dry ashing cannot. Understanding these trade-offs is key to choosing the correct method.
Advantage: Lower Temperatures Preserve Volatile Elements
The main reason to choose wet ashing is its lower operating temperature, typically between 100°C and 350°C. High-temperature dry ashing (500-600°C) can cause volatile elements like mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), and selenium (Se) to be lost.
Wet ashing, especially when performed in a closed-system microwave digester, effectively traps these elements in the liquid solution, making it the preferred method for their analysis.
Disadvantage: A Labor-Intensive Process
Unlike dry ashing, where samples can be placed in a muffle furnace to run overnight, open-vessel wet ashing requires active management. An analyst must be present to monitor the digestion, preventing it from boiling dry and adding acids as needed.
This makes it more demanding on personnel time and less suitable for high-throughput batch processing compared to automated or furnace-based methods.
Disadvantage: Incomplete Digestion
Some complex sample matrices, particularly those high in fats or oils, can be very resistant to acid digestion. This can result in incomplete destruction of the organic material, leaving behind a residue that may trap analytes or interfere with subsequent analysis by techniques like ICP-MS.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between wet and dry ashing should be dictated entirely by your analytical objective and the resources available.
- If your primary focus is quantifying total mineral content (total ash): Dry ashing is the simpler, safer, and standard method for determining a sample's inorganic residue by weight.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for volatile elements like mercury or selenium: Wet ashing, ideally in a closed-system microwave digester, is essential to prevent the loss of these elements.
- If your primary focus is minimizing contamination for ultra-trace analysis: Dry ashing can be superior as it introduces no reagent-based contaminants, though you must guard against airborne contamination.
- If your primary focus is safety and simplicity: Dry ashing avoids the use of hazardous liquid acids and requires far less hands-on supervision.
Ultimately, selecting the correct sample preparation method requires a clear understanding of the target elements and the inherent limitations of each technique.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Hazardous Acids | Requires handling corrosive reagents (e.g., HNO₃, H₂SO₄) with explosion risks. |
| High Contamination Risk | Introduces reagent blanks, requiring expensive high-purity acids for accuracy. |
| Labor-Intensive Process | Demands constant supervision, preventing high-throughput, unattended operation. |
| Incomplete Digestion | Some complex samples (high in fats/oils) may not fully digest, trapping analytes. |
Need a Safer, More Efficient Sample Preparation Solution?
Wet ashing's disadvantages—like safety hazards and contamination risks—can hinder your lab's productivity and accuracy. At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment designed to optimize your workflows. Whether you require advanced digestion systems or safer alternatives for trace metal analysis, our solutions are tailored to meet the specific needs of laboratories like yours.
Let us help you enhance safety and precision in your sample preparation. Contact our experts today to find the ideal equipment for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace in a lab? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Heat for Your Materials
- What is a muffle furnace used for in microbiology? Essential for Depyrogenation and Ashing
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Unlock Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What type of insulation is used in a muffle furnace? Essential Materials for High-Temperature Performance
- What 5 safety precautions should be taken when heating anything in the lab? Essential Rules for Lab Safety



















