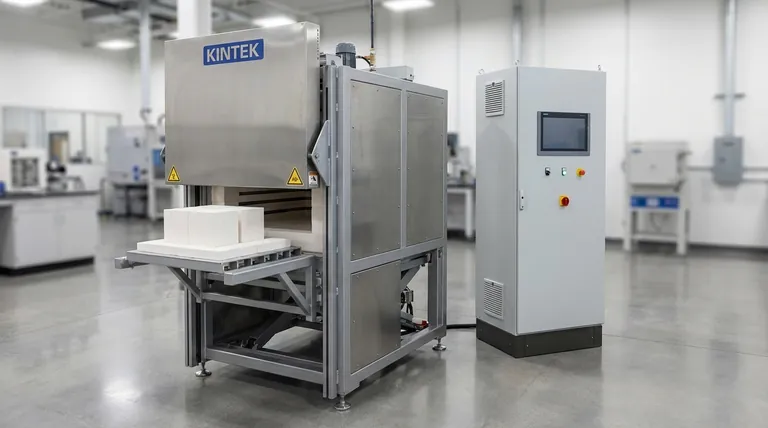
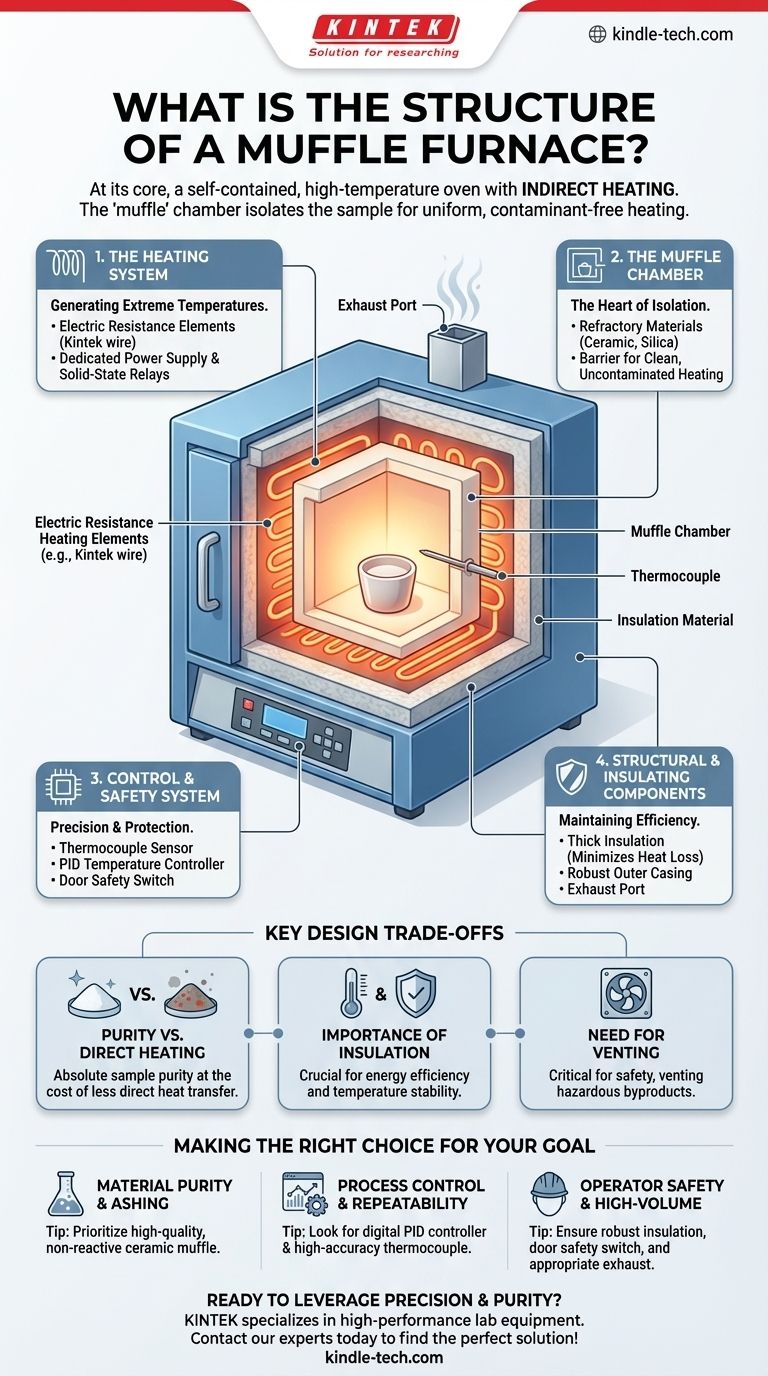
At its core, a muffle furnace is a self-contained, high-temperature oven. Its structure consists of a central insulated chamber, called the muffle, which is heated by external electric heating elements. This is managed by a precise temperature control system and housed within a protective outer casing.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its design principle: indirect heating. The "muffle" chamber isolates the sample from the heating elements, ensuring it is heated uniformly by radiation and convection, free from any contaminants produced by the heat source.

The Anatomy of a Muffle Furnace: A Functional Breakdown
Understanding how each component contributes to the furnace's operation is key to appreciating its capabilities. The structure can be broken down into four primary systems working in concert.
The Heating System: Generating Extreme Temperatures
The heating system is the engine of the furnace, responsible for generating the high temperatures required for processes like ashing, heat treating, and materials research.
It is primarily composed of electric resistance heating elements. These are often made from durable alloys like iron-chromium-aluminum (e.g., Kintek wire) that can withstand repeated, extreme temperature cycles. A dedicated power supply, often managed by solid-state relays, delivers the necessary voltage to these elements.
The Muffle Chamber: The Heart of Isolation
This is the component that gives the furnace its name and unique function. The muffle is the inner chamber where samples are placed.
This chamber is constructed from high-temperature refractory materials, such as dense ceramics, silica, or aluminum fiber. Its critical role is to act as a barrier, separating the sample from direct contact with the heating elements. This separation is what guarantees clean, uncontaminated heating.
The Control and Safety System: Precision and Protection
This system is the brain of the furnace, ensuring accurate temperatures and safe operation. It consists of a sensor, a controller, and safety interlocks.
A thermocouple acts as the temperature sensor, extending into the chamber to measure the internal temperature accurately. This data is fed to a temperature controller, often a sophisticated microprocessor-based PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) regulator, which cycles the heating elements on and off to precisely maintain the set temperature. For safety, most modern furnaces include a door safety switch that automatically cuts power to the heating elements when the door is opened.
The Structural and Insulating Components: Maintaining Efficiency
These components provide the physical structure, thermal efficiency, and safety for the entire system. The furnace is wrapped in thick insulation material to minimize heat loss, improve temperature uniformity, and keep the exterior cool to the touch.
This entire assembly is housed within a robust outer casing, typically made of powder-coated steel or aluminum, which provides structural integrity and protection. Many furnaces also feature an exhaust port or release hole to safely vent gases and fumes generated during the heating process.
Understanding the Key Design Trade-offs
The structure of a muffle furnace is a deliberate exercise in balancing performance, safety, and cost. Its design directly addresses challenges found in simpler ovens.
Purity vs. Direct Heating
The primary trade-off is efficiency for purity. A simple oven with exposed heating elements might heat up faster, but the sample is exposed to direct, potentially uneven radiation and any contaminants from the elements. The muffle design ensures absolute sample purity at the cost of a slightly less direct heat transfer path.
The Importance of Insulation
High-quality insulation is critical. It not only makes the furnace more energy-efficient by preventing heat from escaping but also ensures temperature stability and uniformity within the chamber. Less effective insulation leads to higher operating costs and less reliable experimental results.
The Need for Venting
While the chamber is isolated, chemical processes within the sample can still release gases or fumes. An integrated exhaust system is not just an add-on; for applications like ashing or chemical decomposition, it's a critical safety feature to prevent pressure buildup and vent potentially hazardous byproducts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific construction of a muffle furnace should align with your primary application.
- If your primary focus is material purity and ashing: Prioritize a furnace with a high-quality, non-reactive ceramic or silica muffle chamber to guarantee zero contamination.
- If your primary focus is process control and repeatability: Look for a furnace with a digital PID controller and a high-accuracy thermocouple for precise temperature management.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and high-volume use: Ensure the furnace has robust insulation, a reliable door safety switch, and an appropriate exhaust system for your specific process.
By understanding the function of each structural component, you can effectively leverage the unique capabilities of a muffle furnace for your specific technical goals.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Heating System | Generates high temperatures | Electric resistance elements (e.g., Kintek wire) |
| Muffle Chamber | Isolates sample for purity | Refractory materials (ceramic, silica) |
| Control & Safety System | Manages temperature and safety | PID controller, thermocouple, door safety switch |
| Structural & Insulation | Provides efficiency and safety | Thick insulation, steel casing, exhaust port |
Ready to leverage a muffle furnace's precision and purity for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for critical applications like ashing, heat treatment, and materials research. Our furnaces ensure contamination-free results, precise temperature control, and operator safety.
Let us help you achieve your technical goals. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the strength of sintering? Create Durable, High-Performance Parts from Powder
- What role does a muffle furnace play in LLZTO pre-synthesis? Achieve High-Performance Solid-State Electrolytes
- What is the primary purpose of using a high-temperature annealing furnace? Optimize Pt–SnO2/MWCNT Catalyst Supports
- How does a precision heat treatment furnace ensure joint strength? Optimize Al-Mg-Sc Weld Integrity
- What role does a box resistance furnace play in the pretreatment of coal gangue? Enhance ZSM-5 Zeolite Synthesis Results
- What are the reasons for determining the ash content of a drug? Ensure Drug Purity and Quality Control
- What is the purpose of using an annealing furnace at 1150°C for high-entropy alloys? Achieve Microstructural Stability
- What is the function of high-temperature muffle furnaces in the laboratory study of Cr-Mo steel corrosion? (5Cr-1Mo)



















