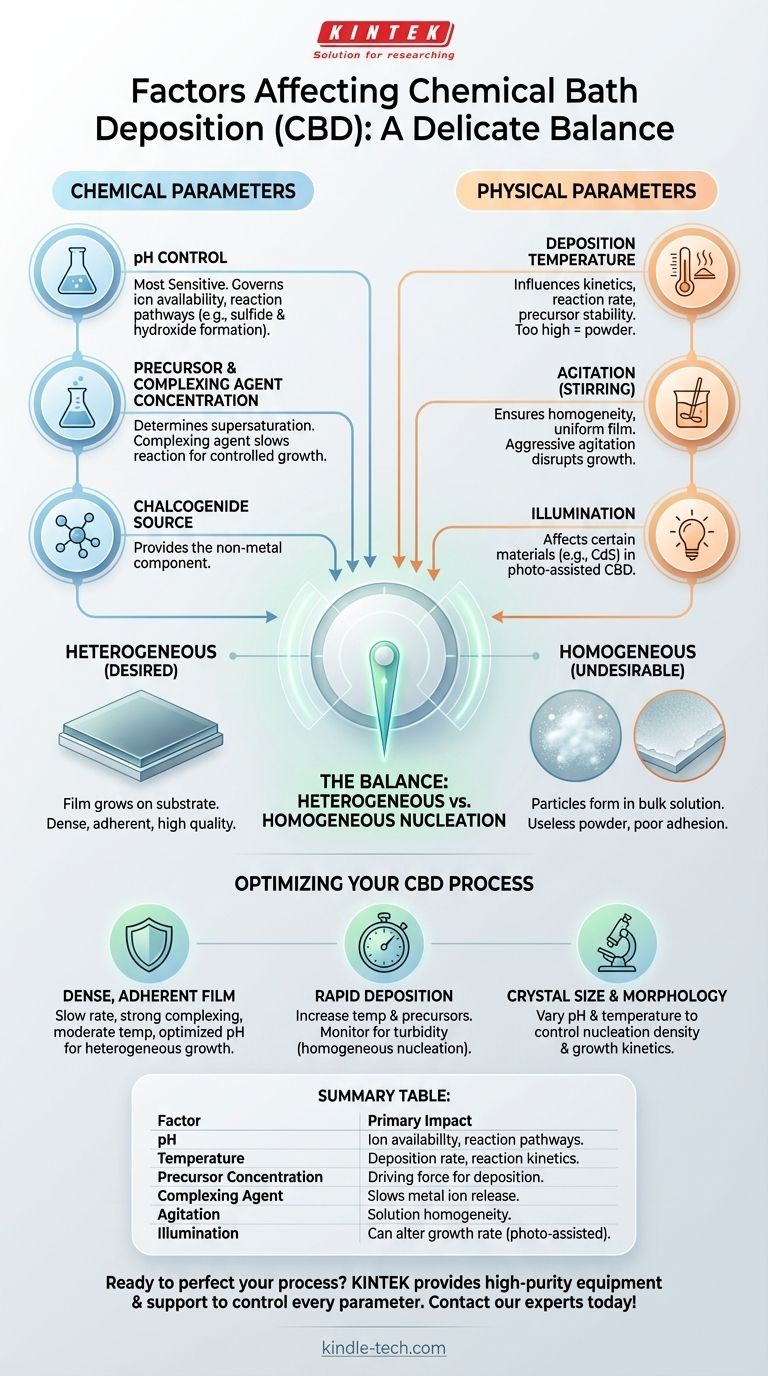
The quality of a film from Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) is determined by a delicate balance of solution chemistry and physical conditions. The most critical factors you must control are the solution's pH, the deposition temperature, and the concentration of chemical precursors. Secondary factors such as bath agitation, illumination, and the nature of the substrate also play a significant role in the final film structure and properties.
Mastering CBD is not about finding a single "correct" recipe, but about understanding how key parameters interact to control the competing processes of particle formation in the solution versus film growth on the substrate.

The Core Chemical Parameters
The chemistry of the bath is the primary driver of the deposition process. Slight changes in these variables can dramatically alter the outcome, shifting from a high-quality film to a useless powder.
The Role of pH
The pH of the solution is arguably the most sensitive parameter in CBD. It directly governs the availability of the ions needed for film formation.
For example, in the deposition of a metal sulfide (like CdS), pH controls the concentration of sulfide ions (S²⁻) by shifting the equilibrium of the sulfide source (e.g., thiourea). It also controls the formation of metal hydroxides, which can compete with the desired reaction.
Precursor and Complexing Agent Concentration
The concentration of the metal salt and the chalcogenide source (the precursors) determines the degree of supersaturation in the solution. This is the thermodynamic driving force for deposition.
To prevent an uncontrolled reaction, a complexing agent (or chelating agent) like ammonia or citrate is almost always added. This agent binds to the metal ions, slowing their release into the solution and ensuring a controlled, gradual film growth on the substrate rather than rapid precipitation in the bulk liquid.
The Key Physical Parameters
Physical conditions of the deposition environment are used to manage the rate and uniformity of the chemical reactions occurring in the bath.
Deposition Temperature
Temperature directly influences the kinetics of the entire process. It affects the decomposition rate of the precursors, the stability of the complexed metal ions, and the diffusion of reactants in the solution.
Increasing the temperature generally increases the deposition rate. However, excessively high temperatures can accelerate particle formation in the bulk solution, leading to powdery, poorly adherent films.
Agitation (Stirring)
Agitation of the chemical bath ensures temperature and chemical homogeneity. It helps transport fresh reactants to the substrate surface and removes byproducts.
Controlled stirring can lead to more uniform films. However, overly aggressive agitation can disrupt the boundary layer at the substrate surface, hindering the delicate process of film growth.
Illumination
For certain semiconductor materials, such as cadmium sulfide (CdS), illumination can influence the deposition process. This effect, known as photo-assisted CBD, can alter the growth rate and film properties by creating photo-generated charge carriers that participate in the chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The central challenge in CBD is managing the competition between two distinct growth mechanisms. Your success depends on favoring one over the other.
Heterogeneous vs. Homogeneous Nucleation
Heterogeneous nucleation is the desired process, where the film forms and grows directly on the surface of the substrate. This leads to dense, adherent, and high-quality thin films.
Homogeneous nucleation is the formation of particles within the bulk solution. If the solution becomes too supersaturated, particles precipitate out everywhere, consuming the reactants and leading to a useless colloidal suspension and a powdery, non-adherent coating on the substrate.
The Balancing Act
Every parameter adjustment is a trade-off between these two pathways. Increasing temperature or precursor concentration speeds up deposition (heterogeneous growth) but also significantly increases the risk of runaway homogeneous nucleation. The role of the complexing agent and precise pH control is to keep the reaction in the "sweet spot" that favors growth on the substrate.
Optimizing CBD for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine how you balance these competing factors. Use the following principles as a guide for process control.
- If your primary focus is a dense, highly-adherent film: Prioritize a slow, controlled deposition rate. Use a strong complexing agent, maintain a moderate temperature, and ensure the pH is carefully optimized to favor heterogeneous nucleation.
- If your primary focus is rapid deposition: Carefully increase the temperature and precursor concentrations. Be prepared to monitor the solution for turbidity (cloudiness), which is the first sign of undesirable homogeneous nucleation.
- If your primary focus is tuning crystal size and morphology: Focus your experiments on varying pH and temperature. These two factors have the most direct and significant impact on nucleation density and crystal growth kinetics.
By systematically controlling these interconnected factors, you can steer the chemical bath deposition process to produce high-quality thin films tailored to your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Primary Impact on CBD Process |
|---|---|
| pH | Controls ion availability and reaction pathways. |
| Temperature | Governs deposition rate and reaction kinetics. |
| Precursor Concentration | Determines the driving force for deposition. |
| Complexing Agent | Slows metal ion release for controlled growth. |
| Agitation | Ensures solution homogeneity and uniform growth. |
| Illumination | Can alter growth rate in photo-assisted CBD. |
Ready to perfect your Chemical Bath Deposition process?
KINTEK is your trusted partner for high-purity lab equipment and consumables. We provide the reliable tools and expert support you need to precisely control every parameter—from pH meters and temperature-controlled baths to high-purity precursors and complexing agents.
Let us help you achieve consistent, high-quality thin films. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the most common method of making graphene? Discover the Industry Standard for High-Quality Production
- Why is argon-rich gas phase chemistry used for UNCD growth? Unlock Precision Nano-Diamond Synthesis
- What is CVD in coating? A Guide to High-Performance Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What are the two main categories of modern CVD processes? Comparing LPCVD and UHVCVD for Precision Film Growth
- What is the rate of physical vapor deposition? A Guide to Controlling Your Thin Film Growth
- Why is high-speed wafer rotation necessary for vertical CVD? Master Flow Engineering for 4H-SiC Thin Films
- Why argon is used in sputtering process? The Perfect Balance of Physics and Economics
- What is RTP technique for annealing? Achieve Ultra-Fast, Low Thermal Budget Processing for Semiconductors

















