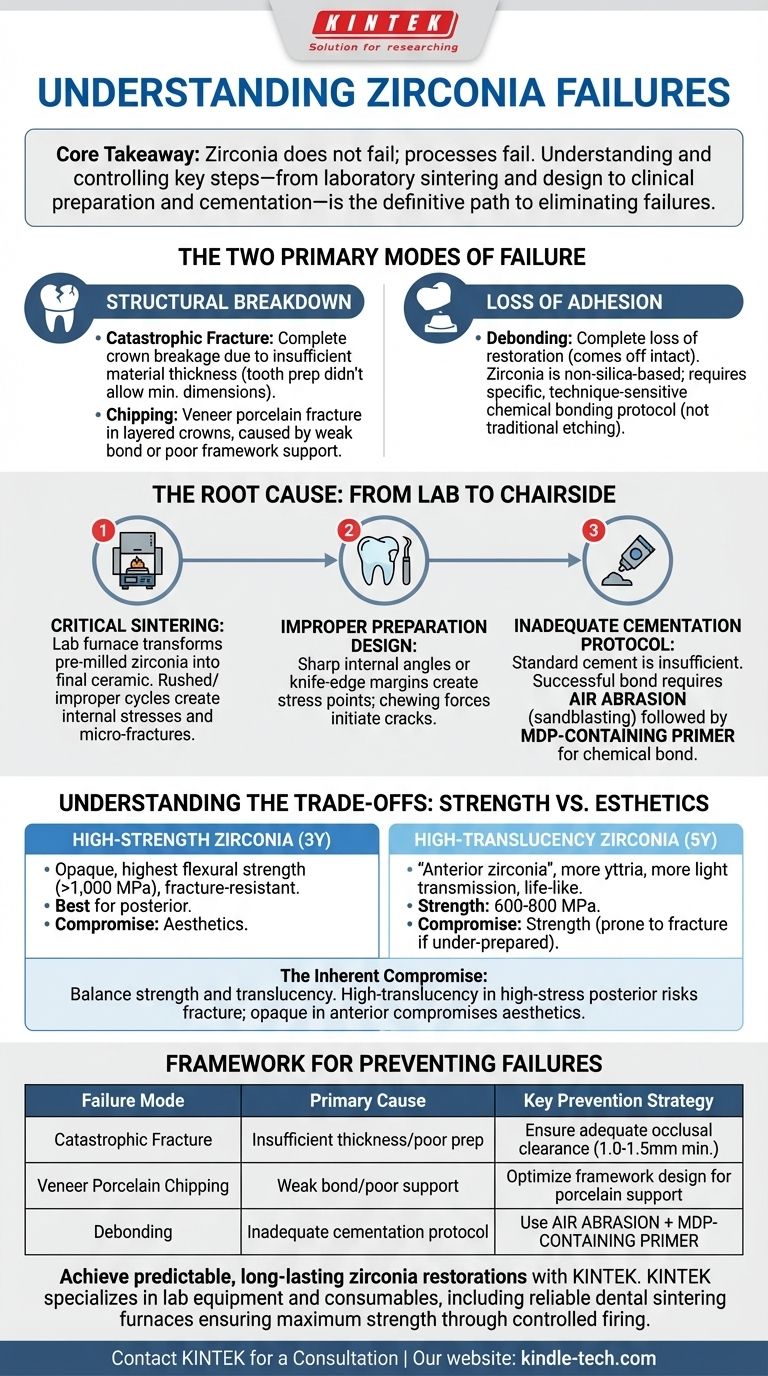
Zirconia failures are rarely a surprise. While the material itself is exceptionally strong, clinical failures almost always point to process-related issues, not an inherent flaw in the material. The two most common modes of failure are fracture (either of the core or veneering ceramic) and debonding, both of which are largely preventable.
The core takeaway is that zirconia does not fail; processes fail. Understanding and controlling the key steps—from laboratory sintering and design to clinical preparation and cementation—is the definitive path to eliminating the vast majority of zirconia restoration failures.
The Two Primary Modes of Failure
To prevent failures, we must first clearly define them. They fall into two distinct categories: structural breakdown and loss of adhesion.
Catastrophic Fracture
This is the complete breakage of the crown itself. While zirconia has a very high flexural strength, it is not invincible. These fractures are almost always a result of insufficient material thickness, meaning the tooth preparation did not allow for the minimum dimensions required by the manufacturer.
Chipping (Veneer Porcelain Fracture)
This failure is specific to layered zirconia crowns, where an aesthetic porcelain is baked onto a zirconia core. The chipping occurs in the weaker porcelain layer, not the strong zirconia substructure. This is often caused by a weak bond between the layers or a framework design that doesn't adequately support the porcelain.
Debonding (Loss of Retention)
This is a complete loss of the restoration, which comes off the tooth intact. Zirconia is a non-silica-based ceramic, which means it cannot be etched with hydrofluoric acid like traditional porcelain. This makes achieving a strong chemical bond more technique-sensitive and is a frequent point of clinical error.
The Root Cause: From Lab to Chairside
Failure is a chain of events. The root cause is often found far before the crown is ever placed in the patient's mouth.
The Critical Role of Sintering
Sintering is the furnace-based heating process that transforms the chalky, pre-milled zirconia into its final, dense ceramic state. This is the single most critical laboratory step. Rushed sintering cycles or improperly calibrated ovens can create internal stresses and micro-fractures, significantly weakening the final restoration and making it prone to failure under normal function.
Improper Preparation Design
Zirconia's strength is leveraged through proper engineering. Sharp internal angles or knife-edge margins on the tooth preparation create stress concentration points. Over time, chewing forces will focus on these points, potentially initiating a crack that leads to a catastrophic fracture.
Inadequate Cementation Protocol
Simply using a standard cement is not sufficient for zirconia, especially in cases with limited mechanical retention. A successful, long-term bond relies on a strict protocol: air abrasion of the internal surface (sandblasting) followed by the application of a primer containing MDP (10-Methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate), a monomer that chemically bonds to zirconia oxides.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Esthetics
Not all zirconia is the same. The choice of material has a direct impact on its potential failure modes and ideal use case.
High-Strength Zirconia (3Y)
This is the original, most opaque version of zirconia. It offers the highest flexural strength (over 1,000 MPa) and is exceptionally resistant to fracture. Its opacity, however, limits its use in highly aesthetic areas. It is the gold standard for posterior crowns and bridges.
High-Translucency Zirconia (5Y)
Often marketed as "anterior zirconia," this material contains more yttria, which arranges the crystals to allow more light to pass through, creating a more life-like appearance. This improved esthetic comes at the cost of strength, which is typically in the 600-800 MPa range. It is more prone to fracture if under-prepared.
The Inherent Compromise
You must accept the compromise between strength and translucency. Using a high-translucency material in a high-stress posterior situation without meticulous attention to preparation thickness is inviting a fracture. Conversely, using an opaque, high-strength material for an anterior tooth compromises the aesthetic outcome.
A Framework for Preventing Zirconia Failures
Success with zirconia is a function of clear communication with your lab and precise clinical protocols.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability (posterior crowns): Use a high-strength (3Y) zirconia and ensure your preparation provides at least 1.0-1.5 mm of occlusal clearance.
- If your primary focus is optimal esthetics (anterior crowns): A high-translucency (5Y) zirconia is appropriate, but you must ensure a robust adhesive bonding protocol to support the material.
- If you are experiencing debonding issues: Immediately implement a protocol of air abrasion followed by an MDP-containing primer on every zirconia restoration.
- If you are concerned about lab quality: Have a direct conversation with your lab about their sintering protocols. Avoid labs that prioritize one-day turnaround times over proven, manufacturer-recommended firing cycles.
Mastering zirconia is not about fearing its failure, but about controlling the processes that guarantee its success.
Summary Table:
| Failure Mode | Primary Cause | Key Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Catastrophic Fracture | Insufficient material thickness / poor preparation design | Ensure adequate occlusal clearance (1.0-1.5mm min.) |
| Veneer Porcelain Chipping | Weak bond between zirconia core and veneering ceramic | Optimize framework design for porcelain support |
| Debonding (Loss of Retention) | Inadequate cementation protocol for non-silica ceramic | Use air abrasion + MDP-containing primer for chemical bond |
Achieve predictable, long-lasting zirconia restorations with KINTEK.
Zirconia's performance hinges on precision from the lab to the chairside. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that form the foundation of success. Our reliable dental sintering furnaces ensure your zirconia reaches its maximum strength through controlled, accurate firing cycles, mitigating the risk of internal flaws that lead to failure.
Partner with us to equip your laboratory for excellence. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your workflow and restoration outcomes.
Contact KINTEK for a Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is dental ceramic made of? Discover the Science Behind Strong, Beautiful Teeth
- What is the function of a high-vacuum sintering furnace in 3Y-TZP? Enhance Dental Restoration Quality
- What is a sintering furnace for dental? The Key to Durable, High-Strength Ceramic Restorations
- What is the future of dental ceramics? A Digitally-Driven Shift to Specialized & Bioactive Materials
- What are the different types of temperature calibration systems used in porcelain furnaces? Ensure Precision for Every Ceramic Type
- What is the furnace in which ceramics are fired? A Guide to Choosing the Right Kiln for Your Project
- What is pre sintered zirconia? The Key to Milling Strong, Precise Dental Restorations
- Are ceramic implants more expensive than titanium? Unpacking the Cost-Benefit Analysis



















