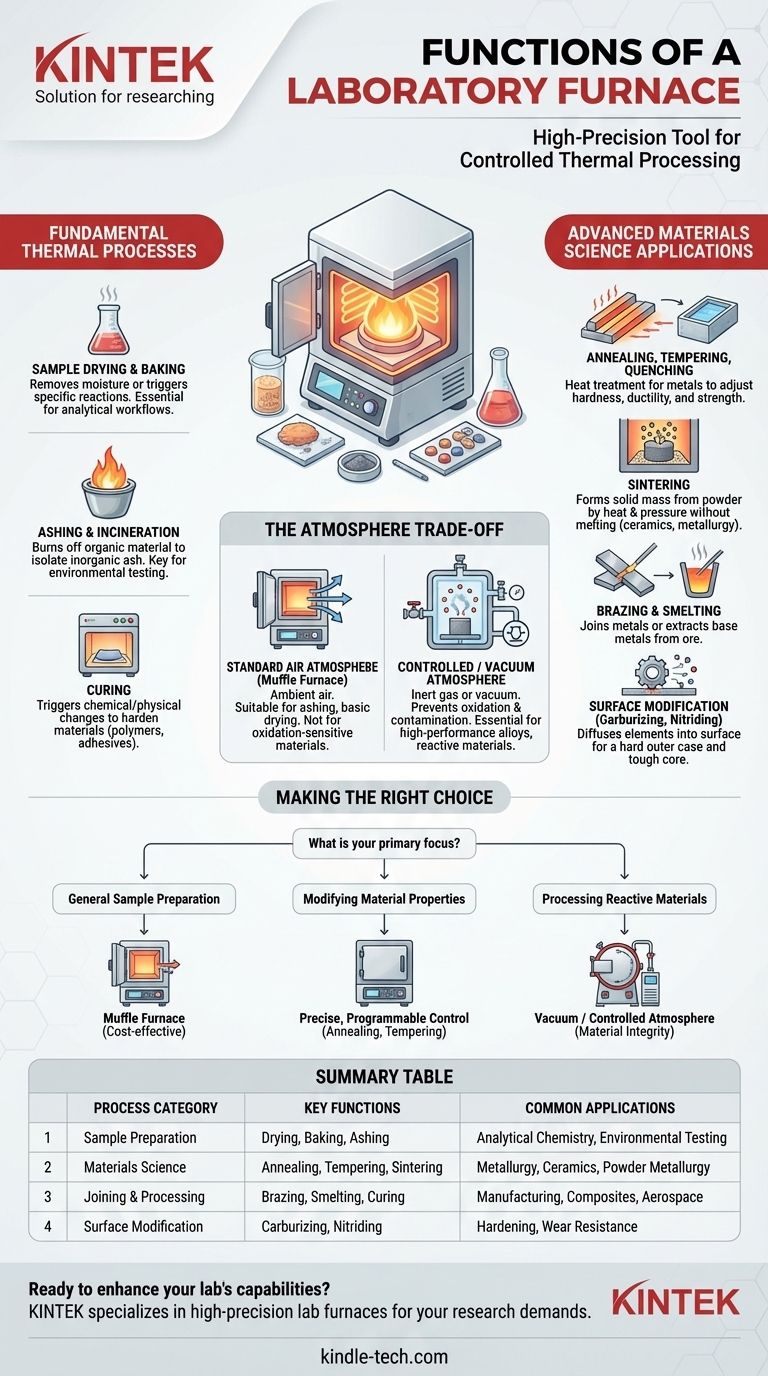
In essence, a laboratory furnace is a high-precision tool for controlled thermal processing. Its functions range from simple sample drying and preparation for chemical analysis to complex metallurgical treatments that fundamentally alter a material's properties. These instruments are critical for materials science, chemistry, and engineering research and development.
The primary purpose of a laboratory furnace is not just to generate heat, but to apply a precise, repeatable thermal cycle to a sample. This control allows researchers to intentionally change a material's physical structure, chemical composition, or mechanical properties to achieve a specific outcome.

Fundamental Thermal Processes
The most common applications for laboratory furnaces involve preparing samples or inducing basic physical and chemical changes.
Sample Drying and Baking
Drying is the process of using heat to remove moisture from a sample. Baking involves heating a substance for a specific time and temperature, often without the primary goal of dehumidification, to trigger a specific reaction.
These are foundational steps in many analytical and manufacturing workflows.
Ashing and Incineration
Ashing is a sample preparation technique that uses high temperatures to burn off all organic material. This isolates the non-combustible inorganic components (the "ash") for subsequent chemical analysis.
This is a critical function in environmental testing, food science, and material composition analysis.
Curing
Curing uses heat to trigger a chemical or physical change, hardening or setting a material. This is common for polymers, adhesives, and composites, where heat initiates cross-linking that solidifies the final product.
Advanced Materials Science Applications
For metallurgists and materials scientists, furnaces are used to precisely manipulate the microscopic structure of materials, thereby controlling their macroscopic properties like strength, hardness, and ductility.
Annealing, Tempering, and Quenching
These are all heat treatment processes for metals and alloys. Annealing softens a metal to make it more workable, while quenching (rapid cooling) and tempering (reheating to a lower temperature) are used in combination to achieve a desired balance of hardness and toughness.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. It is essential for manufacturing ceramics and in powder metallurgy.
Brazing and Smelting
Brazing is a high-temperature process used to join two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint. Smelting is an extractive process used to produce a base metal from its ore.
Surface Modification
Processes like carburizing and nitriding involve heating a metal part in a specific chemical atmosphere. This diffuses elements like carbon or nitrogen into the surface, creating an exceptionally hard outer case while maintaining a tougher core.
Understanding the Trade-off: Atmosphere Control
The most significant differentiator between furnace types is their ability to control the internal atmosphere, which is crucial for preventing unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Standard Air Atmosphere
The simplest furnaces, often called muffle furnaces, operate in ambient air. These are perfectly suitable for processes like ashing, basic drying, or heat-treating materials that are not sensitive to oxidation.
Controlled or Vacuum Atmosphere
Advanced materials often require heating in the absence of oxygen to prevent oxidation and contamination. Vacuum furnaces or those using an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) provide this controlled environment.
This control is essential for processing high-performance alloys, brazing aerospace components, and sintering reactive metal powders.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general sample preparation: A standard muffle furnace for drying, ashing, or basic heat tests is often sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties: You need a furnace with precise, programmable temperature controls for processes like annealing, tempering, or curing.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or high-purity materials: A vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
Ultimately, a laboratory furnace provides the controlled environment needed to transform materials through the precise application of thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Process Category | Key Functions | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Preparation | Drying, Baking, Ashing | Analytical Chemistry, Environmental Testing |
| Materials Science | Annealing, Tempering, Sintering | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Powder Metallurgy |
| Joining & Processing | Brazing, Smelting, Curing | Manufacturing, Composites, Aerospace |
| Surface Modification | Carburizing, Nitriding | Hardening, Wear Resistance |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with the right thermal processing equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-precision lab furnaces, from standard muffle furnaces for sample preparation to advanced vacuum and controlled-atmosphere models for sensitive materials. Our expertise ensures you get the precise temperature control and atmosphere management your research demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the perfect furnace solution for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum retort furnace with integrated argon flow control necessary for industrial aluminizing processes?
- What is the purpose of vacuum hardening? Achieve Flawless, High-Strength Metal Components
- How does a pit furnace work? Prevent Distortion in Long Parts with Vertical Heat Treatment
- What are the variables of the sintering process? Master Temperature, Time, Pressure & Atmosphere
- What is the quenching operation usually followed by? The Essential Tempering Process for Toughness
- How do high-temperature furnaces affect bio-oil yield? Optimize Pyrolysis with Precision Control
- How do you prevent vacuum leaks? A Proactive Strategy for System Integrity
- What are the factors that determine the strength of a brazed joint? Achieve Maximum Strength for Your Metal Assemblies



















