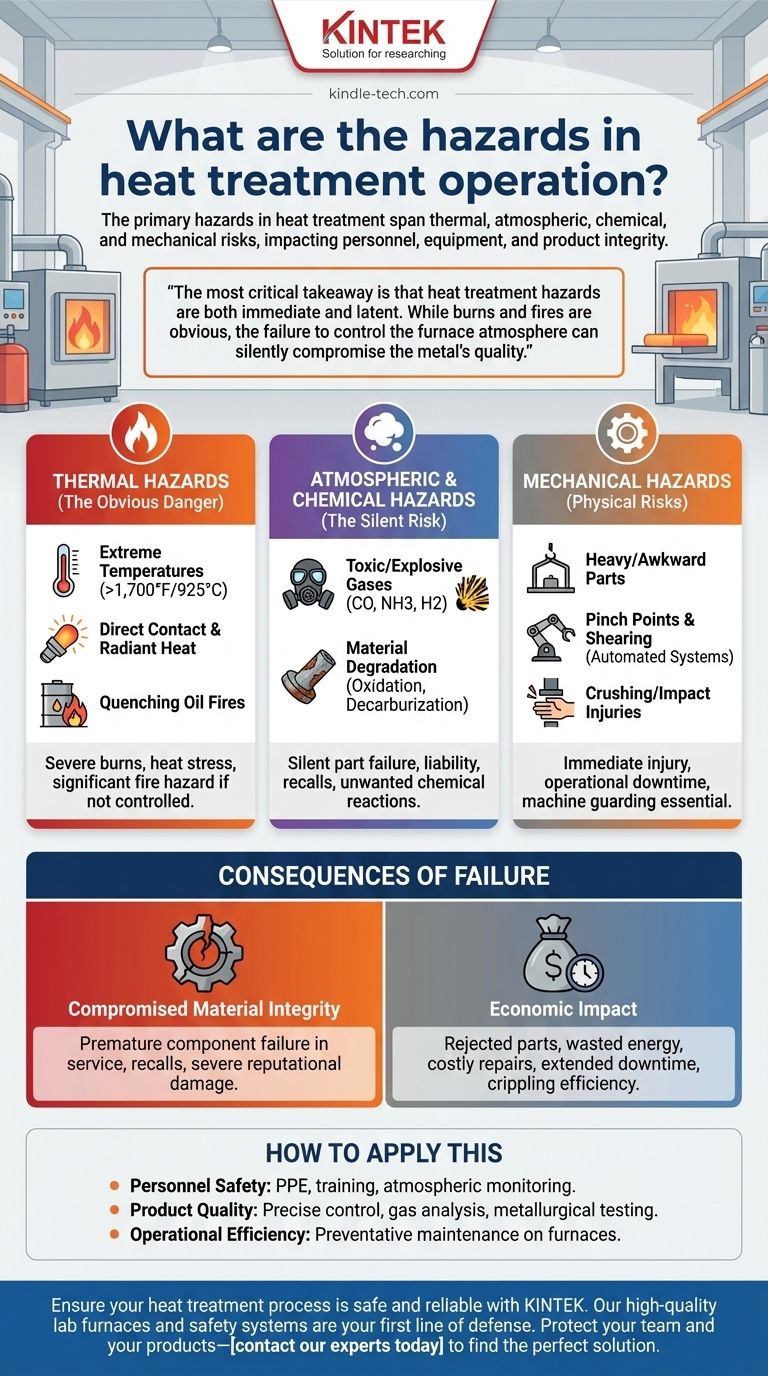
The primary hazards in heat treatment span far beyond simple high temperatures. They encompass a range of thermal, atmospheric, chemical, and mechanical risks that can impact personnel, equipment, and the integrity of the final product. An improperly controlled process not only poses immediate safety threats but can also introduce invisible material defects, leading to catastrophic failure in the field.
The most critical takeaway is that heat treatment hazards are both immediate and latent. While burns and fires are obvious risks, the failure to precisely control the furnace atmosphere can silently compromise the metal's quality, leading to equipment damage, financial loss, and dangerous product failures down the line.

The Primary Hazard Categories
To effectively manage risk, you must understand the distinct categories of hazards inherent to heat treating operations. Each presents a unique set of challenges and requires specific mitigation strategies.
Thermal Hazards (The Obvious Danger)
The most apparent risk comes from the extreme temperatures involved. Furnaces often operate at temperatures exceeding 1,700°F (925°C).
Sources of thermal hazards include direct contact with hot parts, furnace interiors, or fixtures. Radiant heat from the furnace can also cause severe burns and heat stress even without direct contact.
Furthermore, the use of flammable quenching oils presents a significant fire hazard if not handled and maintained within strict temperature and atmospheric controls.
Atmospheric & Chemical Hazards (The Silent Risk)
Many heat treatment processes require a controlled atmosphere within the furnace to achieve specific metallurgical properties. This introduces serious chemical hazards.
An improperly controlled atmosphere can create a toxic or explosive environment. Gases like carbon monoxide, ammonia, or hydrogen are often used and can pose severe risks to employees if they leak.
As the reference highlights, a faulty atmosphere can also cause unwanted chemical reactions on the metal's surface, such as oxidation or decarburization. This silently degrades the material's properties, rendering the part useless or dangerously weak.
Mechanical Hazards
The physical process of loading and unloading furnaces involves significant mechanical risks. This includes handling heavy or awkwardly shaped parts, which can lead to crushing or impact injuries.
Automated systems, conveyors, and furnace doors create pinch points and shearing hazards. Proper machine guarding and lockout/tagout procedures are essential to prevent accidents during operation and maintenance.
Understanding the Consequences of Failure
The repercussions of a hazard materializing extend far beyond an immediate injury on the shop floor. The more subtle process failures can have delayed but catastrophic effects.
Compromised Material Integrity
This is the most insidious hazard. A part with incorrect surface chemistry due to poor atmospheric control may pass visual inspection but lack the required hardness, fatigue resistance, or strength.
This weakness can lead to premature component failure once in service. As noted, this has dangerous repercussions for customers and can lead to liability, recalls, and severe damage to your company's reputation.
Economic Impact
Process failures lead directly to financial loss. Rejected parts, wasted energy, and lost production time are the immediate costs.
Beyond that, an incident involving equipment damage—such as furnace degradation from a reactive atmosphere—can result in costly repairs and extended downtime, crippling operational efficiency.
How to Apply This to Your Operation
A comprehensive safety and quality strategy must address every category of hazard. Your specific focus will determine your priorities.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: Prioritize rigorous training on thermal hazards, proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), atmospheric monitoring for toxic gases, and strict lockout/tagout procedures.
- If your primary focus is product quality and reliability: Implement precise atmospheric control systems, regular gas analysis, and robust post-treatment metallurgical testing to validate every batch.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Emphasize preventative maintenance on furnaces and control systems to avoid equipment damage, costly rework, and unplanned downtime.
Ultimately, effective hazard management in heat treatment recognizes that personnel safety and product quality are inextricably linked.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal | Burns, heat stress, fire from quenching oils | Personnel injury, equipment damage |
| Atmospheric & Chemical | Toxic/explosive gases, material oxidation/decarburization | Silent part failure, liability, recalls |
| Mechanical | Crushing, pinch points, shearing hazards | Immediate injury, operational downtime |
Ensure your heat treatment process is safe and reliable. The right equipment is your first line of defense against thermal, chemical, and mechanical hazards. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, safety systems, and consumables designed for precise atmospheric control and operational safety. Protect your team and your products—contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















