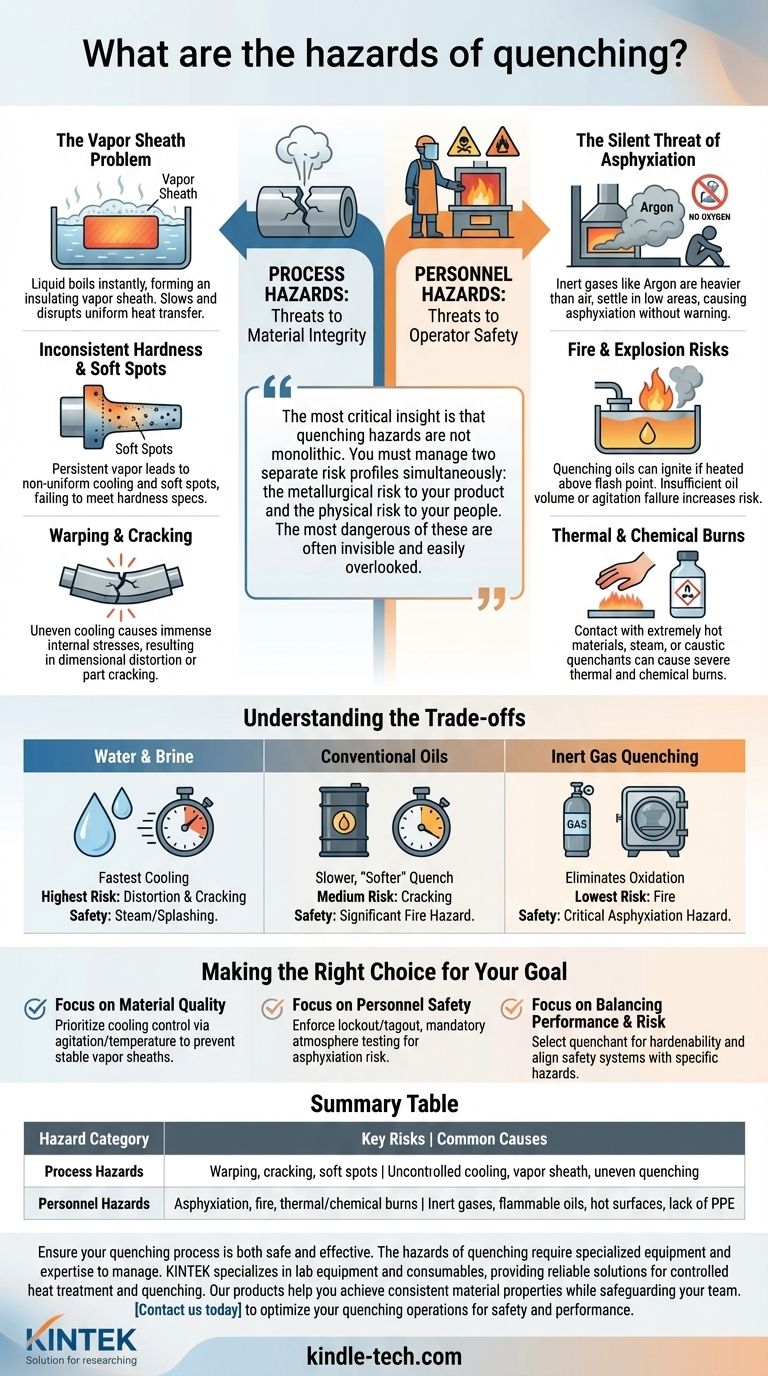
At its core, the hazards of quenching fall into two distinct categories: process hazards that compromise the integrity of the material being treated, and personnel hazards that pose a direct threat to operator safety. Process failures often stem from uncontrolled cooling, leading to warping or cracking, while safety risks include severe asphyxiation from inert gases and fire from flammable quenchants.
The most critical insight is that quenching hazards are not monolithic. You must manage two separate risk profiles simultaneously: the metallurgical risk to your product and the physical risk to your people. The most dangerous of these are often invisible and easily overlooked.
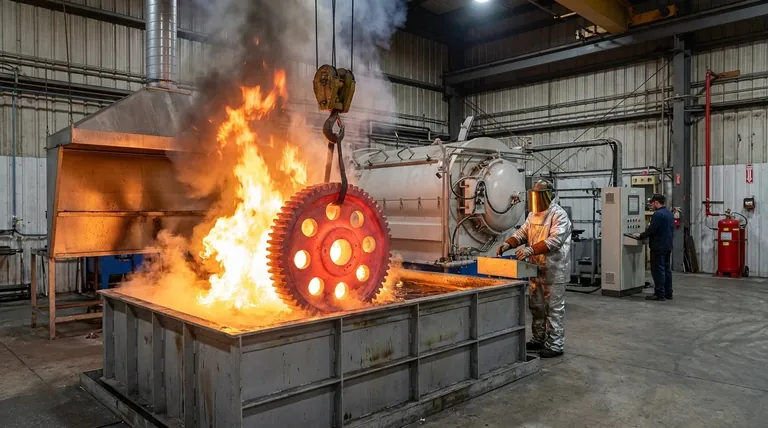

Process Hazards: Threats to Material Integrity
The goal of quenching is to "lock in" a desired metallurgical structure by cooling a part at a specific rate. Any deviation from this controlled cooling introduces a process hazard, which can ruin the workpiece and waste significant time and resources.
The Vapor Sheath Problem
When a hot part is submerged in a liquid quenchant, the liquid at the surface instantly boils. This can form a stable blanket of vapor, known as a vapor sheath or the Leidenfrost effect.
This sheath acts as an insulator, dramatically slowing the rate of heat transfer. If this vapor barrier is too stable or does not collapse uniformly across the part's surface, the cooling becomes inefficient and dangerously uneven.
Inconsistent Hardness and Soft Spots
The primary consequence of a persistent vapor sheath is non-uniform cooling. Areas where the vapor blanket lingers will cool much slower than areas where it has collapsed.
This differential cooling prevents the formation of a consistent hardened structure, resulting in soft spots that fail to meet hardness specifications.
Warping and Cracking
Uneven cooling is the direct cause of dimensional distortion and failure. When one section of a part cools and contracts much faster than another, immense internal stresses are generated.
If these stresses exceed the material's strength, the part will either warp out of its required shape or, in severe cases, crack. This is often the most costly outcome of a poorly controlled quench.
Personnel Hazards: Threats to Operator Safety
While process hazards affect the product, personnel hazards threaten life and health. These risks are present in nearly all industrial heat-treating environments and demand rigorous control measures.
The Silent Threat of Asphyxiation
Many modern quenching operations, especially in vacuum furnaces, use inert gases like argon as part of the process atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Argon is colorless, odorless, and heavier than air. After a cycle, it can settle in the bottom of the furnace chamber or in pits below the furnace door. An operator entering this space can be overcome by a lack of oxygen and lose consciousness without any warning, leading to asphyxiation.
Fire and Explosion Risks
The use of quenching oils is common, but it introduces a significant fire hazard. If the hot part heats the oil above its flash point, the vapors can ignite.
This risk is magnified if there is insufficient oil volume for the part's mass or if the oil agitation system fails. Proper ventilation and automated fire suppression systems are critical when using flammable quenchants.
Thermal and Chemical Burns
The most obvious hazard is contact with extremely hot materials, furnace interiors, or the quenching medium itself. Even water quenching can produce scalding steam.
Furthermore, some quenchants are caustic or contain chemical additives that can cause severe chemical burns upon skin contact, requiring appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of quenchant is a fundamental trade-off between cooling effectiveness and the type of hazard you are willing to manage.
Water and Brine
These offer the fastest cooling rates but also the highest risk of part distortion and cracking due to their severity. While they eliminate fire risk, the violent boiling can cause splashing and steam hazards.
Conventional Oils
Oils provide a slower, "softer" quench, reducing the risk of cracking. However, they introduce a significant fire hazard that requires robust engineering controls, ventilation to handle fumes, and careful temperature management.
Inert Gas Quenching
Using gases like argon or nitrogen in a vacuum furnace eliminates oxidation and fire risk entirely. However, it introduces the critical and often overlooked asphyxiation hazard, which must be managed with strict entry protocols and atmosphere monitoring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your safety and quality protocols must be designed to address the specific hazards of your quenching method. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
- If your primary focus is material quality and consistency: Prioritize controlling the cooling curve by ensuring proper quenchant agitation and temperature to prevent the formation of a stable vapor sheath.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: Enforce strict lockout/tagout procedures and mandatory atmosphere testing with an oxygen meter before any furnace entry to eliminate asphyxiation risk.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and risk: Select your quenchant based on the steel's hardenability and ensure your facility's safety systems (e.g., ventilation, fire suppression) are explicitly designed for that quenchant's hazards.
A successful quenching operation is defined not just by the quality of the final part, but by the rigorous and proactive management of both its process and personnel hazards.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Process Hazards | Warping, cracking, soft spots | Uncontrolled cooling, vapor sheath, uneven quenching |
| Personnel Hazards | Asphyxiation, fire, thermal/chemical burns | Inert gases, flammable oils, hot surfaces, lack of PPE |
Ensure your quenching process is both safe and effective. The hazards of quenching require specialized equipment and expertise to manage. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for controlled heat treatment and quenching. Our products help you achieve consistent material properties while safeguarding your team from fire, asphyxiation, and other risks. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and let us help you optimize your quenching operations for safety and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques



















