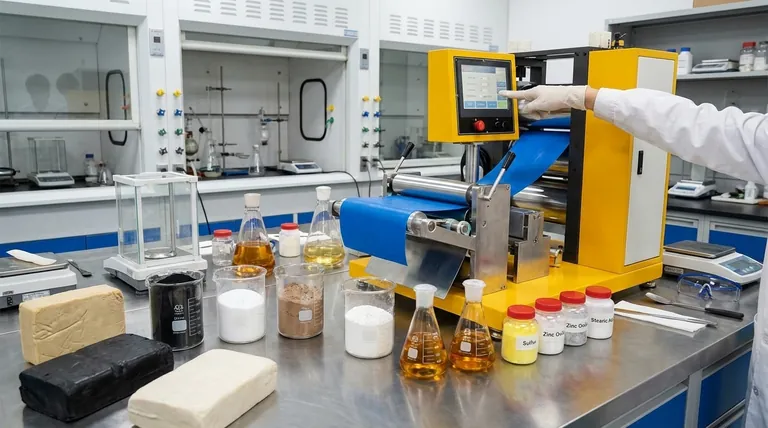
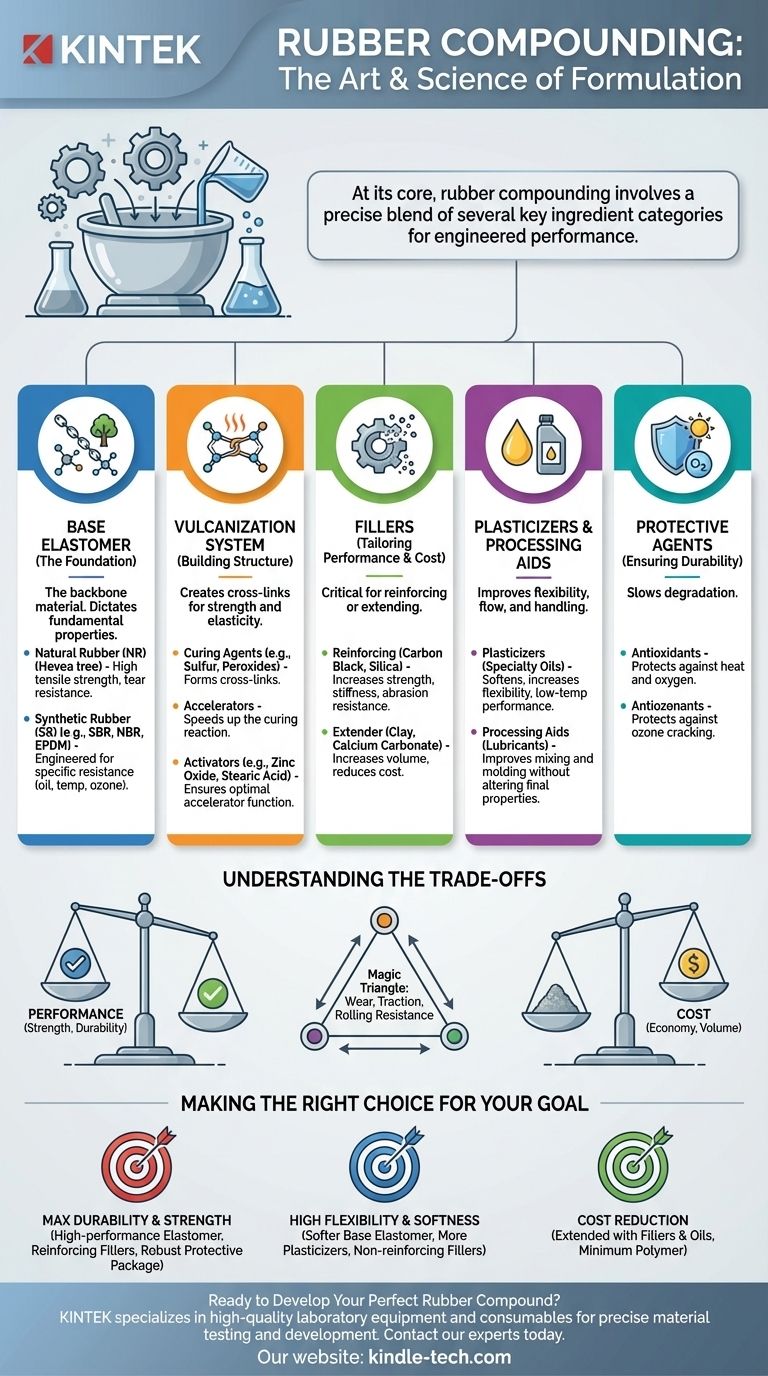
At its core, rubber compounding involves a precise blend of several key ingredient categories. These include the base elastomer (the rubber itself), a vulcanization system to create strength, fillers for reinforcement, plasticizers for flexibility, and protective agents to ensure durability.
A rubber compound is not merely a mixture; it is a carefully engineered recipe. Each ingredient is selected for a specific function, working in concert to transform a raw polymer into a finished material with precise performance characteristics like hardness, elasticity, and resistance to heat or chemicals.

The Foundation: The Base Elastomer
Every rubber compound begins with its primary ingredient: the elastomer. This polymer forms the backbone of the final material and dictates its fundamental properties.
Natural vs. Synthetic Rubber
The initial choice is between natural rubber (NR), derived from the hevea tree, or a wide array of synthetic rubbers (SR) like SBR, NBR, or EPDM. Natural rubber is known for its excellent tensile strength and tear resistance, while synthetics can be engineered for specific properties like oil, temperature, or ozone resistance.
The Vulcanization System: Building the Molecular Structure
Raw rubber is weak and sticky. The vulcanization or "curing" process creates a stable, elastic material by forming chemical cross-links between the long polymer chains. This system typically has three parts.
Curing Agents
The curing agent is the primary ingredient that creates the cross-links. For most common rubbers, this is sulfur. Other agents, like peroxides, are used for specialty elastomers that cannot be cured with sulfur.
Accelerators
Vulcanizing with sulfur alone is extremely slow and inefficient. Accelerators are chemicals that dramatically increase the speed of the curing reaction, allowing for commercially viable production times and improving the final properties of the rubber.
Activators
Activators work with accelerators to make the curing process even more efficient. The most common activator system is a combination of zinc oxide and stearic acid. They ensure the accelerator can perform its function optimally.
Modifiers: Tailoring Performance and Cost
Once the base elastomer and cure system are chosen, modifiers are added to fine-tune the compound's properties, processability, and price.
Fillers
Fillers are solid particles added to the rubber. They are one of the most critical components for tailoring performance.
Reinforcing fillers, like carbon black and silica, chemically bond with the elastomer to significantly increase strength, stiffness, and abrasion resistance. They are essential for demanding applications like tire treads.
Non-reinforcing or extender fillers, such as clay or calcium carbonate, are used primarily to increase volume and reduce the overall cost of the compound. They do not provide significant strength improvement.
Plasticizers and Processing Aids
Plasticizers, such as specialty oils, are liquids added to soften the compound, increase its flexibility, and improve its performance at low temperatures.
Processing aids are lubricants that don't significantly alter the final properties but make the sticky rubber easier to mix, handle, and mold during manufacturing.
Protective Agents
To ensure a long service life, compounds include a protective package. Antioxidants slow down degradation caused by heat and oxygen, while antiozonants protect the rubber from being attacked and cracked by atmospheric ozone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Rubber compounding is a constant balancing act. Improving one property often comes at the expense of another, a concept famously known in the tire industry as the "magic triangle."
Performance vs. Cost
The most fundamental trade-off is between performance and cost. High-performance reinforcing fillers, specialty polymers, and advanced protective agents increase capability but also raise the price. Extender fillers and oils can lower the cost but may compromise durability.
The Magic Triangle: Wear, Traction, and Rolling Resistance
In tire design, you cannot simultaneously maximize all key properties. Increasing abrasion resistance (wear) with certain fillers might increase rolling resistance (lowering fuel economy). Changing the compound to improve wet traction might reduce the tread's overall lifespan. A compounder's job is to find the optimal balance for the intended application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific recipe, or formulation, is entirely dependent on the final product's requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and strength: Your formulation will rely on a high-performance elastomer, a significant amount of reinforcing filler like carbon black, and a robust protective package.
- If your primary focus is high flexibility and softness: You will use a softer base elastomer, a higher concentration of plasticizing oils, and likely a non-reinforcing filler.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction for a non-critical part: The compound will be heavily extended with inexpensive fillers like clay and processing oils, using the minimum amount of polymer required.
Ultimately, rubber compounding transforms a simple raw material into a complex, high-performance engineered product designed for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Ingredient Category | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Base Elastomer | Natural Rubber (NR), SBR, NBR, EPDM | Forms the backbone; dictates fundamental properties |
| Vulcanization System | Sulfur, Peroxides, Accelerators, Activators | Creates cross-links for strength and elasticity |
| Fillers | Carbon Black, Silica (Reinforcing); Clay, Calcium Carbonate (Extender) | Increases strength or reduces cost |
| Plasticizers/Processing Aids | Oils, Lubricants | Improves flexibility, low-temperature performance, and processability |
| Protective Agents | Antioxidants, Antiozonants | Ensures durability and long service life |
Ready to Develop Your Perfect Rubber Compound?
Formulating the right rubber compound is a precise science. The balance of ingredients directly impacts the performance, durability, and cost of your final product. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables needed for precise material testing and development.
Whether you are optimizing for maximum durability, flexibility, or cost-efficiency, having the right tools is crucial. Let us help you achieve your goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your rubber compounding and laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How does a grinding mill work? A Guide to Crushing, Grinding, and Pulverizing
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production
- What is the principle of calendering? Enhance Fabric Surface with Heat and Pressure
- What does calendering do for fabric? Transform Fabric's Look, Feel, and Performance
- How are samples prepared for XRF analysis? Achieve Accurate and Reliable Results



















