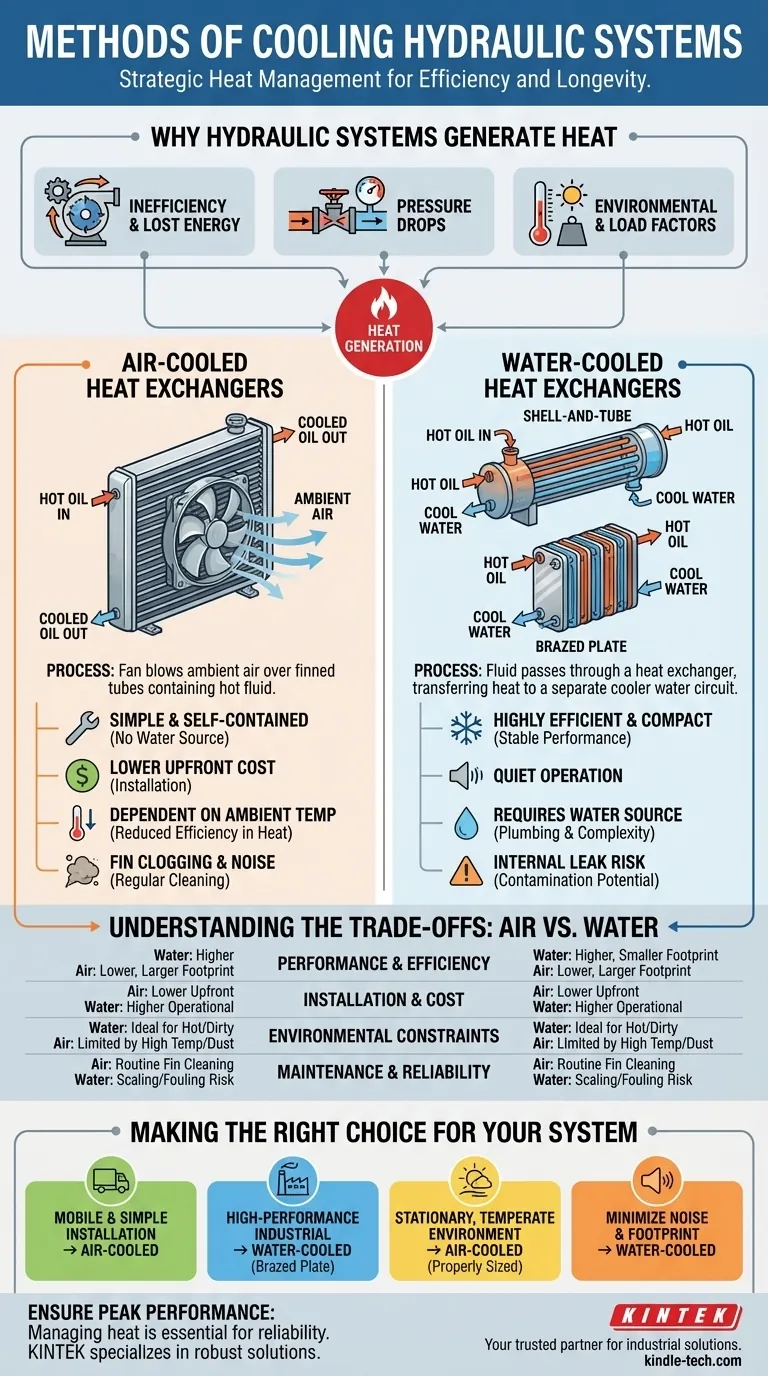
The primary methods for cooling a hydraulic system are air-cooled and water-cooled heat exchangers. An air-cooled system uses a fan to blow ambient air over finned tubes containing the hot hydraulic fluid, much like a car's radiator. A water-cooled system passes the hydraulic fluid through a heat exchanger where its heat is transferred to a separate, cooler water circuit.
Choosing the right cooling method is not just about heat removal. It is a strategic decision based on your operating environment, available utilities, maintenance capabilities, and the overall design of your hydraulic circuit.
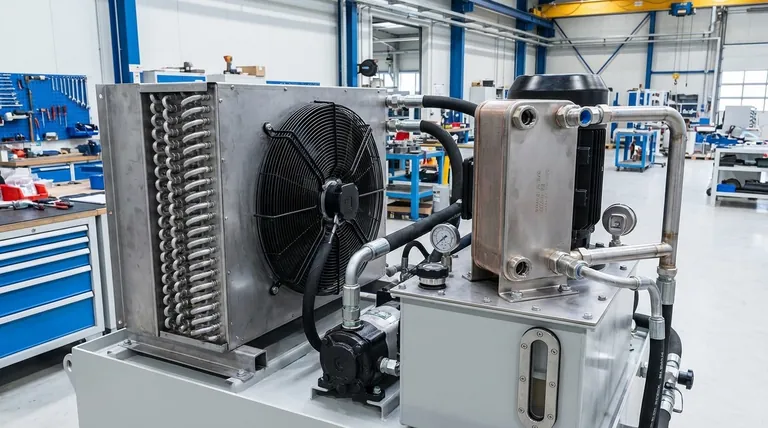

Why Hydraulic Systems Generate Heat
Before selecting a cooler, you must understand why your system needs one. All heat in a hydraulic system is a byproduct of inefficiency. Every watt of heat generated is a watt of input power that was not converted into useful work.
Inefficiency is the Root Cause
Every component in the system, from the pump to the motors and cylinders, has mechanical and volumetric inefficiencies. This lost energy is converted directly into heat and transferred into the hydraulic fluid.
The Role of Pressure Drops
A primary source of heat is the pressure drop that occurs as fluid is forced through hoses, valves, and orifices. When oil flows from an area of high pressure to one of low pressure without performing work, the energy is released as heat.
Environmental and Load Factors
The ambient temperature of the operating environment directly impacts the system's ability to passively cool itself. High external temperatures reduce the effectiveness of any cooling method, especially air-coolers, while heavy, continuous workloads generate more heat than intermittent use.
Primary Cooling Method: Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Air-cooled heat exchangers, often called oil-to-air coolers, are the most common solution for many hydraulic applications, particularly in mobile equipment.
How They Work
Hot hydraulic fluid is pumped through a series of tubes. These tubes are covered in thin metal fins, which dramatically increase the surface area exposed to the air. A fan, powered by an AC, DC, or hydraulic motor, forces ambient air across these fins, drawing heat away from the fluid and dissipating it into the atmosphere.
Advantages
The main benefit of an air-cooled system is its simplicity and self-contained nature. It does not require an external water source, making installation less complex and less expensive, especially in mobile or remote applications.
Disadvantages
Their performance is directly tied to the ambient air temperature. In hot environments, their efficiency drops significantly. The cooling fans can also be a source of noise, and the fins are susceptible to clogging from dust, dirt, and debris, requiring regular cleaning to maintain performance.
Primary Cooling Method: Water-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Water-cooled heat exchangers, or oil-to-water coolers, offer much higher performance in a more compact package, making them ideal for stationary industrial applications with high heat loads.
Shell-and-Tube Coolers
This traditional design consists of a bundle of small tubes (the tube-side) housed within a larger cylindrical shell (the shell-side). Typically, hot oil flows through the shell while cool water flows through the tube bundle, transferring heat through the tube walls.
Brazed Plate Coolers
A more modern and compact design, the brazed plate cooler uses a stack of thin, corrugated metal plates. These plates are brazed together, creating complex channels where oil and water flow in alternating layers. This provides an extremely large heat transfer surface area in a very small volume.
Advantages
Water-cooled systems are highly efficient and compact. Their performance is independent of the ambient air temperature, providing stable and predictable cooling. They are also much quieter than their air-cooled counterparts.
Disadvantages
The primary drawback is the requirement for a reliable source of cool water. This adds complexity and cost to installation, including plumbing for both the supply and discharge. They also carry the risk of internal failure, which could lead to contamination of the hydraulic oil with water or vice-versa.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Air vs. Water
The choice between air and water cooling involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs.
Performance and Efficiency
Water is a far more effective heat transfer medium than air. For a given amount of heat rejection, a water-cooled exchanger will be significantly smaller and more efficient than an air-cooled one.
Installation and Operating Costs
Air coolers have a lower upfront installation cost due to their self-contained design. Water coolers, however, may have higher ongoing operational costs related to pumping, treating, and disposing of the cooling water.
Environmental Constraints
Air coolers are limited by high ambient air temperatures. Water coolers are ideal for hot, dirty environments where an air cooler's fins would quickly clog or be overwhelmed by high ambient temperatures.
Maintenance and Reliability
Air coolers require routine cleaning of the fins. Water coolers can suffer from scaling or biological fouling if the water quality is poor, reducing their effectiveness. The risk of an internal leak, while low in quality units, is a critical consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct cooling solution begins with understanding your system's heat load and operating environment.
- If your primary focus is mobile equipment or installation simplicity: An air-cooled heat exchanger is the clear and standard choice.
- If your primary focus is high-performance industrial machinery with large heat loads: A water-cooled system, particularly a brazed plate design, offers superior and more stable performance.
- If your primary focus is a stationary system in a temperate environment: A properly sized air cooler often provides the most economical and straightforward solution.
- If your primary focus is minimizing noise and physical footprint: A water-cooled heat exchanger is significantly quieter and more compact for its cooling capacity.
Ultimately, managing heat is fundamental to ensuring the reliability and longevity of any hydraulic system.
Summary Table:
| Cooling Method | How It Works | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Cooled | Fan blows ambient air over finned tubes containing hot oil. | Mobile equipment, simple installations. | Self-contained, no external water needed. | Performance drops in high ambient temperatures. |
| Water-Cooled | Cool water flows through a heat exchanger, absorbing heat from the oil. | High-heat industrial machinery, noisy/size-sensitive areas. | Highly efficient, compact, and quiet. | Requires a reliable, clean water source. |
Ensure Your Hydraulic System's Peak Performance
Managing heat is not optional—it's essential for the reliability and long service life of your hydraulic equipment. The wrong cooling solution can lead to premature failure, downtime, and costly repairs.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all your laboratory and industrial equipment needs. We specialize in providing robust solutions that keep your operations running smoothly.
Let us help you select the perfect cooling system for your specific application. Our experts will analyze your heat load, environment, and performance requirements to recommend the optimal air-cooled or water-cooled heat exchanger.
Contact us today for a consultation and discover how KINTEK's expertise can enhance your system's efficiency and durability.
Get a Free Consultation & Protect Your Investment
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press required for solid-state battery assembly? Essential Tools for Ion Conductivity
- What is the significance of XRF in forensic science? Achieve Rapid, Non-Destructive Elemental Analysis
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- How does the use of a high-pressure uniaxial hydraulic press influence the final phase structure? Optimize Conductivity
- How do you convert hydraulic pressure to force? Master the Core Formula for Maximum Power
- How do a laboratory hydraulic press and lubricated molds form dense refractory bricks? Optimize Density & Integrity
- What role does a uniaxial hydraulic press play in the fabrication of NaSICON ceramic cylinders? Pre-forming Excellence
- How does a screw press work? A Guide to Efficient Liquid-Solid Separation










