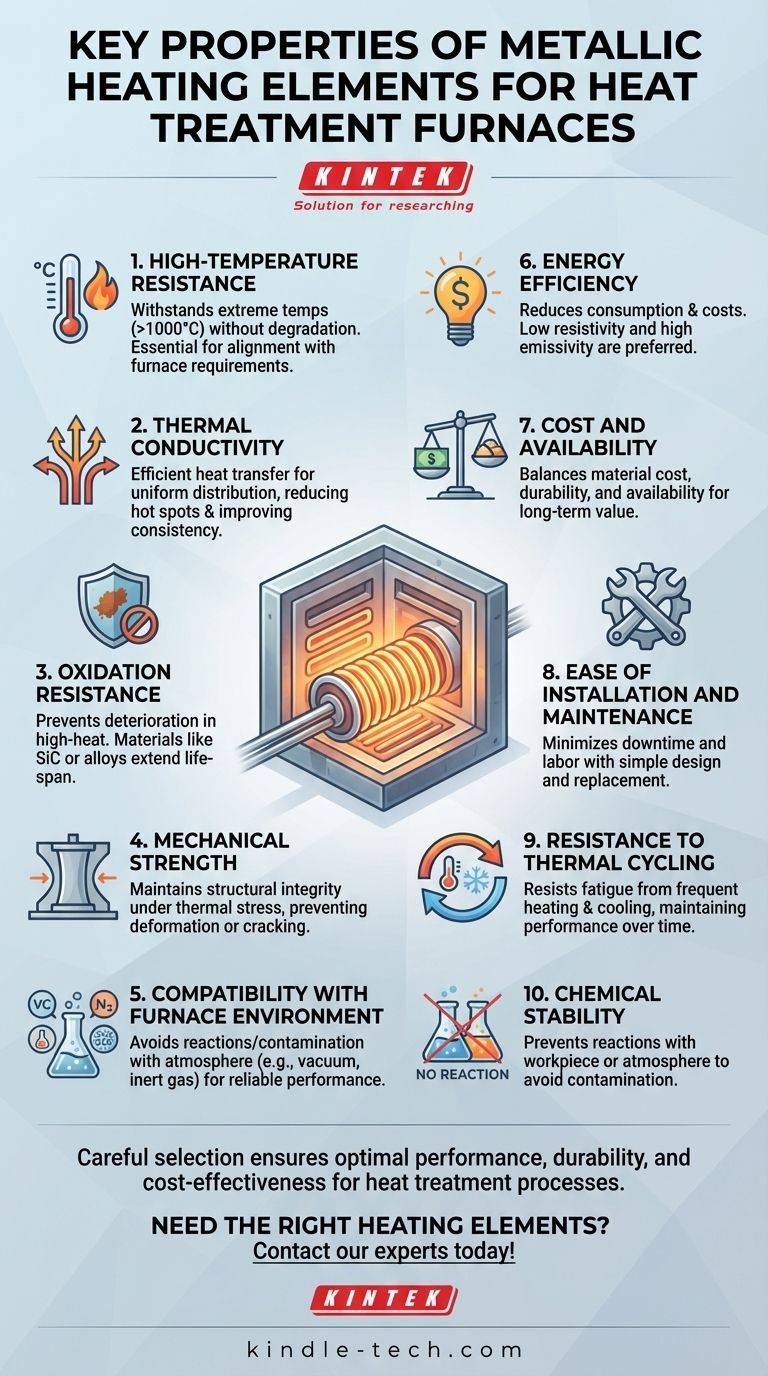
Metallic heating elements are critical components in heat treatment furnaces, as they directly influence the furnace's performance, efficiency, and longevity. The most important properties of these heating elements include high-temperature resistance, thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, mechanical strength, and compatibility with the furnace environment. These properties ensure that the heating elements can withstand extreme temperatures, provide consistent heat distribution, resist degradation, and maintain structural integrity over time. Additionally, factors such as material cost, ease of installation, and energy efficiency are also considered when selecting heating elements for specific applications.
Key Points Explained:
-
High-Temperature Resistance:
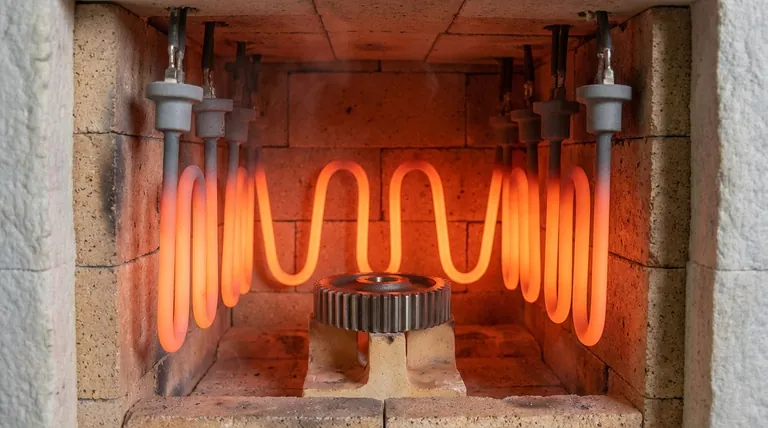
- Heating elements must withstand the extreme temperatures required for heat treatment processes, often exceeding 1000°C.
- Materials like silicon molybdenum rods are commonly used due to their ability to operate at high temperatures without significant degradation.
- The maximum temperature capability of the heating element must align with the furnace's operating requirements.
-
Thermal Conductivity:
- Efficient heat transfer is essential for uniform temperature distribution within the furnace.
- High thermal conductivity ensures that the heating elements can quickly and evenly distribute heat, reducing hot spots and improving process consistency.
-
Oxidation Resistance:
- Oxidation can lead to the deterioration of heating elements, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Materials with strong oxidation resistance, such as silicon carbide or certain alloys, are preferred to extend the lifespan of the heating elements.
-
Mechanical Strength:
- Heating elements must maintain their structural integrity under thermal stress and mechanical loads.
- High mechanical strength prevents deformation, cracking, or failure during operation, ensuring reliable performance.
-
Compatibility with Furnace Environment:
- The heating elements must be compatible with the furnace's atmosphere (e.g., vacuum, inert gas, or air) to avoid chemical reactions or contamination.
- For example, in vacuum furnaces, materials that do not outgas or react with the vacuum environment are essential.
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Efficient heating elements reduce energy consumption and operational costs.
- Materials with low electrical resistivity and high emissivity are preferred for better energy utilization.
-
Cost and Availability:
- The cost of the heating element material and its availability are practical considerations.
- While high-performance materials may be more expensive, their durability and efficiency can offset the initial investment over time.
-
Ease of Installation and Maintenance:
- Heating elements should be easy to install, replace, and maintain to minimize downtime and labor costs.
- Proper design and installation are critical to avoid issues such as uneven heating or premature failure.
-
Resistance to Thermal Cycling:
- Heat treatment furnaces often undergo frequent heating and cooling cycles.
- Heating elements must resist thermal fatigue and maintain performance over repeated cycles.
-
Chemical Stability:
- The heating elements should not react with the workpiece or furnace atmosphere, which could lead to contamination or reduced quality of the heat-treated products.
By carefully considering these properties, equipment purchasers can select the most suitable heating elements for their heat treatment furnaces, ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Resistance | Withstands extreme temperatures (>1000°C) without degradation. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heat distribution and reduces hot spots. |
| Oxidation Resistance | Prevents deterioration in high-temperature environments. |
| Mechanical Strength | Maintains structural integrity under thermal stress and mechanical loads. |
| Compatibility | Matches furnace atmosphere (vacuum, inert gas, or air) to avoid contamination. |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces energy consumption with low electrical resistivity and high emissivity. |
| Cost and Availability | Balances material cost, durability, and availability. |
| Ease of Installation | Minimizes downtime and labor costs with easy installation and maintenance. |
| Thermal Cycling Resistance | Resists fatigue from frequent heating and cooling cycles. |
| Chemical Stability | Prevents reactions with workpiece or furnace atmosphere. |
Need the right heating elements for your furnace? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research



















