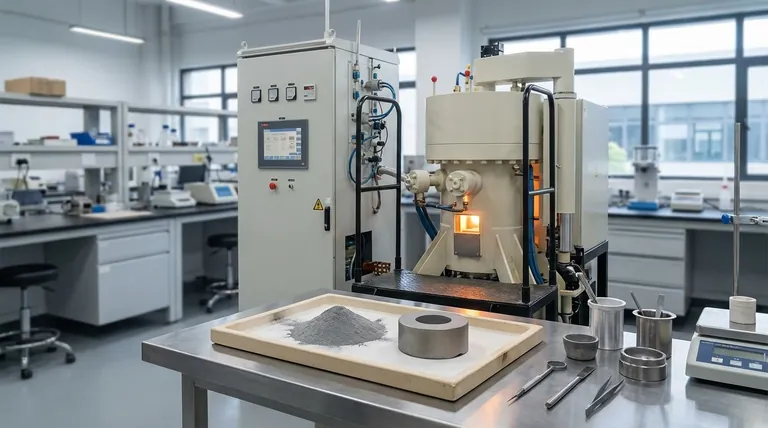
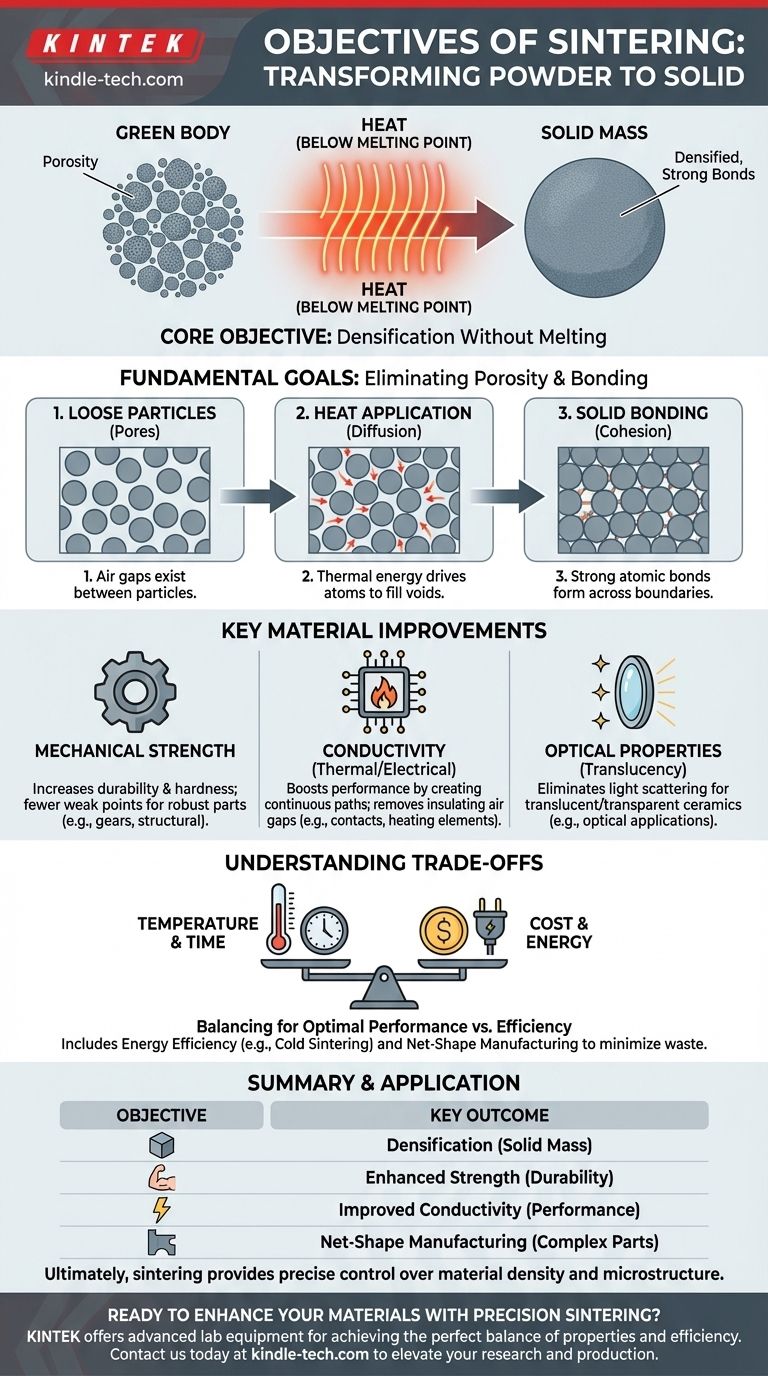
At its core, the primary objective of sintering is to transform a collection of loose particles or a powder compact—known as a 'green body'—into a solid, unified mass. This is achieved by applying heat below the material's melting point, which encourages atoms to bond across particle boundaries, resulting in a denser, stronger final product with significantly enhanced material properties.
The fundamental goal of sintering is not to melt a material, but to use thermal energy to eliminate the empty spaces (pores) between its initial particles. This reduction in porosity is the direct cause of nearly all the desired improvements in strength, conductivity, and other physical characteristics.

The Fundamental Goal: Densification Without Melting
Sintering is a process of consolidation. Its objectives are achieved by fundamentally changing the microstructure of a material, turning a loose aggregate into a cohesive whole.
Eliminating Porosity
The starting material, often a pressed powder, is full of tiny air gaps between particles. The primary mechanical objective of sintering is to drastically reduce or eliminate this porosity. By applying heat, atoms diffuse and migrate to fill these voids, pulling the particles closer together.
Creating Strong Atomic Bonds
As pores are eliminated, the surfaces of adjacent particles are brought into direct contact. The thermal energy facilitates the formation of strong, continuous atomic bonds across these boundaries, effectively fusing the particles into a single, solid piece with high material integrity.
Operating Below the Melting Point
A critical objective of the process is to achieve this consolidation without melting the bulk material. This makes sintering highly energy-efficient and cost-effective compared to casting. It also allows for the processing of materials with extremely high melting points, such as ceramics and refractory metals.
Key Objectives for Material Improvement
By achieving the fundamental goal of densification, sintering improves a wide range of a material's characteristics for specific engineering applications.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Durability
The most common objective is to increase strength, hardness, and durability. A dense, non-porous material has fewer internal points of weakness where cracks can initiate, making the final component much more robust and suitable for applications like gears, bearings, and structural parts.
Increasing Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Pores and air gaps are excellent insulators. By removing them, sintering creates a continuous path through the material, significantly improving its ability to conduct heat and electricity. This is a key objective for producing electrical contacts, heating elements, and components for thermal management.
Improving Optical Properties (Translucency)
In materials like advanced ceramics, internal pores scatter light, making the material opaque. A key objective for optical applications is to sinter the material to full density, eliminating light scattering and creating a translucent or even transparent product.
Understanding the Process Trade-offs
While sintering is powerful, its objectives are balanced against practical and economic considerations. The goal is always to achieve the desired final properties in the most efficient way possible.
The Balance of Temperature and Time
Achieving higher density and better properties typically requires higher temperatures or longer sintering times. However, this increases energy consumption and cost. The objective is to find the optimal combination of temperature and time that meets the performance requirements without excessive cost.
The Goal of Energy Efficiency
Modern variations like Cold Sintering have the specific objective of reducing the process temperature. This dramatically cuts energy consumption, lowers production costs, and enables the co-sintering of materials that would otherwise be incompatible, such as ceramics and polymers.
Creating Net-Shape Components
For many industries, a major objective is not just material improvement but also manufacturing efficiency. Sintering excels at producing complex parts to their final or "net" shape, minimizing or eliminating the need for costly and wasteful secondary machining operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific objective of sintering is always tied to the intended application of the final component.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, durable mechanical parts: Sintering is used to achieve maximum density, providing the strength required for gears, couplings, and structural components.
- If your primary focus is optimizing functional properties: Sintering is tailored to enhance conductivity for electrical contacts or translucency for optical ceramics by carefully controlling the elimination of pores.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing efficiency: The objective is to use sintering to create complex, net-shape parts directly from powder, minimizing material waste and post-processing costs.
Ultimately, sintering provides precise control over a material's final density and microstructure, making it a cornerstone of modern materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Objective | Key Outcome |
|---|---|
| Densification | Eliminates porosity, creating a solid mass |
| Enhanced Strength | Increases durability and hardness |
| Improved Conductivity | Boosts thermal and electrical performance |
| Net-Shape Manufacturing | Produces complex parts with minimal waste |
Ready to enhance your materials with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to help you achieve the perfect balance of material properties, strength, and manufacturing efficiency for your laboratory needs. Whether you're developing durable mechanical parts or optimizing functional materials, our expertise ensures you get the results you need.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can support your sintering objectives and elevate your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature laboratory furnace control hydrated RuO2 conversion? Achieve Precision Phase Transformation
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control
- What design considerations are necessary for high-temperature muffle furnaces with MoSi2 heating elements?
- How is a high-temperature box resistance furnace utilized in the rejuvenation of P91 steel? Restore Material Integrity
- What is the purpose of pre-treating precursor mixtures at 700°C? Ensure Pure Spinel Phase Synthesis
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using wet ashing technique? Speed vs. Safety in Sample Prep
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- How does a program-controlled furnace ensure T91 alloy steel recovery? Master Precision Post-Weld Heat Treatment



















