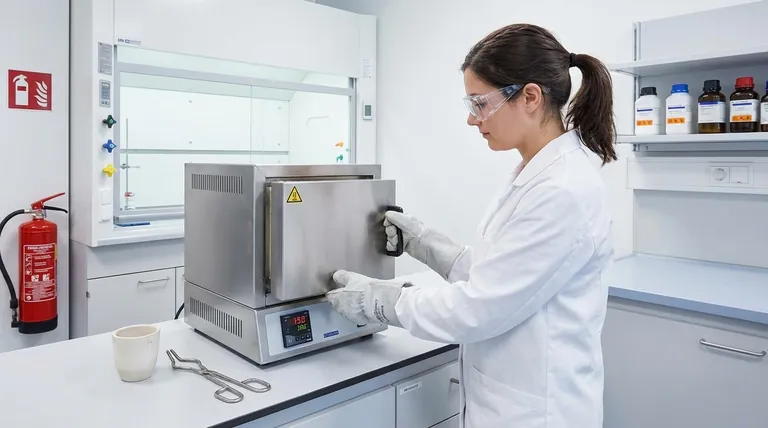
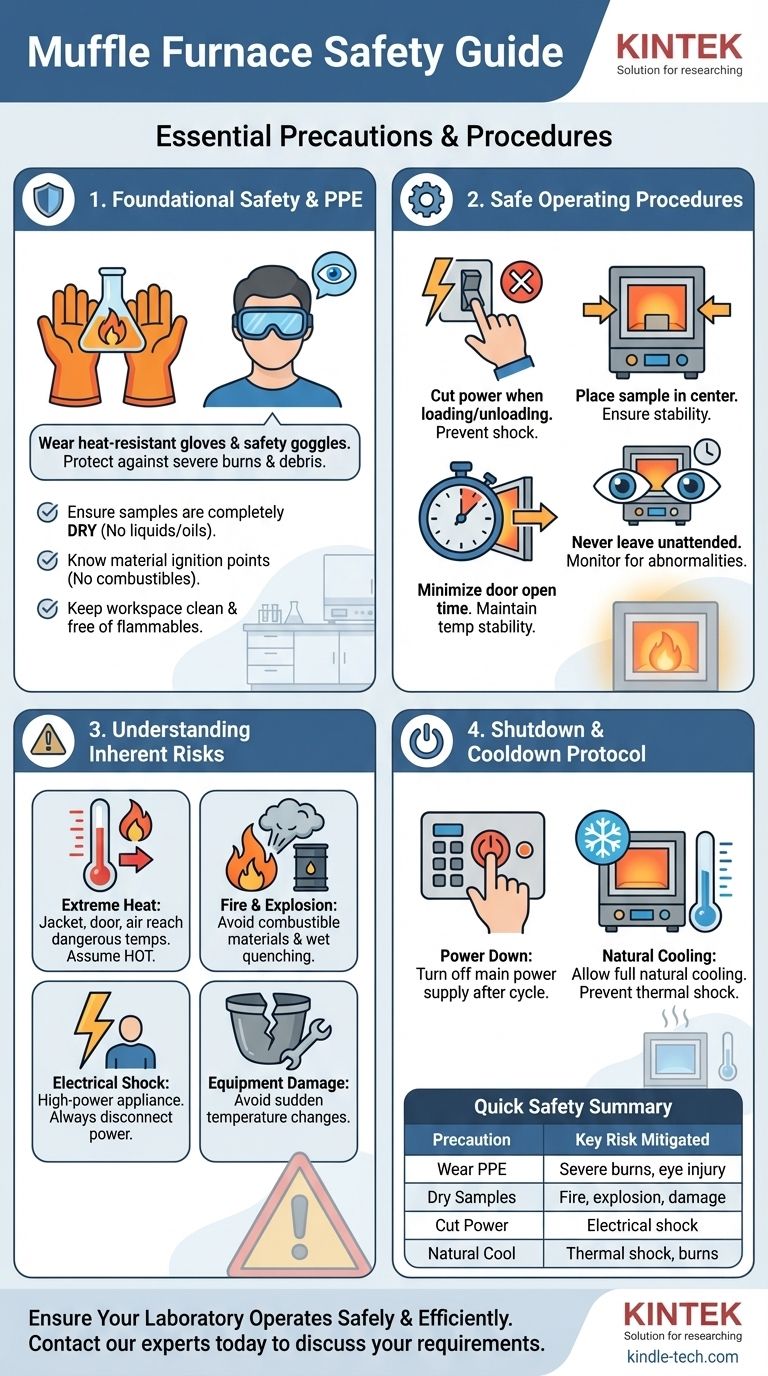
The essential safety precautions for a muffle furnace involve a systematic approach that covers personal protection, correct sample preparation, and vigilant operational procedures. You must always wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) like heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles, ensure all materials placed inside are dry and can withstand the extreme temperatures, and never leave the furnace unattended while it is operating.
A muffle furnace combines extreme heat with high-voltage electricity, creating significant potential hazards. True safety is not about a single checklist, but about adopting a disciplined process for preparation, operation, and shutdown to mitigate risks of severe burns, electrical shock, and fire.

Foundational Safety: Preparation and PPE
Before you even turn the furnace on, you must prepare yourself, your materials, and your workspace. This foundational step is the most critical for preventing accidents.
Selecting the Right Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Your first line of defense is proper PPE. The intense heat radiated by the furnace can cause severe burns even without direct contact.
Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from heat and potential debris.
Use heat-resistant gloves specifically rated for the temperatures you will be working with. The type of glove is critical and depends on the operating temperature.
Preparing Your Samples Correctly
What you put inside the furnace is as important as how you operate it. Improperly prepared samples are a primary cause of equipment damage and hazardous situations.
Ensure all samples are completely dry. Introducing liquids, water, or oil can cause rapid steam generation, damage the furnace, or create a fire risk.
You must know the melting or ignition points of all materials being heated. Never place combustible, volatile, or explosive materials inside the furnace.
For glassware like Pyrex, cover any open ends with aluminum foil to prevent pressure buildup issues. It is also good practice to wrap smaller items in foil.
Inspecting the Furnace and Work Area
The furnace and its immediate environment must be clear and ready for high-temperature operation.
Keep the area surrounding the furnace free of all flammable and combustible materials. The exterior jacket of the furnace becomes extremely hot during use.
Ensure the workspace is clean and tidy. This prevents impurities like dust and fibers from entering the furnace chamber.
If the furnace has been unused for a long period, verify it is internally dry before heating. If necessary, perform a low-temperature drying cycle.
Safe Operating Procedures
During operation, your full attention is required. Complacency is the biggest risk once the heating cycle begins.
Loading and Unloading Samples
To prevent electrical shock, always cut the power supply when loading or taking samples out of the furnace.
Place your sample in the center of the furnace chamber, ensuring it is stable and positioned neatly.
Keep the time the furnace door is open to an absolute minimum to maintain temperature stability and reduce your exposure to extreme heat.
Managing Temperature and Heating Cycles
Never exceed the maximum rated temperature of the furnace, as this can cause permanent damage to the heating elements.
Adjust the temperature carefully and according to procedure.
Be aware that materials containing fats or certain polymers can release volatile and corrosive gases during heating, which can damage the furnace elements over time.
Active Monitoring is Non-Negotiable
A muffle furnace should never be left unattended during operation, especially overnight. Control failures can lead to overheating and create a fire hazard.
If you observe any abnormalities, such as unusual smoke, strange noises, or a rapidly rising temperature, shut off the power immediately and contact maintenance personnel.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
To operate a muffle furnace safely, you must respect its inherent dangers. Understanding these risks is key to avoiding them.
The Hazard of Extreme Heat
The most obvious risk is severe burns. The furnace jacket, door, and surrounding air all reach dangerous temperatures. Always assume any part of the furnace is hot.
The Risk of Fire and Explosion
Using oil as a quenchant presents a significant fire risk. Quench tanks should be covered when not in use. Contamination of quenching oil with even a small amount of water can cause a violent eruption.
The Danger of Electrical Shock
A muffle furnace is a high-power electrical appliance. Never attempt to perform maintenance or load samples without first disconnecting the power supply.
The Potential for Equipment Damage
Sudden temperature changes can damage the furnace. Do not pull out the thermocouple suddenly at high temperatures, as this can cause the protective jacket to burst. Similarly, avoid placing cold items into a hot furnace.
The Shutdown and Cooldown Protocol
Proper shutdown procedures are essential for your safety and the longevity of the equipment.
Powering Down Correctly
After your heating cycle is complete, always ensure the main power supply is turned off.
The Importance of Natural Cooling
Allow the furnace to cool down naturally before opening the door to retrieve your samples. Opening the door while the furnace is extremely hot can cause thermal shock to both your sample and the furnace chamber, potentially cracking them.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach to safety should be tailored to mitigating the most relevant risks for your work.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always prioritize wearing the correct PPE, disconnecting power before reaching into the chamber, and allowing for a full cooldown period.
- If your primary focus is preventing equipment damage: Meticulously prepare your samples, ensure they are dry and non-reactive, and never exceed the furnace's maximum temperature rating.
- If your primary focus is avoiding lab-wide accidents: Never leave the furnace unattended, maintain a clean and clear workspace free of flammables, and have a fire extinguisher readily accessible.
A methodical and informed approach transforms the muffle furnace from a potential hazard into a powerful and reliable tool.
Summary Table:
| Safety Category | Key Precaution | Key Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Protection (PPE) | Wear heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles. | Severe burns, eye injury |
| Sample Preparation | Ensure samples are completely dry and non-combustible. | Fire, explosion, equipment damage |
| Operation | Never leave the furnace unattended; cut power when loading/unloading. | Fire, electrical shock |
| Shutdown | Allow furnace to cool naturally; turn off main power. | Thermal shock, burns |
Ensure your laboratory operates safely and efficiently.
Proper safety protocols are fundamental to reliable lab work. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality, safe, and durable laboratory equipment, including muffle furnaces, alongside expert guidance to meet your specific needs.
Let us help you enhance your lab's safety and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- Will brazing stick to cast iron? A Low-Heat Joining Solution for Crack-Free Repairs
- What is the temperature for a furnace? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal
- How do you choose calcination temperature? A Guide to Optimizing Material Properties
- What is a natural sintering? Uncover the Geological Process That Forms Ore Deposits



















