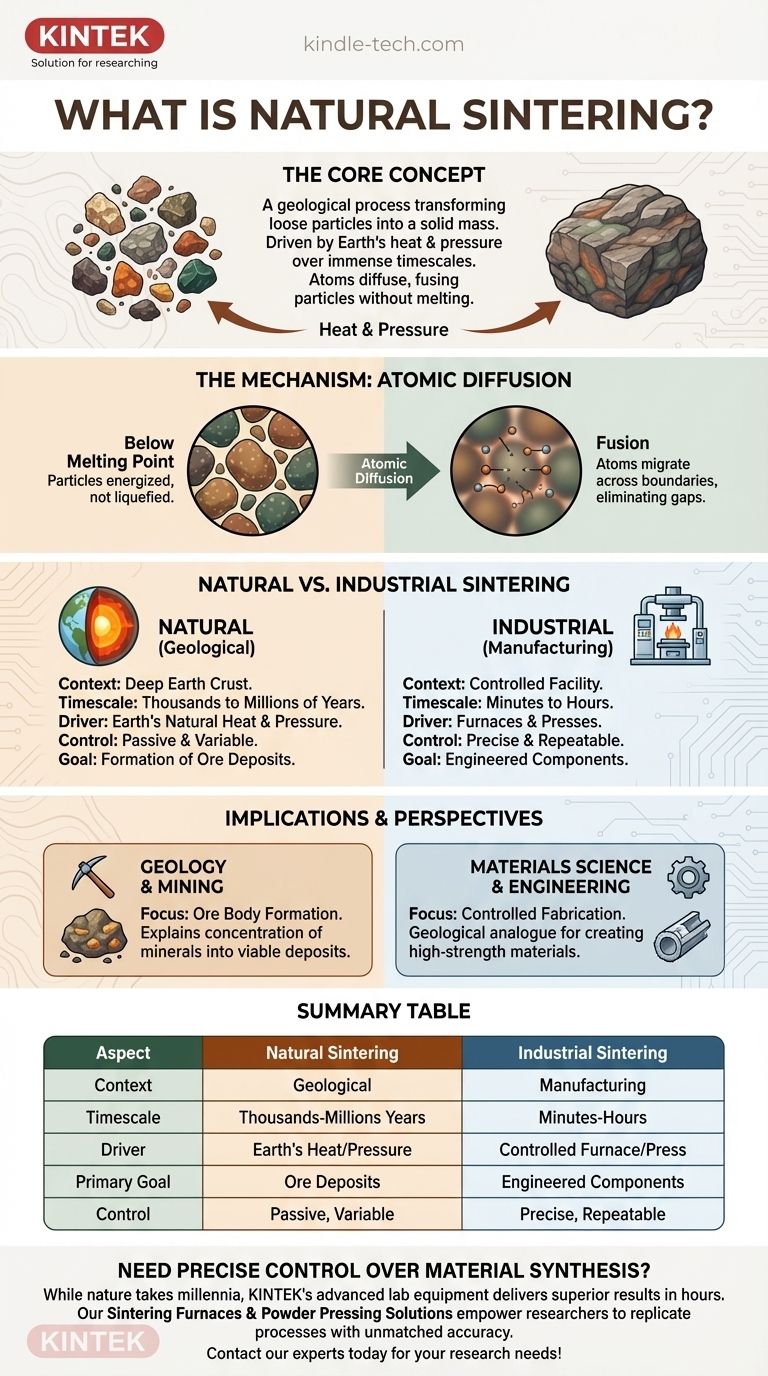
At its core, natural sintering is a geological process that transforms loose mineral particles into a solid, high-density mass. Driven by the Earth's natural heat and pressure over immense timescales, atoms diffuse across particle boundaries, fusing them together to form ore deposits without ever melting the material.
The critical distinction is not the physical mechanism, but the context. While both natural and industrial sintering rely on atomic diffusion to fuse particles, one is a slow, passive geological event, and the other is a fast, controlled manufacturing technique.

The Fundamental Mechanism: How Sintering Works
A Process Without Melting
Sintering compacts and forms a solid mass of material using heat and pressure. Crucially, the temperature remains below the material's melting point.
Instead of liquefying, the particles are energized just enough for their atoms to become mobile. This technique is essential for processing materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten.
The Power of Atomic Diffusion
The scientific principle behind sintering is atomic diffusion. When heated, atoms gain enough energy to migrate from their own particle and cross the boundary into an adjacent one.
This migration effectively blurs the lines between individual particles. They fuse together at a microscopic level, eliminating the gaps between them and creating a single, dense, and solid piece.
Natural vs. Industrial Sintering
The Geological Context (Natural)
Natural sintering occurs deep within the Earth's crust over thousands or millions of years. The sustained, moderate heat and immense pressure from overlying rock and geological activity provide the energy for the process.
This is a fundamental mechanism in the formation of many mineralogical deposits. It is how loose sediments or mineral grains are transformed into the solid, high-density ore that is extracted through mining.
The Manufacturing Context (Industrial)
Industrial sintering is a deliberate, highly controlled, and rapid process. Powdered materials are placed in a mold and subjected to high heat and/or pressure in a furnace or press.
This allows engineers to create strong, precisely shaped components from materials that are difficult or impossible to melt and cast. It is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and ceramics manufacturing.
Understanding the Implications
Why Natural Sintering Matters
Understanding natural sintering is crucial for geologists and mining engineers. It explains how valuable minerals become concentrated and consolidated into economically viable ore bodies.
The process is responsible for the physical characteristics of many types of rock and mineral deposits, influencing their density, porosity, and strength.
The Trade-off: Control vs. Scale
The primary trade-off is control. The natural process is passive and uncontrolled, resulting in complex and variable geological formations.
The industrial process, by contrast, offers complete control over temperature, pressure, and time. This precision allows for the engineering of materials with specific, repeatable properties for advanced applications.
How to Apply This Knowledge
The lens through which you view sintering depends entirely on your field.
- If your primary focus is Geology or Mining: Regard natural sintering as the fundamental process that transforms loose mineral grains into dense, valuable ore bodies over geological time.
- If your primary focus is Materials Science or Engineering: See natural sintering as the geological analogue to the controlled industrial process used to fabricate high-strength components from powdered materials.
Ultimately, understanding this natural phenomenon provides a powerful foundation for appreciating the controlled engineering of modern materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Natural Sintering | Industrial Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Context | Geological process | Manufacturing technique |
| Timescale | Thousands to millions of years | Minutes to hours |
| Driver | Earth's heat and pressure | Controlled furnace/press |
| Primary Goal | Formation of ore deposits | Creation of engineered components |
| Control | Passive and variable | Precise and repeatable |
Need precise control over your material synthesis? While nature takes millennia, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment delivers superior results in hours. Our sintering furnaces and powder pressing solutions empower geologists and materials scientists to replicate and study these processes with unmatched accuracy. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your research or quality control needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What 5 safety precautions should be taken when heating anything in the lab? Essential Rules for Lab Safety
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- How to use a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Operation
- What PPE is required for a muffle furnace? Essential Gear for High-Temperature Safety
- How does heat affect strength materials? The Science of Thermal Degradation Explained



















