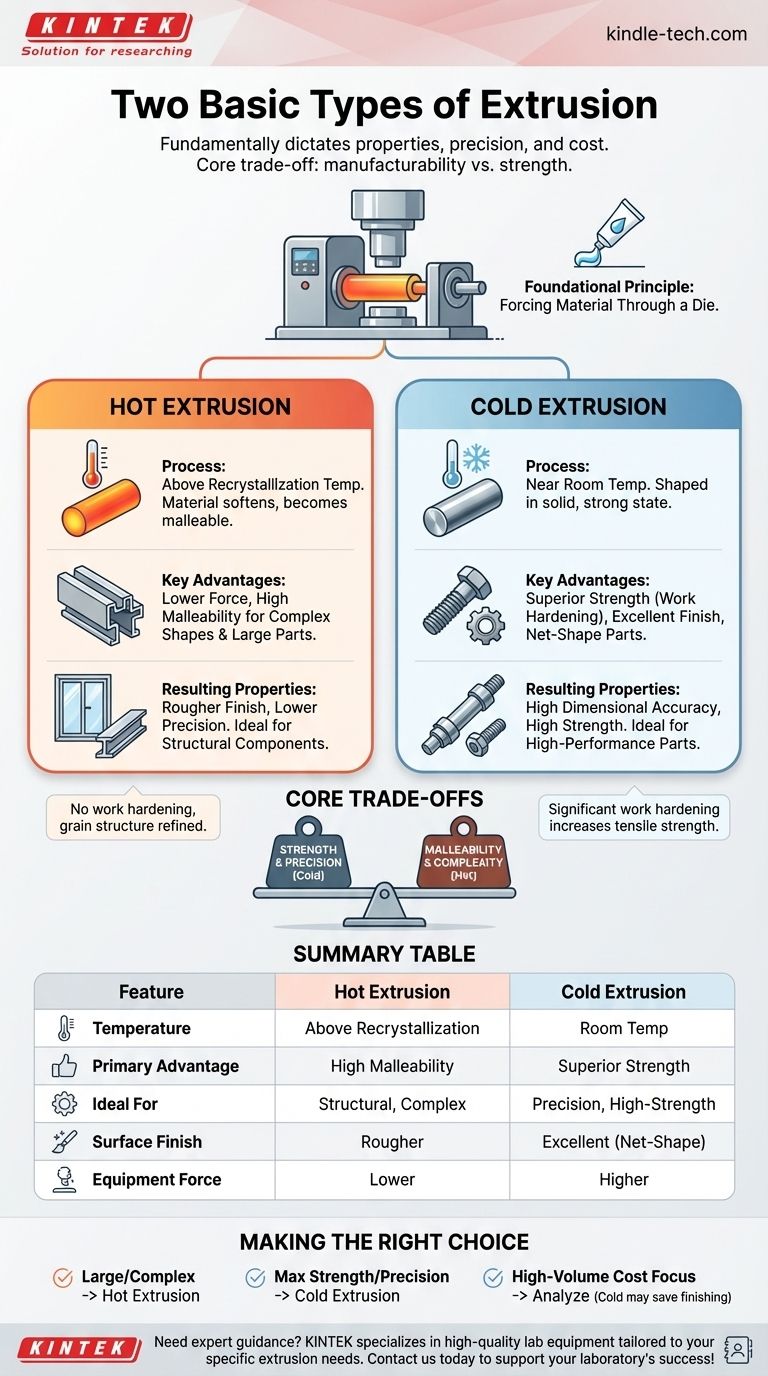
In manufacturing, the two fundamental types of extrusion are hot extrusion and cold extrusion. The primary difference is the temperature of the material (the billet) relative to its recrystallization point, a choice that fundamentally dictates the final properties, precision, and cost of the extruded part.
The decision between hot and cold extrusion is a core engineering trade-off. Hot extrusion prioritizes manufacturability for complex shapes and large parts, while cold extrusion prioritizes material strength and dimensional accuracy for high-performance components.
What is Extrusion? A Foundational Overview
The Basic Principle: Forcing Material Through a Die
At its core, extrusion is a compression process that forces a material through a die with a specific cross-sectional profile. Imagine squeezing toothpaste from a tube—the toothpaste is the material, and the circular opening of the tube is the die.
This process creates an elongated piece of material with the same profile as the die opening. It is an extremely efficient way to produce parts with a constant cross-section.
Hot Extrusion: Shaping Materials with Heat
The Process: Above Recrystallization Temperature
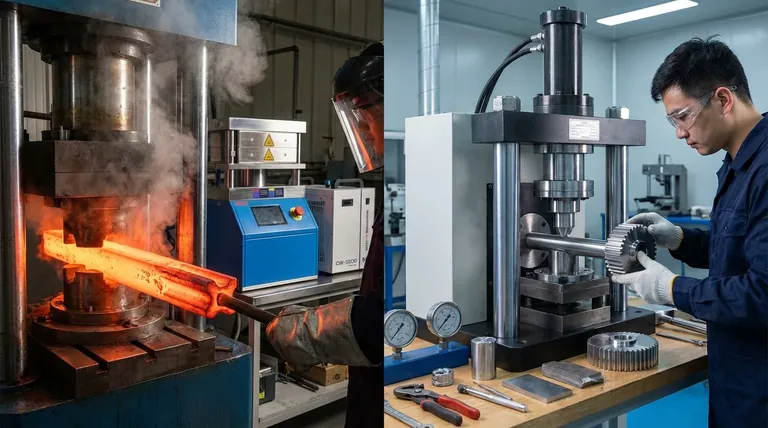
Hot extrusion is performed on a billet heated above its recrystallization temperature. At this temperature, the material softens and becomes highly malleable without hardening as it is deformed.
Key Advantages: Lower Force and High Malleability
Because the material is soft, it requires significantly less force to push it through the die. This allows for the production of very large parts and highly complex cross-sections that would be impossible to achieve with cold extrusion.
Resulting Properties: Ideal for Structural Components
The high temperatures prevent the material from gaining strength during the process (work hardening). While this can refine the grain structure, the final part may have a rougher surface finish and lower dimensional accuracy due to thermal expansion and contraction.
This makes it perfect for applications like window frames, railings, and large structural components for aerospace and automotive bodies, where overall shape is more critical than microscopic precision.
Cold Extrusion: Precision Forged at Room Temperature
The Process: Near Room Temperature
Cold extrusion is performed with the billet at or near room temperature, well below its recrystallization point. The material is shaped in its solid, strong state.
Key Advantages: Superior Strength and Finish
Forcing the material through the die at this temperature causes work hardening (or strain hardening). This process fundamentally changes the material's grain structure, significantly increasing its tensile strength and hardness.
Resulting Properties: High-Strength, Net-Shape Parts
Cold extrusion produces parts with an excellent surface finish and exceptional dimensional accuracy. These components are often considered "net-shape," meaning they require little to no secondary machining.
This is why cold extrusion is the method of choice for high-performance parts like fasteners (bolts, screws), small gears, and critical automotive shafts, where strength and precision are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Strength vs. Malleability
Cold extrusion produces a stronger, harder part due to work hardening. Hot extrusion allows for much greater ductility during manufacturing, enabling more complex shapes to be formed.
Dimensional Accuracy vs. Complexity
Cold extrusion delivers superior dimensional tolerances and a smooth surface finish. Hot extrusion can produce more intricate and larger cross-sectional profiles but with less precision.
Equipment and Tooling Costs
The immense forces required for cold extrusion demand more powerful presses and extremely durable (and expensive) tooling. Hot extrusion machinery and dies can be less robust, lowering initial capital costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct extrusion process requires aligning the method's strengths with your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is large structural components or complex profiles: Hot extrusion is the superior choice due to lower force requirements and the ability to shape highly malleable material.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength, precision, and surface finish: Cold extrusion is the only option, as the work-hardening effect yields stronger, net-shape parts ready for immediate use.
- If your primary focus is overall cost on a high-volume part: The analysis is more complex; cold extrusion can eliminate secondary finishing costs, potentially making it cheaper overall despite higher initial tooling and energy expenses.
Understanding this fundamental choice between forming with heat or with force is the first step toward mastering the design of any extruded component.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Extrusion | Cold Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Above material's recrystallization point | At or near room temperature |
| Primary Advantage | High malleability for complex shapes | Superior strength and dimensional accuracy |
| Ideal For | Large structural components, complex profiles | High-strength, precision parts like fasteners and gears |
| Surface Finish | Rougher | Excellent, often net-shape |
| Equipment Force | Lower force required | Higher force required |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right extrusion process for your lab or production needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you're working on complex structural components or precision high-strength parts, our team can help you choose the right tools for optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for nanocomposites? Ensure Precise Material Characterization
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic hot press in the assembly of solid-state photoelectrochemical cells?
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- How does a laboratory hydraulic hot press ensure the quality of PHBV/natural fiber composites? Expert Guide



















