In essence, a hydraulic press is a force multiplier. It is a machine that uses a liquid-based hydraulic system to generate immense compressive force. This capability allows it to perform a vast range of tasks, from shaping massive steel components in aerospace manufacturing and forming automotive body panels to compacting tiny, delicate samples for scientific analysis in a laboratory.
The true value of a hydraulic press is not just the raw force it generates, but its ability to apply that force in a highly controlled and scalable manner. This principle is what makes it a fundamental tool in both heavy industry and precision science.
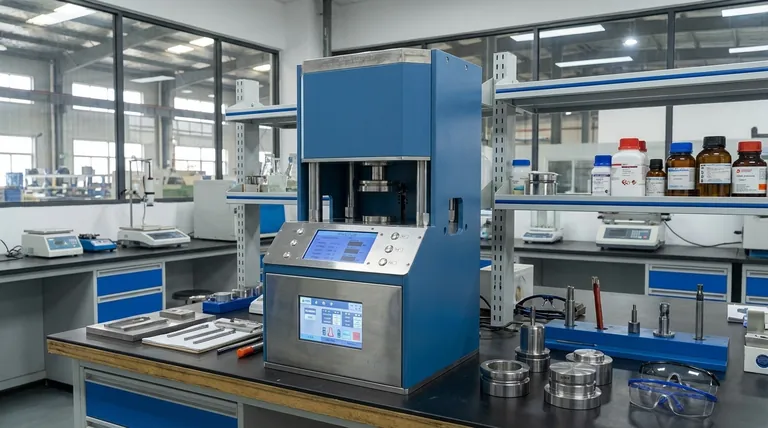

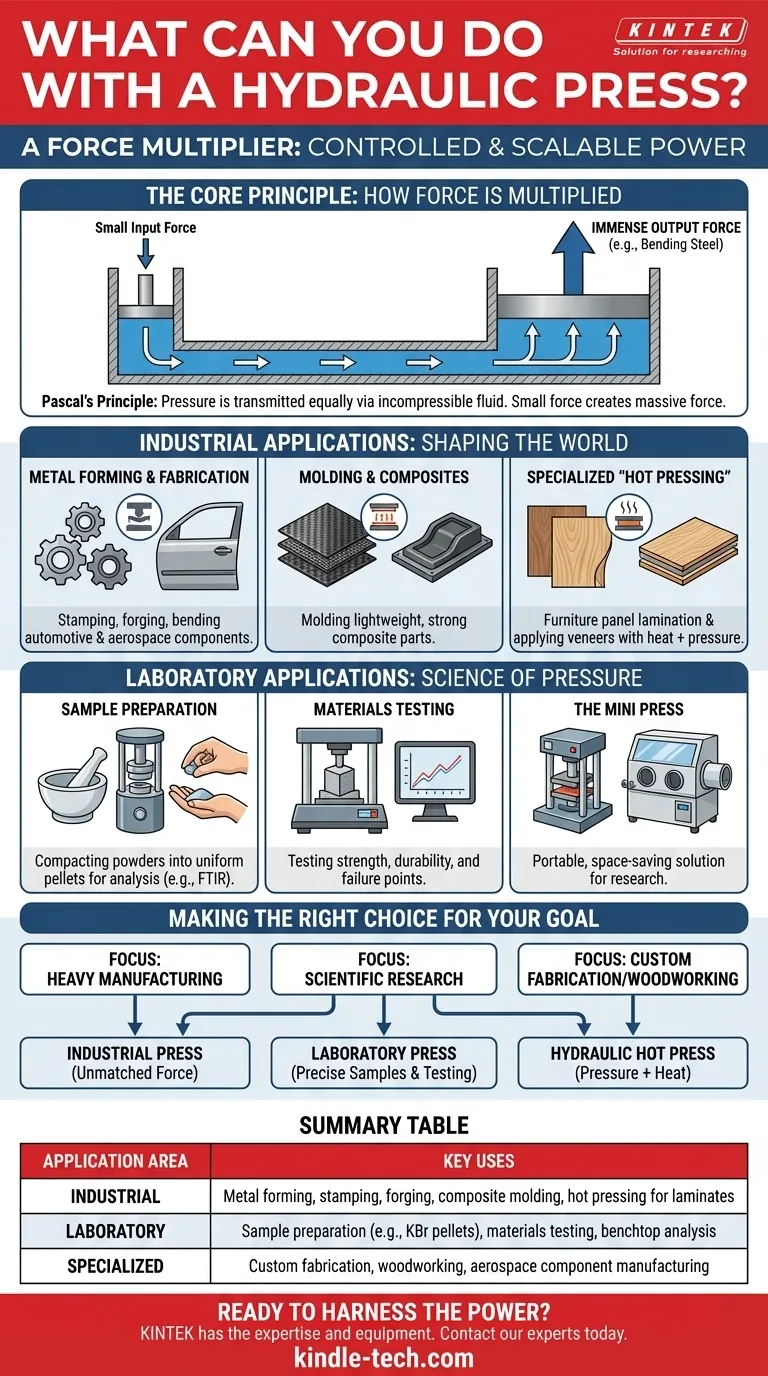
The Core Principle: How Force is Multiplied
A hydraulic press operates on a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics. Understanding this concept is key to appreciating its versatility.
The Power of Incompressible Fluid
A press uses a hydraulic cylinder filled with an incompressible fluid, typically oil. When a small force is applied to the fluid via a small piston, that pressure is transmitted equally throughout the entire fluid.
This pressure then acts on a much larger piston, which multiplies the initial force significantly. A small, manageable input force can be converted into an output force capable of bending steel or crushing rock.
Why This Matters: Control and Scale
Unlike mechanical presses that rely on flywheels and clutches, a hydraulic system's force is directly related to the fluid pressure.
This pressure can be precisely controlled, allowing for exact and repeatable force application. It also provides inherent overload protection; the system simply cannot generate more force than its maximum pressure setting allows, protecting the machine and the tooling.
Industrial Applications: Shaping the Modern World
In industrial settings, hydraulic presses are workhorses used for forming, shaping, and assembling a wide variety of products.
Metal Forming and Fabrication
This is the most common application. Presses are used for stamping, bending, forging, and deep drawing metal sheets into complex shapes.
These processes are critical for manufacturing automotive parts, aerospace components, appliance bodies, and military hardware.
Molding and Composites
Hydraulic presses are essential for molding materials like carbon fiber, fiberglass, and other composites.
By applying immense pressure (and sometimes heat), the press consolidates layers of material into a strong, lightweight, and unified part. This is common in the production of high-performance automotive and aerospace components.
Specialized "Hot Pressing"
A hydraulic hot press adds heated platens to the process. The combination of intense pressure and high temperature is used in woodworking and furniture manufacturing.
This is ideal for gluing furniture panels, applying wood veneers, and laminating decorative surfaces like PVC onto boards, ensuring a perfect, durable bond.
Laboratory Applications: The Science of Pressure
On a much smaller scale, hydraulic presses are indispensable tools in scientific and quality control laboratories.
Sample Preparation for Analysis
Many analytical techniques, such as FTIR and XRF spectroscopy, require samples to be in a very specific form, like a thin, uniform pellet.
A laboratory press is used to compact powdered material (such as potassium bromide, KBr) into a solid pellet. This ensures the analytical instrument gets a consistent and readable result.
Materials Testing
Engineers and scientists use laboratory presses to test the strength, durability, and behavior of materials under high pressure.
By precisely controlling the applied force, researchers can determine a material's compressive strength and failure points, which is crucial for developing new alloys, polymers, and ceramics.
The Role of the Mini Press
For labs where space and mobility are concerns, a mini press offers a solution. These small, portable units can weigh less than 10 pounds but still generate tons of force.
They are favored in pharmaceutical and research settings for their low cost and ability to be used directly on a benchtop or inside a glove box.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select or utilize a hydraulic press effectively, you must align its capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is heavy manufacturing: A large-tonnage industrial press offers the unmatched force needed for forging, stamping, and molding large components.
- If your primary focus is scientific research: A laboratory press is essential for preparing consistent analytical samples and accurately testing material properties under pressure.
- If your primary focus is custom fabrication or woodworking: A hydraulic hot press provides the necessary combination of pressure and heat for laminating, veneering, and forming materials.
Ultimately, understanding that a hydraulic press is a tool for applying controlled force is the key to unlocking its potential for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Industrial | Metal forming, stamping, forging, composite molding, hot pressing for laminates |
| Laboratory | Sample preparation (e.g., KBr pellets for FTIR), materials testing, benchtop analysis |
| Specialized | Custom fabrication, woodworking, aerospace component manufacturing |
Ready to harness the power of a hydraulic press for your specific needs? Whether you're in heavy industry requiring robust metal forming or in a laboratory needing precise sample preparation, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your goals. Our range of hydraulic presses is designed to deliver controlled, scalable force for applications from aerospace manufacturing to scientific research. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can enhance your productivity and precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- How does a vacuum furnace environment influence sintered Ruthenium powder? Achieve High Purity and Theoretical Density
- What is the role of a laboratory-grade heated hydraulic press in MEA fabrication? Optimize Fuel Cell Performance
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing



















