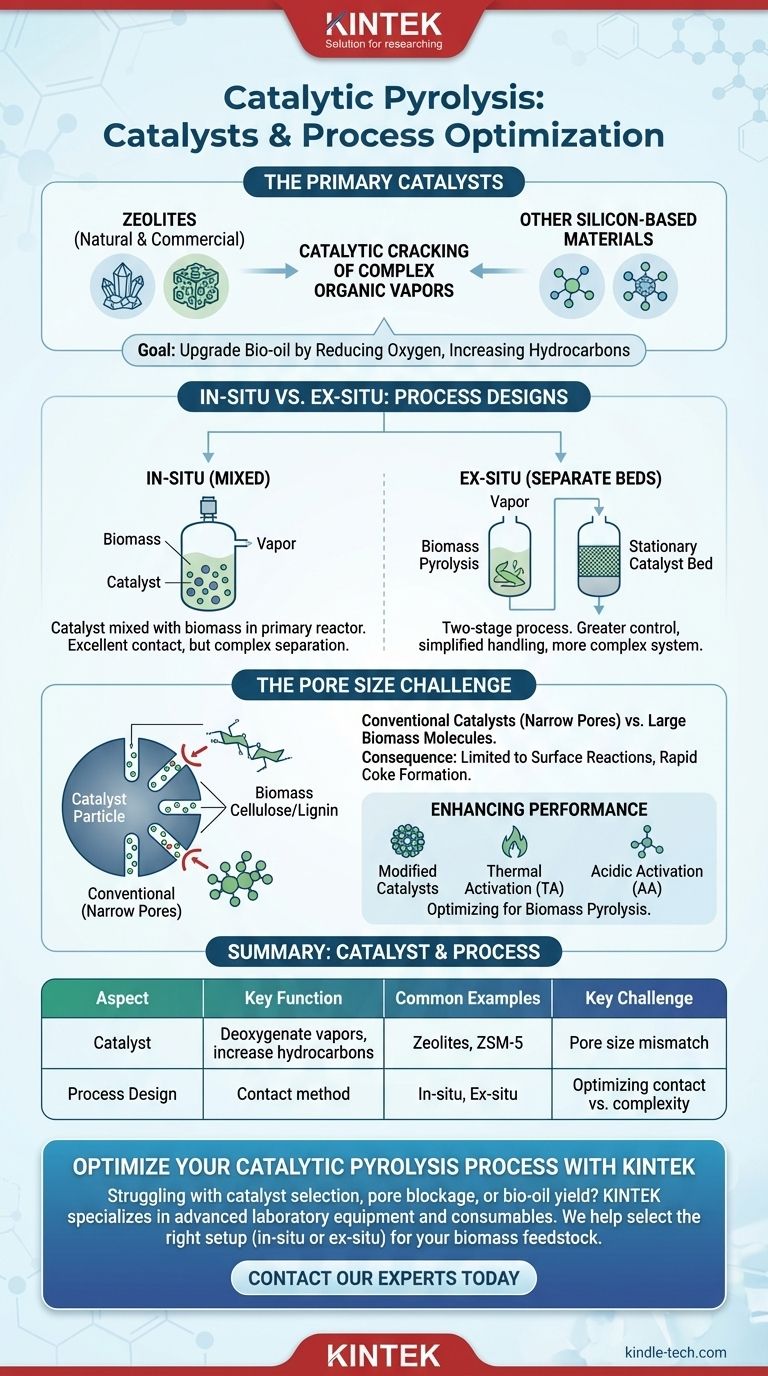
In catalytic pyrolysis, the most prevalent catalysts used are zeolites, both natural and commercial, along with other silicon-based materials. These substances are introduced into the pyrolysis process to catalytically "crack" the complex organic vapors produced from biomass, upgrading them into a more stable and valuable bio-oil by reducing oxygen content and increasing hydrocarbon yield.
While zeolites are the most common catalysts, their standard forms are often a poor fit for raw biomass. The core challenge is not just choosing a material, but overcoming the mismatch between the catalyst's narrow pores and the large, bulky molecules present in biomass polymers.

The Role of Key Catalysts
Catalysts are the critical element that transforms standard pyrolysis into a more refined upgrading process. Their primary function is to deoxygenate the pyrolysis vapors, which improves the quality and stability of the final liquid product, known as bio-oil.
The Primary Catalyst Family: Zeolites
Zeolites are crystalline, microporous aluminosilicates that are the workhorses of catalytic pyrolysis. They are favored for their high acidity and shape-selective properties.
Both natural zeolites (NZ) and commercially produced zeolites are used. However, their effectiveness can vary significantly based on their structure and the specific application.
Enhancing Catalyst Performance
Standard catalysts are often not optimized for biomass. Therefore, modification methods are frequently employed to improve their performance.
Techniques like thermal activation (TA) and acidic activation (AA) are used to alter the properties of natural zeolites, enhancing their catalytic activity for the pyrolysis of large biomass molecules.
In-situ vs. Ex-situ: Two Process Designs
The way a catalyst is introduced into the process dramatically impacts the outcome. There are two fundamental configurations for catalytic pyrolysis.
In-situ Catalysis (Mixed)
In the in-situ method, the catalyst is physically mixed with the biomass feedstock inside the primary pyrolysis reactor.
This approach ensures excellent contact between the biomass vapors and the catalyst, but it can make catalyst separation and regeneration more difficult.
Ex-situ Catalysis (Separate Beds)
In the ex-situ method, the process is separated into two stages. Biomass is first pyrolyzed in one reactor, and the resulting vapors are then passed over a stationary catalyst bed in a second reactor.
This dual-bed setup offers greater control over reaction conditions and simplifies catalyst handling, though it requires a more complex and expensive system.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Pore Size
The central challenge in catalytic pyrolysis of biomass is a fundamental structural mismatch between the fuel and the catalyst.
The Problem with Conventional Catalysts
Most commercial catalysts, including many zeolites, were originally developed for the petrochemical industry, which deals with relatively small hydrocarbon molecules.
These catalysts have narrow pores that are simply too small for the bulky natural polymers found in biomass, such as cellulose and lignin, to enter.
The Consequence: Surface-Level Reactions
When large biomass molecules cannot access the internal active sites of the catalyst, reactions are limited to the catalyst's external surface. This severely reduces efficiency and can lead to the rapid formation of coke, which deactivates the catalyst.
This physical limitation is a primary reason why direct catalytic pyrolysis of biomass remains a significant technical challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a catalytic strategy depends entirely on your project's specific objectives, whether they are focused on product quality, cost, or feedstock flexibility.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil quality: An ex-situ approach with a highly active, shape-selective zeolite offers the most control over the final product composition.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity and lower initial cost: An in-situ method using a robust, less-expensive catalyst like modified natural zeolite is a more direct and economical starting point.
- If your primary focus is processing raw biomass: You must prioritize catalysts with larger pores or consider an ex-situ process where initial thermal cracking can break down large molecules before they encounter the catalyst.
Ultimately, success in catalytic pyrolysis comes from matching the catalyst's properties and the process design to the unique characteristics of your biomass feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst / Aspect | Key Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Zeolites | Deoxygenate vapors, increase hydrocarbons | Natural Zeolites (NZ), Commercial ZSM-5 |
| Process Design | How catalyst contacts biomass vapors | In-situ (mixed), Ex-situ (separate bed) |
| Key Challenge | Overcoming pore size mismatch with biomass | Use of modified catalysts (TA, AA) |
Optimize Your Catalytic Pyrolysis Process with KINTEK
Struggling with catalyst selection, pore blockage, or low bio-oil yield for your biomass feedstock? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. We can help you select the right catalyst setup—whether in-situ or ex-situ—to efficiently upgrade your bio-oil and improve process efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific biomass and goals, and let us provide the tailored solutions you need to succeed.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What are the storage requirements for the PTFE electrode stand after cleaning? Preserve Purity and Equipment Longevity
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What is the difference between wet and dry sieve analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Particle Sizing
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car



















