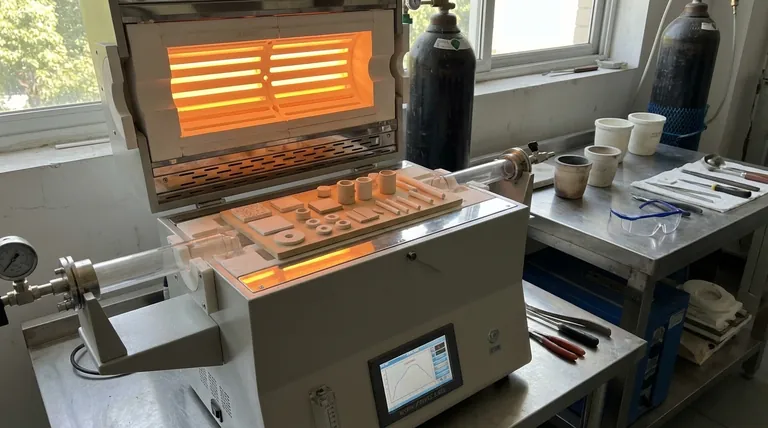
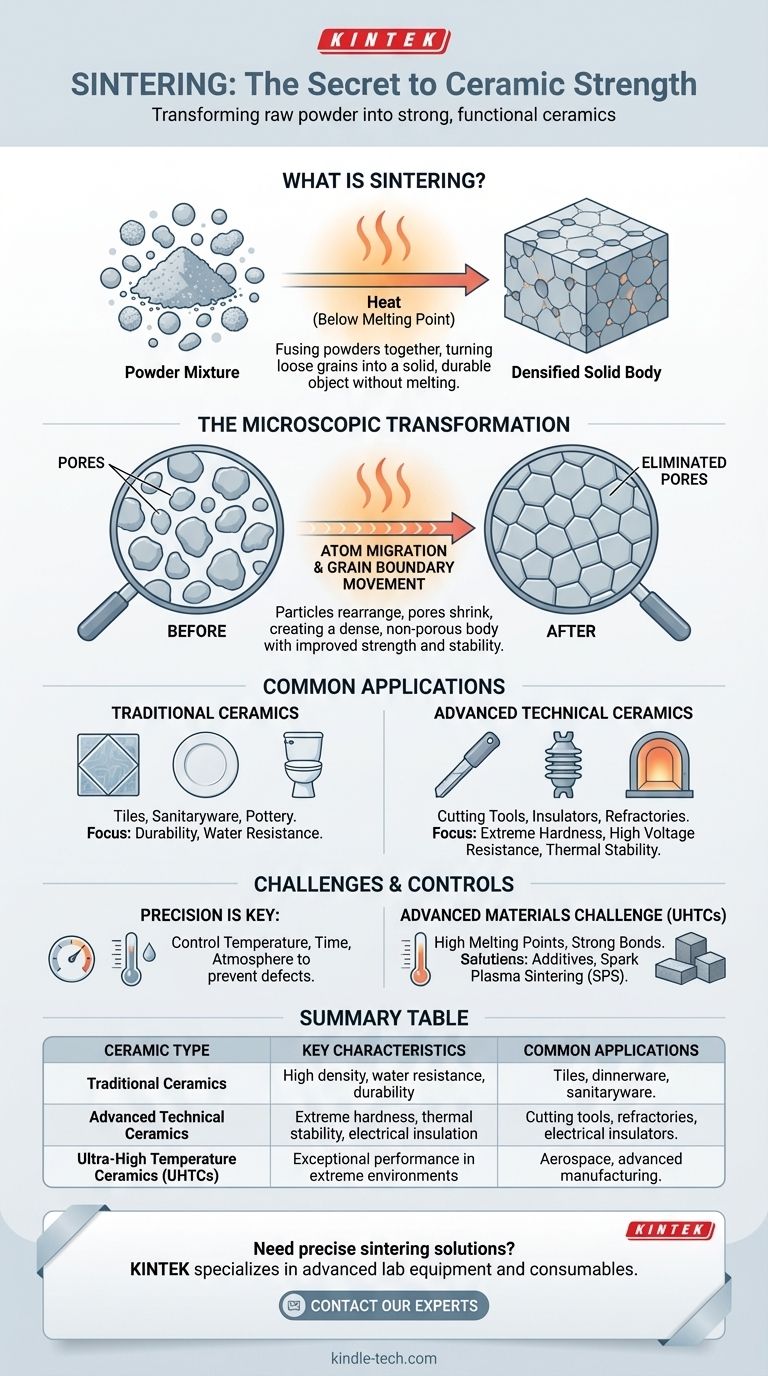
Virtually all modern ceramics are created through a process called sintering. From common household items like tiles and dinnerware to advanced industrial components, sintering is the fundamental step that transforms raw powder into a strong, dense, and functional ceramic material.
Sintering is not a specific type of ceramic, but rather the essential manufacturing process that gives ceramics their characteristic properties. It involves fusing powders together with heat, turning a loose collection of grains into a solid, durable object without melting it.

What is Sintering? The Foundation of Ceramic Strength
Sintering is the most critical stage in the preparation of nearly all ceramic products. It is a thermal treatment that fundamentally changes the material's internal structure.
From Powder to Solid
The process begins with a mixture of fine powders, such as silica, clay, feldspar, or quartz. These powders are shaped and then heated to high temperatures, but crucially, below their melting point.
Instead of melting and re-solidifying, the heat energizes the atoms in the powder particles. This energy causes the atoms to migrate and diffuse across the boundaries of neighboring particles, effectively welding them together.
The Microscopic Transformation
During sintering, the material undergoes densification. The individual particles rearrange, and the empty spaces (pores) between them gradually shrink and are eliminated.
This grain boundary movement and material migration create a tightly interlocked polycrystalline structure. The result is a dense, non-porous body with vastly improved mechanical strength, hardness, and stability compared to the original powder.
Common Applications of Sintered Ceramics
Because sintering is so fundamental, its applications are incredibly broad, covering both traditional and highly advanced materials.
Traditional Ceramics
Everyday ceramic items rely on sintering for their durability and function. This includes products like ceramic tiles, sanitaryware (sinks and toilets), and pottery. The process ensures they are hard, resistant to water, and chemically stable.
Advanced Technical Ceramics
In engineering and technology, sintering is used to create materials with specific, high-performance properties. Examples include:
- Cutting Tools: Sintering produces extreme hardness for machining metals.
- Electrical Insulators: The process creates a dense, non-conductive material capable of withstanding high voltages.
- Refractory Materials: These are sintered to achieve exceptional thermal stability for use in furnaces and kilns.
Understanding the Challenges and Controls
Achieving the desired properties in a finished ceramic product requires precise control over the sintering process. It is not a simple "one-size-fits-all" operation.
The Importance of Process Parameters
The final density, porosity, and microstructure of a ceramic are determined by the sintering parameters. Factors like temperature, time, and the surrounding atmosphere must be carefully managed to prevent defects and ensure the material performs as expected.
The Challenge of Advanced Materials
Some materials are inherently difficult to sinter. Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics (UHTCs), for example, have extremely high melting points and strong covalent bonds, which resist the atomic diffusion necessary for densification.
To overcome this, engineers may use additives like toughening fibers to create composite materials. They may also employ advanced techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), which can achieve densification at lower temperatures and in shorter times than conventional methods.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding that sintering is a process, not a material, helps you evaluate a ceramic based on its intended function.
- If your primary focus is household or architectural use: You are dealing with sintered ceramics like porcelain, where the goal is achieving high density for durability and water resistance.
- If your primary focus is industrial performance: You are using advanced ceramics where sintering is precisely controlled to engineer specific properties like extreme hardness, thermal stability, or electrical insulation.
- If your primary focus is materials innovation: You are concerned with overcoming sintering challenges in advanced materials to unlock new levels of performance for extreme environments.
Ultimately, knowing that a ceramic is sintered is the starting point for understanding how its properties were engineered for its specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Ceramics | High density, water resistance, durability | Tiles, dinnerware, sanitaryware |
| Advanced Technical Ceramics | Extreme hardness, thermal stability, electrical insulation | Cutting tools, refractories, electrical insulators |
| Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics (UHTCs) | Exceptional performance in extreme environments | Aerospace, advanced manufacturing |
Need precise sintering solutions for your ceramic materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for sintering processes. Whether you're developing traditional ceramics or innovating with UHTCs, our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect density and microstructure for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















