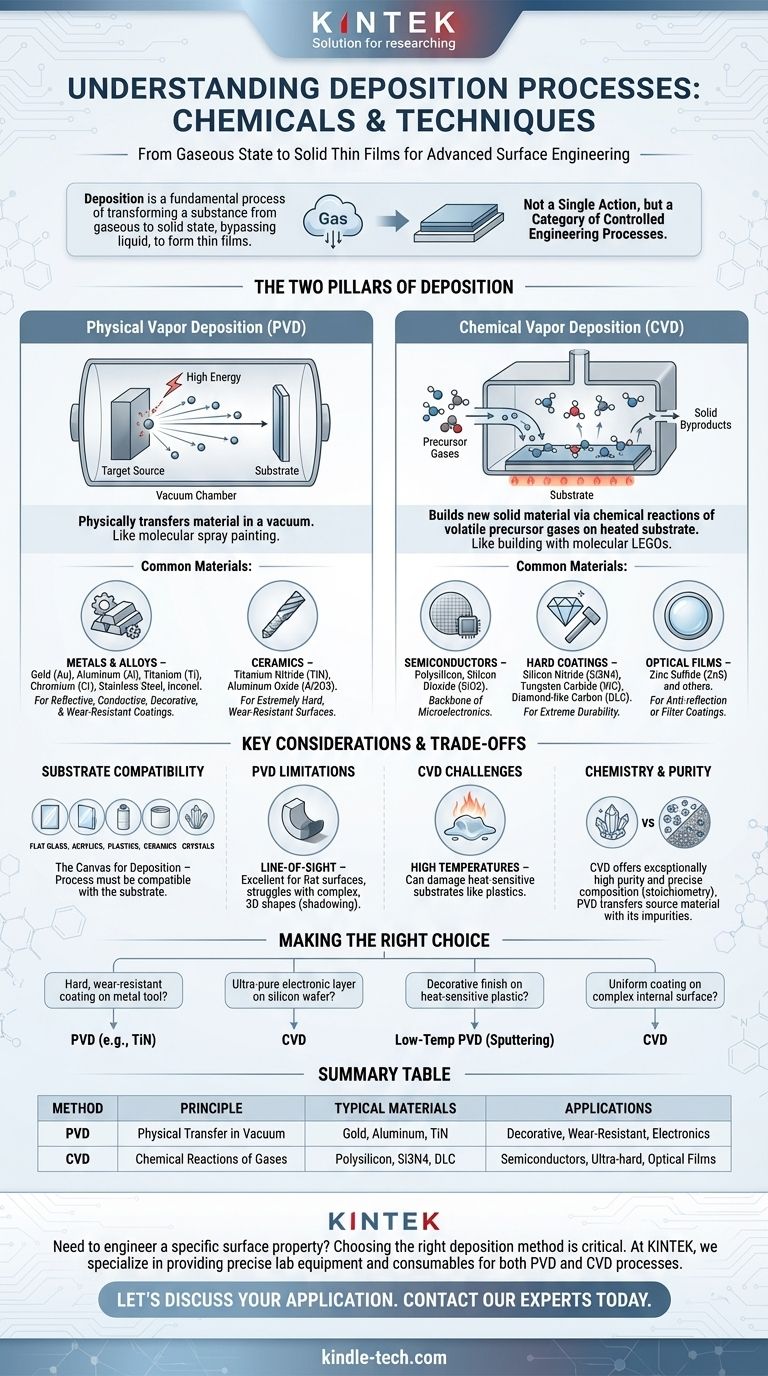
Deposition is a fundamental process where a substance in a gaseous state transforms directly into a solid, bypassing the liquid phase. While simple examples include water vapor forming frost, in technical and industrial contexts, deposition refers to a wide range of processes used to apply thin films of materials onto a surface. Virtually any material can be deposited, including metals like gold and aluminum, hard ceramics, and even polymers like plastics.
The core concept to understand is that "deposition" is not a single action but a category of highly controlled engineering processes. The specific "chemical" or material used depends entirely on the chosen method—either Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)—and the desired properties of the final coating.

The Two Pillars of Deposition: Physical vs. Chemical
The materials that can be deposited are best understood by dividing the methods into two primary families. Each works on a different principle and is suited for different materials and outcomes.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Moving Matter
PVD is a process that physically transfers material from a source (called a "target") onto the object to be coated (the "substrate"). Think of it as a type of molecular spray painting that happens in a vacuum.
The source material is a solid block of the coating you want to apply. High energy is used to knock atoms or molecules off this target, which then travel through the vacuum and condense as a solid film on the substrate's surface.
Common materials deposited via PVD include:
- Metals: Gold (Au), Aluminum (Al), Titanium (Ti), Chromium (Cr). These are used for reflective, conductive, or decorative coatings.
- Alloys: Stainless Steel, Inconel.
- Ceramics: Titanium Nitride (TiN), Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3). These create extremely hard, wear-resistant surfaces.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Building with Molecules
CVD is fundamentally different. Instead of physically moving existing material, it builds a new solid material directly on the substrate through chemical reactions.
In this process, one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber. When these gases come into contact with the heated substrate, they react or decompose, leaving behind a solid film. It's like building with molecular LEGOs.
Common materials grown via CVD include:
- Semiconductors: Polysilicon, Silicon Dioxide (SiO2). This is the backbone of the microelectronics industry.
- Hard Coatings: Silicon Nitride (Si3N4), Tungsten Carbide (WC), and Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) for extreme durability.
- Optical Films: Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) and other materials for anti-reflection or filter coatings.
The Substrate: The Canvas for Deposition
The material being coated, or the substrate, is just as critical. The deposition process must be compatible with it. Materials mentioned in your reference, such as flat glass, acrylics, plastics, ceramics, and crystals, all serve as common substrates for receiving a deposited film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method is a matter of balancing requirements. There is no single "best" process; each has inherent strengths and limitations.
PVD: Line-of-Sight Limitations
Because PVD is a physical, line-of-sight process (like a spray can), it is excellent for coating flat or gently curved surfaces. However, it struggles to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with deep grooves or holes, creating a "shadowing" effect.
CVD: The Challenge of High Temperatures
Many CVD processes require very high temperatures to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This can easily damage or melt heat-sensitive substrates like plastics or certain metals, limiting its application.
Chemistry and Purity
CVD can produce films of exceptionally high purity and precise chemical composition (stoichiometry), which is why it dominates semiconductor manufacturing. PVD, while excellent for many applications, is essentially transferring a source material that may contain its own impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, you must first define your objective for the coating.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant coating on a metal tool: PVD is a robust and common choice for applying ceramics like Titanium Nitride.
- If your primary focus is creating an ultra-pure electronic layer on a silicon wafer: CVD is the industry standard for its atomic-level control and chemical precision.
- If your primary focus is applying a decorative metallic finish to a heat-sensitive plastic part: A low-temperature PVD process like sputtering is the ideal method to avoid damaging the substrate.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating a complex internal surface: CVD has an advantage because the precursor gas can flow into and react within intricate geometries where PVD cannot reach.
Ultimately, deposition is a powerful and versatile tool for engineering the properties of a material's surface.
Summary Table:
| Deposition Method | Principle | Common Materials Deposited | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Physically transfers material in a vacuum. | Gold, Aluminum, Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Decorative coatings, wear-resistant surfaces, electronics |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Builds material via chemical reactions of gases. | Polysilicon, Silicon Nitride (Si3N4), Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) | Semiconductor devices, ultra-hard coatings, optical films |
Need to engineer a specific surface property?
Choosing the right deposition method and material is critical to your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for both PVD and CVD processes. Whether you are developing wear-resistant tools, advanced semiconductors, or specialized optical coatings, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect deposition solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in thin film optical coating? Key Materials for Precise Light Control
- What are the advantages of carbon nanotubes? Unlock Superior Strength, Conductivity & Performance
- What are the characteristics of a coating produced by low-temperature arc vapor deposition (LTAVD)? Key Performance Insights
- What does the deposition rate depend on? Key Factors for Thin-Film Process Control
- How does sputtering deposition work? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Coating
- Why do carbon nanotubes have high strength? The Atomic Secret to Unmatched Material Performance
- What is the alternative material for graphene? Discover the Top 2D Materials for Your Specific Application
- What are the advantages of chemical bath deposition? A Low-Cost, Scalable Thin Film Solution



















