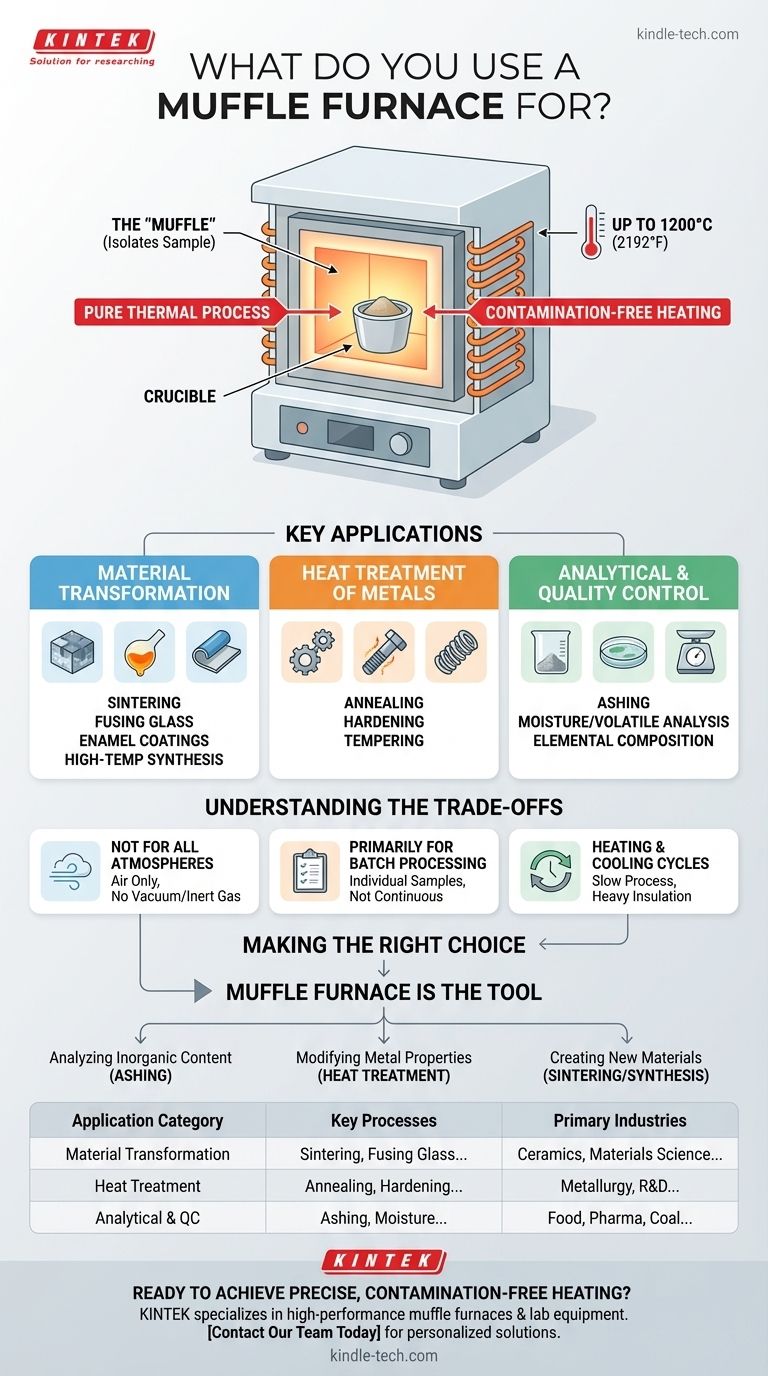
In essence, a muffle furnace is used for any process that requires heating a material to a very high temperature in a controlled environment. Its core applications fall into three main categories: transforming materials (like sintering ceramics or heat-treating metals), analyzing samples (like ashing), and creating new compounds through high-temperature synthesis.
The critical function of a muffle furnace isn't just to get hot, but to do so cleanly. It uses an inner chamber—the "muffle"—to isolate the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, preventing contamination and ensuring a pure thermal process.

The Core Principle: Contamination-Free Heating
A muffle furnace is fundamentally different from a simple high-temperature oven. The design is engineered to protect the integrity of the sample being heated.
What "Muffle" Means
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber that encloses the material being processed. This chamber is heated from the outside by coils.
This design is crucial because it shields the sample from any combustion byproducts or impurities that could be released by the heating elements themselves. This ensures the process is purely thermal.
Achieving High Temperatures
Muffle furnaces are designed for applications that begin where standard ovens leave off. They typically operate at temperatures up to 1200°C (2192°F) or higher.
This capability is essential for causing physical or chemical changes in materials, such as melting metals, fusing glass, or burning off all organic matter from a sample.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to provide clean, high-temperature heat makes the muffle furnace an indispensable tool in laboratories, research units, and specialized industrial settings.
Material Transformation and Creation
One of the primary uses is to fundamentally change a material's structure.
This includes sintering (fusing powdered materials like ceramics or metals into a solid piece), fusing glass, creating enamel coatings, and performing high-temperature synthesis of new materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
In metallurgy and manufacturing, muffle furnaces are used for small-scale heat treatment processes.
These processes, like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering (toughening), modify the physical properties of steel and other alloys to meet specific performance requirements.
Analytical and Quality Control Processes
The furnace is a standard instrument for sample preparation and analysis in many fields.
The most common analytical use is ashing, where a sample (from food, coal, or pharmaceuticals) is incinerated to burn off all organic content, leaving only the inorganic ash for measurement and analysis. It is also used to determine moisture content, volatile matter, and elemental composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific limitations that are important to recognize.
Not for All Atmospheres
A standard muffle furnace operates in an air atmosphere. It is not designed for processes that require a vacuum or a specific inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. Specialized furnaces are required for those applications.
Primarily for Batch Processing
Muffle furnaces are ideal for processing individual samples or small batches of parts. They are not suited for continuous, high-volume industrial production lines.
Heating and Cooling Cycles
The heavy insulation required to reach and maintain extreme temperatures means that heating up and cooling down a muffle furnace can be a slow process. This must be factored into any workflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analyzing inorganic content (ashing): A muffle furnace is the standard tool for completely removing organic material to measure what remains.
- If your primary focus is modifying metal properties (heat treatment): It provides the precise, high-temperature environment needed for processes like annealing or hardening small parts.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials (sintering/synthesis): The furnace offers a stable, controlled chamber for fusing powders or reacting solids at extreme temperatures.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when your process demands pure, high-temperature transformation in a controlled air environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Sintering, Fusing Glass, Enamel Coating | Ceramics, Materials Science, Manufacturing |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Metallurgy, R&D, Small-Scale Production |
| Analytical & Quality Control | Ashing, Moisture/Volatile Matter Analysis | Food, Pharmaceuticals, Coal, Environmental |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free heating for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces and lab equipment, designed to meet the rigorous demands of sintering, ashing, and heat treatment processes. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace to enhance your research and quality control. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
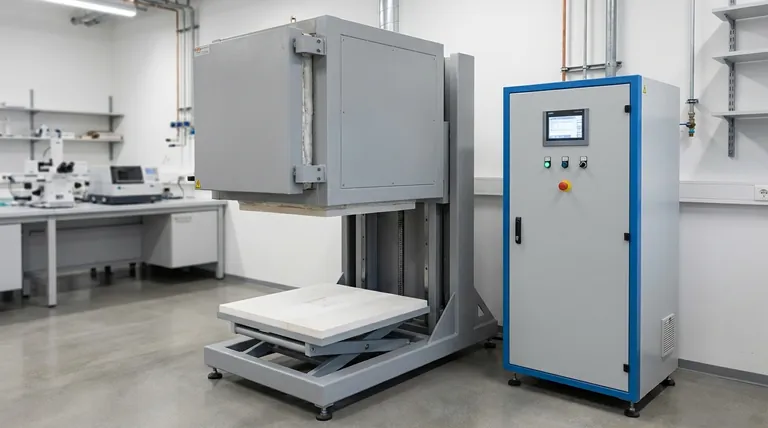
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the condition of a muffle furnace? Ensuring Clean, Controlled Heat for Your Lab
- What hazard is involved when using a furnace? Protect Your Home from the Silent Killer
- What is the difference between a crucible and a furnace? Understanding the Heat Source and Container Partnership
- What is a laboratory furnace called? A Guide to Muffle and Tube Furnaces
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application



















