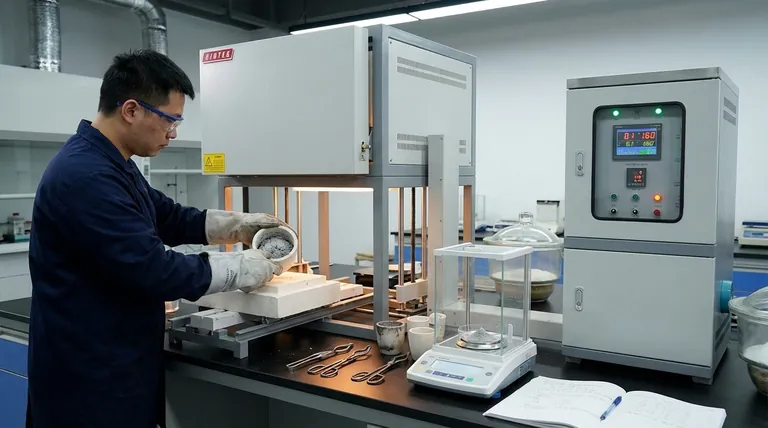
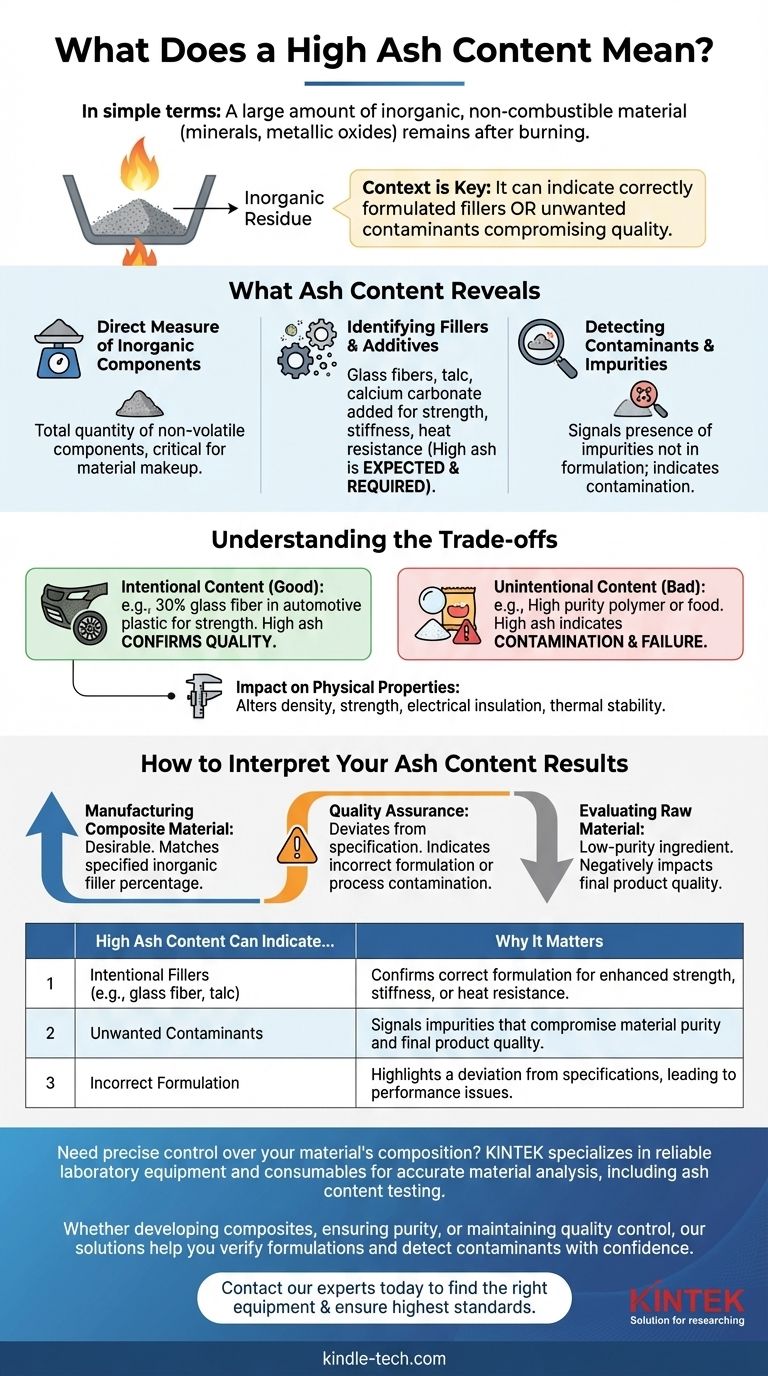
In simple terms, a high ash content means a sample contains a large amount of inorganic, non-combustible material. This residue, which consists of minerals and metallic oxides, is what remains after the organic components of the material have been completely burned away.
The significance of high ash content is entirely dependent on context. It can either indicate a material is correctly formulated with performance-enhancing fillers or reveal the presence of unwanted contaminants that compromise quality.

What Ash Content Reveals About a Material
Ash content is a fundamental metric used in quality control and material analysis. The test itself involves burning a sample under controlled conditions and weighing the non-combustible residue. The result provides a clear picture of a material's inorganic composition.
A Direct Measure of Inorganic Components
The "ash" is the residue left after complete combustion. It is typically composed of oxides from the inorganic elements present in the original sample.
This measurement provides a total quantity of these non-volatile components, offering a critical data point for understanding the material's overall makeup.
Identifying Fillers and Additives
In many industries, particularly plastics and composites, inorganic materials are intentionally added as fillers or reinforcements.
Materials like glass fibers, talc, or calcium carbonate are added to enhance properties such as strength, stiffness, or heat resistance. In these cases, a specific, high ash content is not only expected but required to meet product specifications.
Detecting Contaminants and Impurities
Conversely, a high ash content can be a red flag. It may signal the presence of impurities or contaminants that were not part of the intended formulation.
This is crucial for ensuring the purity of raw materials and the quality of finished products. An unexpectedly high ash value often points to contamination during sourcing or processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Interpreting ash content is not a simple matter of "high is bad" or "low is good." The value is only meaningful when compared against a known standard or specification for that specific material.
Intentional vs. Unintentional Content
The central distinction is whether the inorganic material is supposed to be there. A plastic part designed for automotive use might require 30% glass fiber filler to achieve necessary strength. Here, a high ash content confirms quality.
However, in a food product or a high-purity polymer, even a small ash percentage could indicate significant contamination and product failure.
Impact on Physical Properties
The amount of inorganic material directly influences a product's physical characteristics. An incorrect ash content can alter density, tensile strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability.
Therefore, measuring ash content is a critical step in verifying that a material will perform as designed in its final application.
How to Interpret Your Ash Content Results
Your interpretation of a high ash content result depends entirely on your objective and the material you are analyzing. It is a powerful diagnostic tool when used correctly.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing a composite material: A high ash content is desirable, provided it precisely matches the specified percentage of inorganic filler required for performance.
- If your primary focus is quality assurance: A high ash content that deviates from the product's specification is a clear indicator of an incorrect formulation or process contamination.
- If your primary focus is evaluating a raw material: A high ash content often signifies a lower-purity ingredient that could negatively impact the quality of your final product.
Ultimately, understanding a material's ash content allows you to verify its composition and control its quality with confidence.
Summary Table:
| High Ash Content Can Indicate... | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Intentional Fillers (e.g., glass fiber, talc) | Confirms correct formulation for enhanced strength, stiffness, or heat resistance. |
| Unwanted Contaminants | Signals impurities that compromise material purity and final product quality. |
| Incorrect Formulation | Highlights a deviation from specifications, leading to performance issues. |
Need precise control over your material's composition?
Understanding ash content is critical for quality assurance and product performance. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables for accurate material analysis, including ash content testing.
Whether you're developing composites, ensuring raw material purity, or maintaining strict quality control, our solutions help you verify formulations and detect contaminants with confidence.
Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your laboratory's specific needs and ensure your materials meet the highest standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a muffle furnace? From 1100°C to 1800°C Based on Heating Elements
- What are the specs of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Key Features & Selection
- What is the difference between melting and sintering temperatures? A Guide to Material Processing Methods
- What are the features of muffle furnace? Unlock Clean, Precise High-Temperature Processing
- How hot can a muffle furnace get? Find the Right Temperature for Your Lab



















