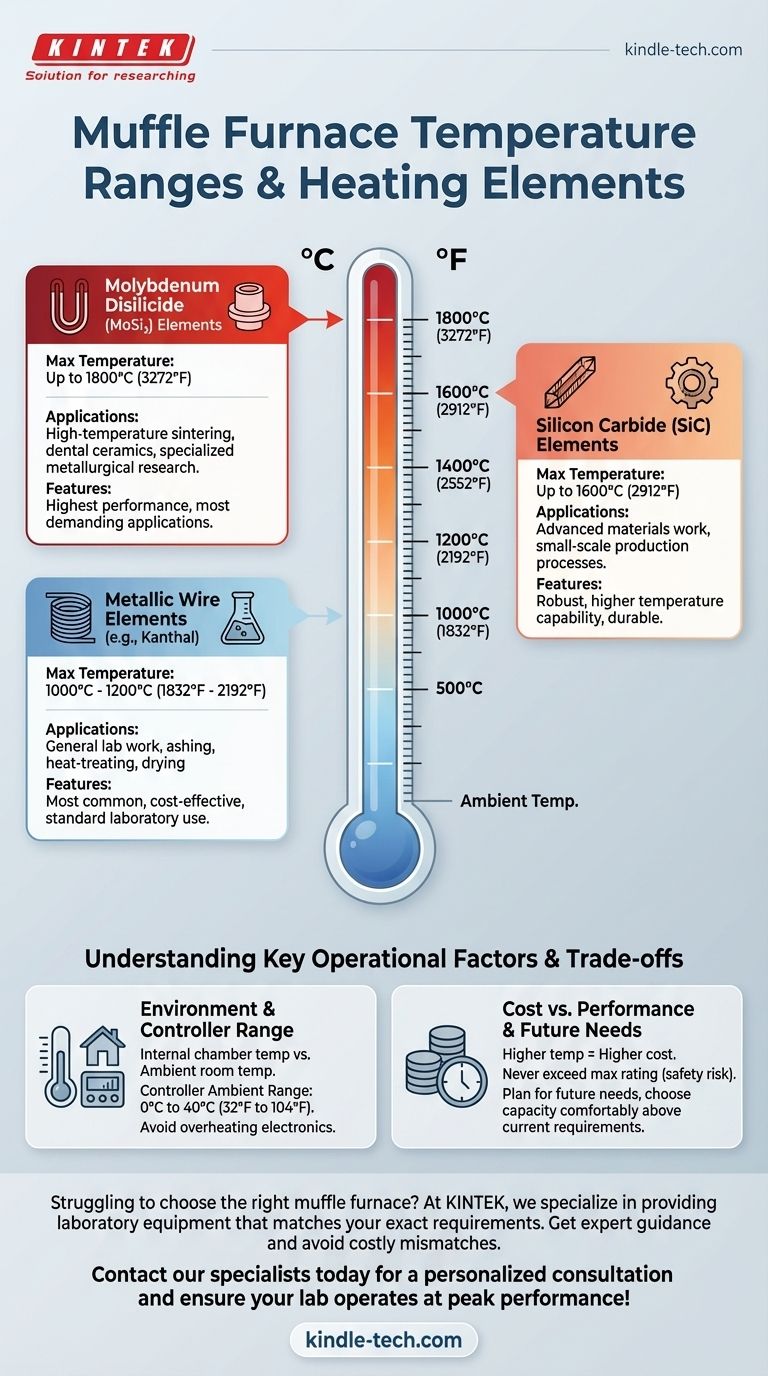
The temperature range of a muffle furnace is not a single, fixed value; it varies significantly based on the furnace's construction. While many common models operate up to 1100°C or 1200°C, high-performance units can reliably reach temperatures as high as 1800°C (3272°F). The key determining factor is the material used for the internal heating elements.
A muffle furnace's maximum temperature is not a generic specification but a direct consequence of its heating element technology. Understanding this relationship is the single most important factor in selecting the correct furnace for your specific high-temperature application.

What Determines a Muffle Furnace's Temperature?
The wide variation in temperature ratings seen across different models can be confusing. The discrepancy is almost entirely due to the materials science of the components responsible for generating heat.
The Critical Role of Heating Elements
The core of any electric muffle furnace is its heating element. These components resist the flow of electricity, generating intense heat. However, each material has a maximum operating temperature beyond which it will degrade, melt, or fail rapidly.
Common Heating Element Types and Their Limits
Furnaces are engineered around the capabilities of their elements. The most common types fall into three tiers.
Metallic Wire Elements (e.g., Kanthal) These are the most common and cost-effective elements. They are typically found in general-purpose laboratory furnaces.
- Maximum Temperature: 1000°C to 1200°C (1832°F to 2192°F)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements For applications requiring higher temperatures than metallic elements can provide, Silicon Carbide is the next step up. These are robust and suitable for many materials science and small-scale production processes.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to 1600°C (2912°F)
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements These are the highest-performance elements commonly used in laboratory muffle furnaces. They are reserved for the most demanding applications, such as ceramic sintering or specialized metallurgical research.
- Maximum Temperature: Up to 1800°C (3272°F)
Understanding Key Operational Factors
Beyond the maximum temperature, you must consider the entire operating environment to ensure safety, accuracy, and longevity of the equipment.
The Full Operating Range
While we focus on the maximum temperature, these furnaces operate from ambient room temperature upwards. The lower end of the effective range for most applications, like ashing or melting, is typically several hundred degrees Celsius.
The External Environment Matters
It is critical to distinguish between the furnace's internal chamber temperature and the ambient temperature of the room where it operates. The furnace's electronic controller has its own, much narrower, safe operating range.
- Controller Ambient Range: Typically 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
Operating the furnace in a room that is too hot can cause the control electronics to overheat and fail, even if the internal chamber is operating normally.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is not just about picking the highest number. You must balance performance, cost, and future needs.
Cost vs. Temperature
There is a direct and significant correlation between maximum temperature and price. A furnace equipped with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements can cost several times more than a standard metallic element furnace.
Never Exceed the Maximum Rating
Attempting to push a furnace beyond its specified maximum temperature is a critical mistake. It will drastically shorten the life of the heating elements and can cause catastrophic failure, posing a significant safety risk.
Planning for Future Needs
A common pitfall is selecting a furnace that only just meets your current temperature requirements. This leaves no flexibility for future projects. A good rule of thumb is to choose a furnace with a maximum temperature that comfortably exceeds your immediate needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct muffle furnace, match the heating element technology to your specific temperature goals.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing, heat-treating, or drying below 1200°C: A standard furnace with metallic wire elements is the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials work or processes requiring up to 1600°C: You will need a furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering, dental ceramics, or research needing up to 1800°C: Your only option is a high-performance furnace with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements.
By aligning the furnace's capabilities with your procedural demands, you ensure safe, efficient, and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Maximum Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (e.g., Kanthal) | 1000°C - 1200°C | General lab work, ashing, heat-treating |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Advanced materials work, small-scale production |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C | High-temperature sintering, dental ceramics, research |
Struggling to choose the right muffle furnace for your specific temperature needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing laboratory equipment that matches your exact requirements. Our experts can help you select the ideal muffle furnace based on your application, budget, and future goals—whether you need a standard model for routine testing or a high-performance unit for advanced research.
We provide:
- Furnaces with precise temperature control from 1100°C to 1800°C
- Durable equipment built for safety and longevity
- Expert guidance to avoid costly mismatches
Don't risk your experiments with the wrong equipment—contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and ensure your lab operates at peak performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Which metals cannot be hardened by heat treatment? Understand the limits of thermal hardening.
- What is difference between crucible and furnace? Understand the Heat Source vs. Containment Vessel
- What is SV and PV in a muffle furnace? Master Temperature Control for Precision Results
- Why is it important to hardening a steel? To Achieve Superior Strength and Wear Resistance
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis



















