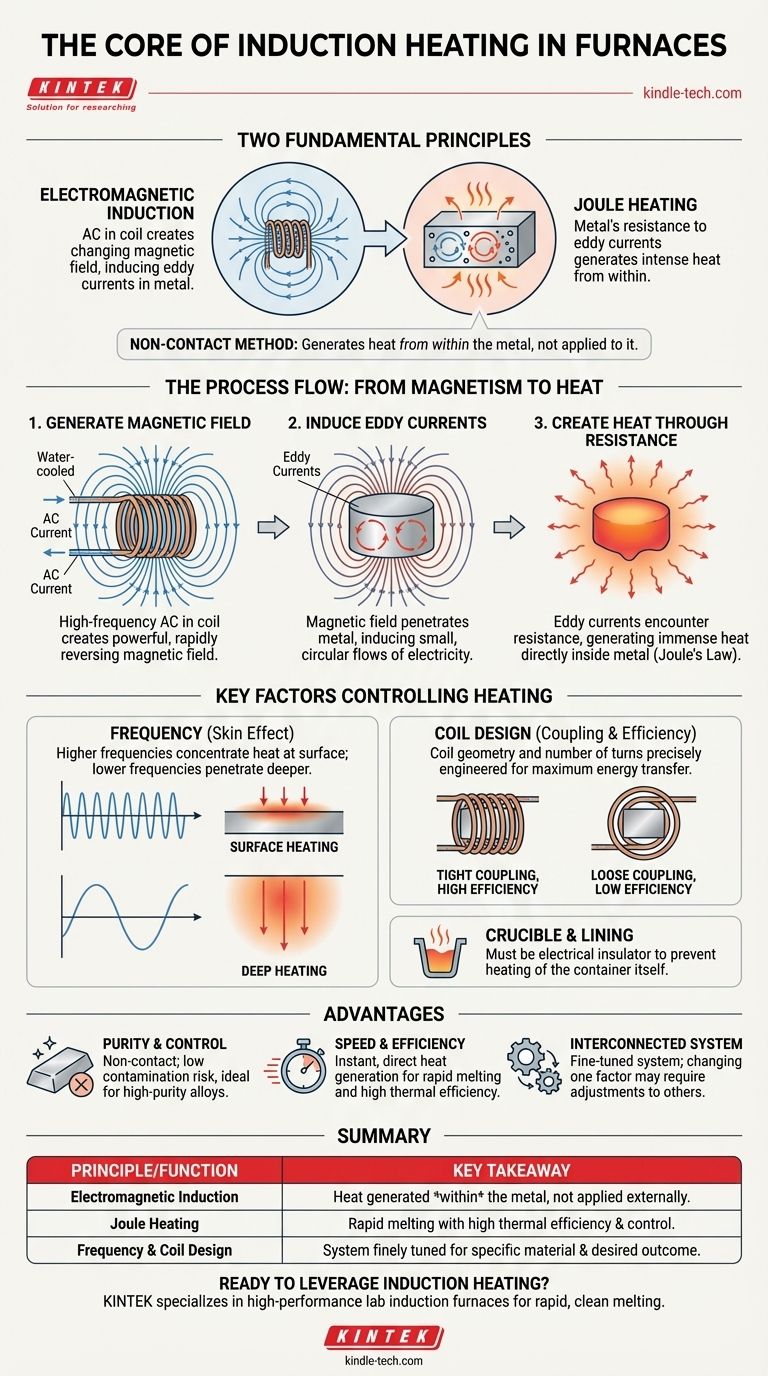
At its core, induction heating in an induction furnace relies on two fundamental physics principles: electromagnetic induction and Joule heating. An alternating current in a copper coil creates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field, which in turn induces electrical currents directly within the metal charge, generating intense heat due to the metal's own electrical resistance.
The central concept to grasp is that induction heating is a non-contact method. Unlike other furnaces, it doesn't apply heat to the metal; it uses magnetic fields to generate heat from within the metal itself, leading to rapid, clean, and controllable melting.
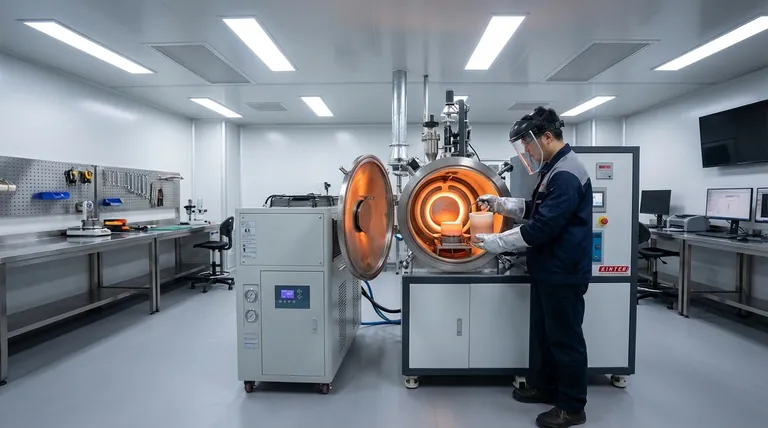

The Core Principle: From Magnetism to Heat
To understand how an induction furnace works, it's best to break the process down into a sequence of events. Each step is a direct consequence of the last.
Step 1: Generating a Powerful Magnetic Field
The furnace is built around a water-cooled coil, typically made of copper. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil.
This flow of electricity generates a strong, rapidly reversing magnetic field in the space at the center of the coil, where the metal to be melted (the "charge") is placed.
Step 2: Inducing Electrical Currents (Eddy Currents)
According to Faraday's Law of Induction, a changing magnetic field will induce an electrical current in any conductor placed within it.
The furnace's magnetic field penetrates the metal charge, inducing small, circular flows of electricity within the material. These are known as eddy currents.
Step 3: Creating Heat Through Resistance (Joule's Law)
All electrical conductors have some resistance to the flow of electricity. As the induced eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter this inherent resistance.
This struggle is similar to friction, and it generates immense heat directly inside the metal. This phenomenon is called Joule heating, and it is the direct cause of the temperature rise that melts the charge.
Key Factors Controlling the Heating Process
The efficiency and characteristics of induction heating are not accidental; they are controlled by several key parameters.
The Role of Frequency
The frequency of the alternating current in the coil is a critical variable. Higher frequencies tend to concentrate the heating effect near the surface of the metal (a phenomenon known as the skin effect).
Lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the metal, providing more uniform heating for larger pieces. The choice of frequency is therefore tailored to the size and type of material being melted.
The Importance of Coil Design
The efficiency of energy transfer depends heavily on the coupling between the coil and the charge. A coil that is closely shaped to the charge ensures that the maximum amount of magnetic field energy is intercepted by the metal.
The number of turns in the coil and its overall geometry are precisely engineered to create the most effective magnetic field for a given application.
The Crucible and Lining
The metal charge is held within a container called a crucible, which is made of a refractory (heat-resistant) material. This material must be an electrical insulator.
If the crucible were conductive, the magnetic field would also heat it, wasting energy and potentially causing it to fail. The quality and composition of this lining are critical for the furnace's safety and operational life.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
The physics of induction heating gives rise to unique benefits and considerations compared to other melting technologies.
Advantage: Purity and Control
Because heating is non-contact, the risk of contaminating the metal is extremely low. There are no graphite electrodes or combustion byproducts to introduce impurities.
This makes induction furnaces ideal for melting high-purity alloys or, as noted in reference material, steels with very low carbon content that would be compromised by other methods.
Advantage: Speed and Efficiency
Heat is generated instantly and directly within the material. This results in very rapid melting cycles and high thermal efficiency, as less heat is lost to the furnace structure and surrounding environment.
Consideration: The System is Interconnected
The effectiveness of an induction furnace relies on a finely tuned system. The power supply, coil design, crucible material, and the properties of the metal being melted are all interdependent.
A change in one factor, such as the type of metal alloy, may require adjustments to the operating frequency or power level to maintain optimal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principle helps you leverage this technology effectively for specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Induction is the superior choice for specialty alloys, medical-grade metals, or low-carbon steels where contamination from electrodes or fuel is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is speed and process control: The rapid, direct heating of an induction furnace provides fast turnaround times and precise temperature management, ideal for foundries with high production demands.
- If you are melting diverse materials: You must consider that the material's electrical resistivity and magnetic properties directly impact heating efficiency, requiring a system designed with the correct frequency and power flexibility.
Ultimately, the induction furnace is a powerful tool precisely because it elegantly transforms the invisible force of magnetism directly into heat.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Function | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | AC in a coil creates a changing magnetic field, inducing eddy currents in the metal. | Heat is generated within the metal itself, not applied externally. |
| Joule Heating | The metal's resistance to the induced eddy currents creates intense, direct heat. | This leads to rapid melting with high thermal efficiency and control. |
| Frequency & Coil Design | Higher frequencies heat the surface (skin effect); lower frequencies penetrate deeper. Coil geometry is critical for efficient energy transfer. | The system is finely tuned for the specific material and desired outcome. |
Ready to leverage the power of induction heating for your lab or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for rapid, clean melting of high-purity metals and alloys. Our systems offer the precise control and material purity essential for advanced research and manufacturing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an induction furnace from KINTEK can enhance your efficiency, improve your product quality, and meet your specific melting goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















