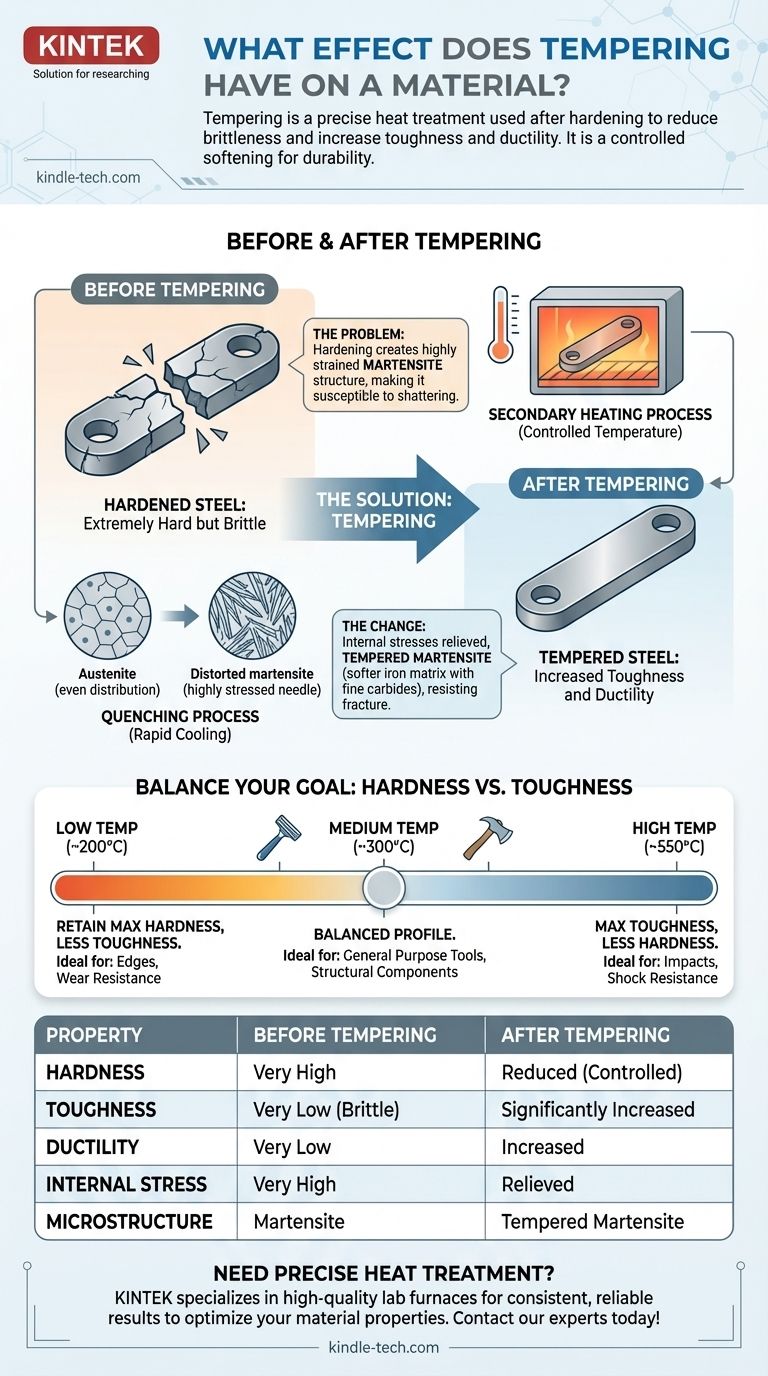
In short, tempering is a precise heat treatment process used after a material has been hardened. It reduces the excessive hardness and brittleness of the hardened metal, resulting in a significant increase in its toughness and ductility. This controlled "softening" makes the material more durable and resistant to shattering under impact or stress.
Tempering is the critical engineering compromise that makes hardened steel useful. It strategically sacrifices a degree of hardness—the property that resists wear—to gain a significant amount of toughness, the property that resists fracture.

The Problem: Why Hardening Creates Brittleness
To understand tempering, you must first understand the process that precedes it: hardening. These two processes are inseparable parts of a whole.
The Hardening Process and Martensite
Hardening involves heating steel to a very high temperature, where its internal crystal structure changes into a state called austenite.
In this state, carbon atoms dissolve and spread evenly throughout the iron crystals. If the steel is then cooled very rapidly—a process called quenching—the carbon atoms are trapped.
This rapid cooling forces the iron crystals into a new, highly strained, and distorted structure called martensite.
The Unwanted Side Effect: Extreme Brittleness
Martensite is extremely hard, which is often desirable for creating a sharp edge or a wear-resistant surface.
However, the internal stress created by this distorted structure also makes it incredibly brittle. An untempered, fully hardened piece of steel is much like glass; it has high hardness but will fracture or shatter with a sharp impact rather than bend or deform.
How Tempering Solves the Problem
Tempering is the carefully controlled remedy for the brittleness induced by hardening. It is a secondary heating process that modifies the martensitic structure.
The Tempering Process Explained
After quenching, the hardened steel is cleaned and then reheated to a specific temperature that is well below the initial hardening temperature.
The steel is held at this tempering temperature for a set amount of time to allow the internal structure to stabilize. It is then allowed to cool, typically in still air.
The Microstructural Change
During tempering, the heat provides enough energy for the trapped carbon atoms to move slightly and precipitate out of the distorted martensite. They form tiny, extremely hard particles of iron carbide (cementite).
This process relieves the immense internal stresses within the material. The original martensite transforms into a new microstructure called tempered martensite, which is a composite of a softer iron matrix and a fine dispersion of hard carbide particles.
Temperature: The Master Control Knob
The tempering temperature is the most critical variable in this process. It directly dictates the final balance of hardness and toughness.
- Low Temperatures (e.g., 200°C / 400°F): Relieve some stress but allow the steel to retain most of its hardness. This results in a material with excellent wear resistance but only a modest gain in toughness.
- High Temperatures (e.g., 550°C / 1025°F): Relieve significant stress and allow for more carbide formation. This results in much lower hardness but a dramatic increase in toughness and ductility.
For centuries, blacksmiths have used the temper colors—the thin oxide film that forms on the steel's surface as it heats—as a visual guide to gauge the temperature and achieve the desired properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hardness vs. Toughness
The core purpose of tempering is to manage the fundamental trade-off between hardness and toughness. These two properties are often in opposition.
Defining Hardness
Hardness is a material's ability to resist localized plastic deformation, such as scratching, abrasion, or indentation. A hard material is excellent at holding a sharp edge and resisting wear.
Defining Toughness
Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. A tough material can withstand sudden shocks and impacts. It is the opposite of brittleness.
The Inseparable Relationship
For most tool steels, increasing toughness means decreasing hardness, and vice versa. Tempering does not create new properties; it allows an engineer or craftsperson to move along a spectrum between these two attributes, dialing in the perfect combination for a specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal temper is entirely dependent on the intended use of the final product. There is no single "best" tempering temperature.
- If your primary focus is maximum edge retention and wear resistance: Temper at a low temperature (e.g., light straw color). This is ideal for tools like razors, files, and some types of cutting dies.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance and durability: Temper at a high temperature (e.g., blue or gray color). This is necessary for tools like hammers, chisels, shock-resistant components, and springs.
- If your primary focus is a balanced profile: Temper at a medium temperature (e.g., brown or purple color). This provides a versatile mix of good hardness and reliable toughness, suitable for general-purpose knives, axes, and structural components like axles.
By mastering tempering, you gain precise control over a material's final properties, transforming brittle steel into a reliable and purpose-built tool.
Summary Table:
| Property | Before Tempering | After Tempering |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Very High | Reduced (Controlled) |
| Toughness | Very Low (Brittle) | Significantly Increased |
| Ductility | Very Low | Increased |
| Internal Stress | Very High | Relieved |
| Microstructure | Martensite | Tempered Martensite |
Need precise heat treatment for your lab materials?
Tempering is a critical step to achieve the exact balance of hardness and toughness your project demands. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—including furnaces for precise heat treatment processes—that laboratories rely on for consistent, reliable results.
Let us help you optimize your material properties. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of calcination? Transform and Purify Materials for Industrial Use
- What is the use of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity with Precise High-Temp Analysis
- What is the function of an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What is the heat capacity of a muffle furnace? Understanding Thermal Mass for Optimal Performance
- What is the temperature of heat treatment? It Depends on Your Metal and Desired Properties



















