In a furnace, the primary energy transfer involves converting a source energy—typically chemical (from fuel) or electrical—into thermal energy, which is then delivered to a target material. This delivery of heat happens through a combination of three fundamental mechanisms: convection, conduction, and radiation. The specific process, like annealing or smelting, dictates which of these mechanisms is most critical.
The core principle of a furnace is not just generating heat, but managing its transfer. The efficiency and success of any furnace operation hinge on controlling the interplay between convection (fluid movement), radiation (electromagnetic waves), and conduction (direct contact) to deliver the right amount of energy to the right place at the right time.

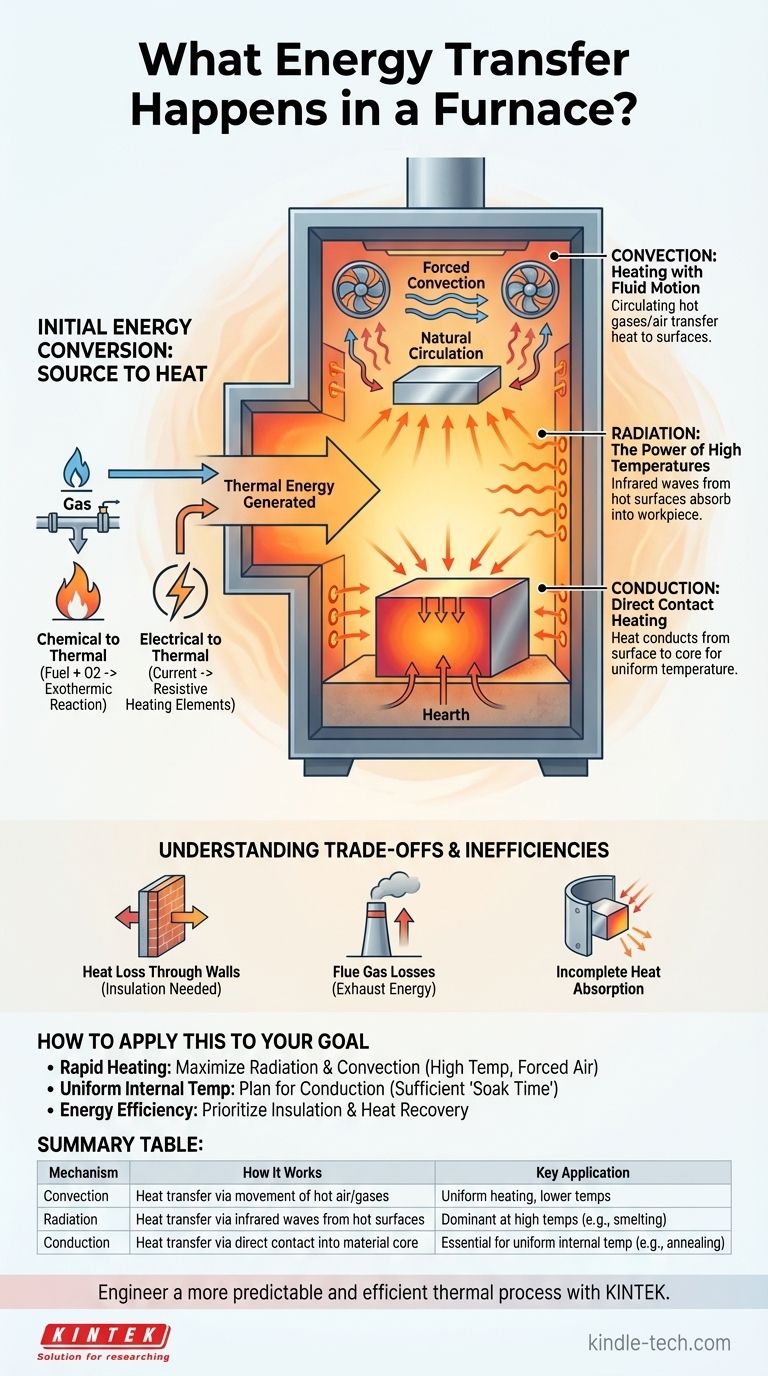
The Initial Energy Conversion: From Source to Heat
Before heat can be transferred to the material, it must first be generated. This happens in one of two primary ways.
Chemical to Thermal Energy
In combustion furnaces, fuels like natural gas, oil, or coal react with oxygen in an exothermic reaction. This chemical process releases a tremendous amount of energy in the form of high-temperature gases and radiant flame.
Electrical to Thermal Energy
Electric furnaces do not use combustion. Instead, they pass a high electrical current through resistive heating elements. The resistance of these elements causes them to heat up significantly, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy that radiates into the furnace chamber.
The Three Pillars of Heat Transfer in a Furnace
Once heat is generated, it moves from the source (flame or heating element) to the workpiece (the material being heated) through a combination of the following mechanisms.
Convection: Heating with Fluid Motion
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid, in this case, the hot air or combustion gases inside the furnace. These hot gases circulate, transferring thermal energy to the furnace walls and the surface of the material being heated.
In many furnaces, fans are used to create "forced convection," which dramatically increases the rate of heat transfer and helps ensure a more uniform temperature distribution, especially at lower temperature ranges.
Radiation: The Power of High Temperatures
As objects get hotter, they radiate thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic waves (specifically infrared radiation). The intensely hot furnace walls (refractory) and the heating elements themselves become powerful sources of radiation.
This radiated energy travels in a straight line and is absorbed by the surface of the workpiece, causing its temperature to rise. At the high temperatures required for processes like smelting, radiation is often the dominant mode of heat transfer.
Conduction: Direct Contact Heating
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical contact. Heat first arrives at the surface of the material via convection and radiation, and it then conducts from the surface into the material's core.
This process is critical for achieving a uniform internal temperature, which is essential for metallurgical processes like annealing. The rate of conduction depends on the material's thermal conductivity. Heat also conducts from the furnace hearth into any part of the workpiece resting on it.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inefficiencies
No energy transfer is perfectly efficient. Understanding where energy is lost is key to designing and operating an effective furnace.
Heat Loss Through Walls
The furnace walls are heavily insulated with refractory materials, but some heat will always conduct through them and be lost to the surrounding environment via convection and radiation from the furnace's outer shell. This is a primary source of energy inefficiency.
Flue Gas Losses
In combustion furnaces, the hot gases produced by burning fuel must eventually be exhausted through a flue or stack. This exhaust carries a significant amount of thermal energy with it, representing a major and often unavoidable energy loss.
Incomplete Heat Absorption
Not all energy radiated from the heat source and walls strikes the workpiece. Some energy may be lost through openings or re-absorbed by other parts of the furnace structure, reducing the overall efficiency of the transfer to the intended material.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The dominance of each heat transfer mechanism is directly related to the process you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating of a large surface area: Your goal is to maximize radiative and convective heat transfer by operating at high temperatures and, if possible, using forced air circulation.
- If your primary focus is achieving a uniform internal temperature (like in annealing): You must plan for conduction by allowing sufficient "soak time" at a stable temperature for heat to penetrate from the surface to the core.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Your design must prioritize high-quality insulation to minimize conduction losses through the walls and potentially include heat exchangers to recover energy from exhaust flue gases.
By understanding these fundamental energy transfers, you move from simply using a furnace to truly engineering a predictable and efficient thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | How It Works | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Convection | Heat transfer via movement of hot air/gases | Uniform heating, especially at lower temperatures |
| Radiation | Heat transfer via infrared waves from hot surfaces | Dominant method at high temperatures (e.g., smelting) |
| Conduction | Heat transfer via direct contact into material core | Essential for uniform internal temperature (e.g., annealing) |
Engineer a more predictable and efficient thermal process with KINTEK.
Understanding energy transfer is the first step; applying it effectively is the next. Whether your goal is rapid surface heating, uniform internal temperatures, or maximizing energy efficiency, the right lab equipment is crucial.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and consumables, designed to give you superior control over convection, conduction, and radiation. We help laboratories achieve consistent, repeatable results while optimizing energy use.
Ready to optimize your furnace operation? Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Which furnace can produce highest temperature? Discover the Power of Electric Arc Furnaces
- How does the use of a vacuum drying oven affect the performance of LiMn2O4 (LMO) cathodes? Unlock Battery Stability
- What material is used for melting furnace? It's a System of Specialized Components
- Why must a vacuum drying oven be used after preparing composite electrolytes? Ensure Battery Stability and Purity
- What is the significance of maintaining a high vacuum environment during the sintering of ODS iron-based alloys?
- What is the function of a high-frequency induction plasma reactor? Synthesis of Nano-scale Magnéli Phase Titanium Oxide
- What is the difference between annealing and tempering? Master the Heat Treatment Process for Your Metals
- Will heat transfer occur in vacuum? Yes, Through Radiation, the Sun's Method



















