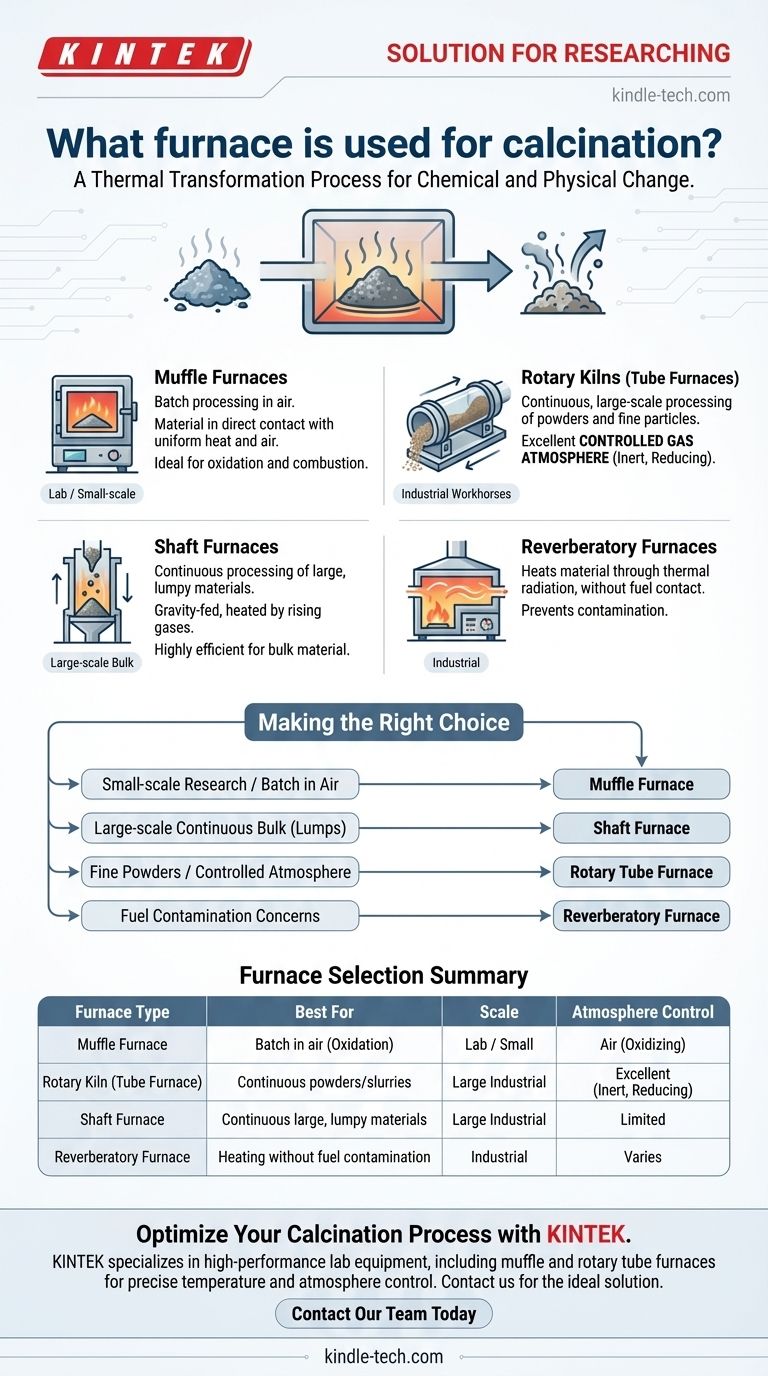
The primary furnaces used for calcination are muffle furnaces, shaft furnaces, and reverberatory furnaces. In many modern industrial applications, a specialized type of reactor called a rotary kiln (or calciner) is the most common choice, particularly for continuous, large-scale processes like cement manufacturing.
The specific furnace you choose for calcination is not arbitrary; it is dictated entirely by the material you are processing, the scale of your operation, and whether you need to control the atmospheric conditions during heating.

What is Calcination?
A Process of Thermal Transformation
Calcination is a thermal treatment process that heats a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point.
The goal is not to melt the substance but to induce a chemical or physical change. This often involves thermal decomposition or the removal of a volatile fraction from the material.
Common Industrial Applications
This process is fundamental in many industries. It is used to remove water from hydrated minerals, drive off carbon dioxide from limestone to create lime for cement, or to remove sulfur from certain ores.
The Primary Types of Calcination Furnaces
The term "calciner" often refers to the industrial reactor where this process happens. This can be a dedicated furnace or a large-scale kiln, with the choice depending on the specific industrial need.
Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace is an excellent choice for processes that require the material to be in direct and complete contact with air.
It works by heating the sample inside a chamber (the "muffle") that is itself heated from the outside. This design ensures uniform heating while allowing for an air atmosphere, which is ideal for oxidizing a substance or ensuring complete combustion of volatile components.
Rotary Kilns (Tube Furnaces)
Rotary kilns, also known as rotary tube furnaces, are the workhorses of large-scale, continuous calcination. These are large, rotating cylindrical vessels where material is fed in one end and slowly moves to the other as it is heated.
Their key advantage is the ability to handle fine particles and powders. The rotation ensures consistent mixing and heat exposure. Critically, rotary kilns are highly effective at maintaining a controlled gas atmosphere, making them suitable for processes that require reducing or reoxidizing conditions.
Shaft Furnaces
A shaft furnace is a tall, vertical furnace where material is loaded in at the top and moves downward by gravity as it is heated by hot gases rising from the bottom.
These are best suited for processing larger, lumpy materials rather than fine powders. They are highly efficient for very large-scale bulk material processing, such as the production of lime from limestone.
Reverberatory Furnaces
In a reverberatory furnace, the material is heated without coming into direct contact with the fuel source.
Instead, a flame and hot gases are passed over the material from a separate combustion chamber, heating it through thermal radiation from the furnace roof and walls. This separation prevents contamination of the material by the fuel or its byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing efficiency, cost, and process requirements. There is no single "best" furnace for all calcination tasks.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Muffle furnaces are typically used for batch processing in laboratory or smaller-scale production environments.
Rotary kilns and shaft furnaces are designed for continuous, high-throughput operations that run 24/7, which is essential for industries like cement and large-scale mining.
Atmosphere Control is Critical
If your process simply requires heating in air, a muffle furnace is a simple and effective solution.
However, if you need to perform calcination in a specific atmosphere (e.g., an inert or reducing gas) to prevent oxidation or achieve a specific chemical reaction, a rotary tube furnace offers far superior control.
Material Size and Form
The physical form of your raw material is a major deciding factor. Shaft furnaces are ineffective for powders, which would obstruct gas flow. Conversely, rotary kilns are specifically designed to handle powders, granules, and slurries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision must be guided by the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is small-scale research or batch production in air: A muffle furnace is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous processing of bulk materials like limestone: A shaft furnace or a large rotary kiln is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is processing fine particles or powders under a tightly controlled gas atmosphere: A rotary tube furnace is the superior technical solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is the first step in ensuring an efficient, consistent, and successful calcination process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Scale | Atmosphere Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Batch processing in air (e.g., oxidation) | Lab / Small-scale | Air (Oxidizing) |
| Rotary Kiln (Tube Furnace) | Continuous processing of powders/slurries | Large-scale Industrial | Excellent (Inert, Reducing) |
| Shaft Furnace | Continuous processing of large, lumpy materials | Large-scale Industrial | Limited |
| Reverberatory Furnace | Heating without fuel contamination | Industrial | Varies |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? The right furnace is critical for efficiency and product quality. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including robust muffle furnaces and advanced rotary tube furnaces for precise temperature and atmosphere control. Our experts will help you select the ideal solution for your specific material and production scale. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity



















