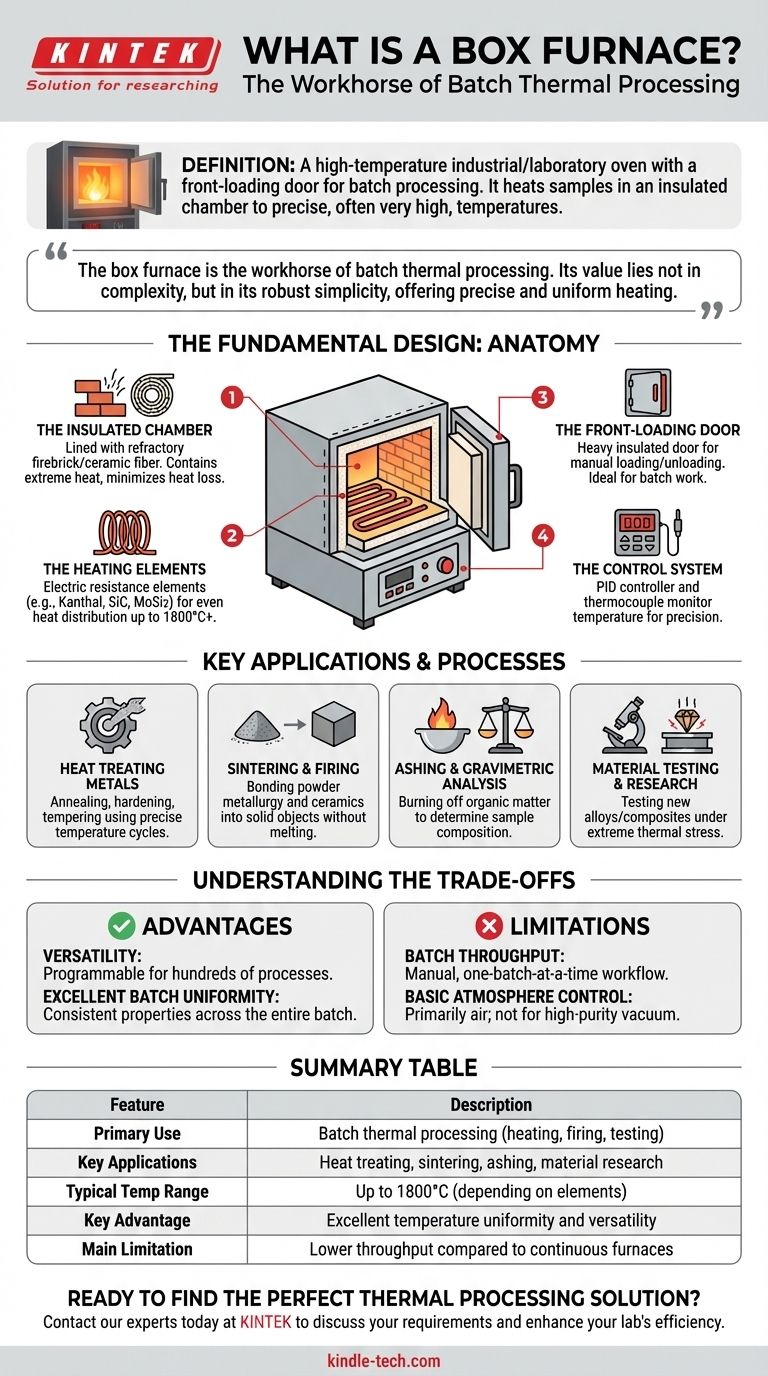
In the simplest terms, a box furnace is a high-temperature industrial or laboratory oven with a front-loading door, designed for processing materials in batches. It operates by heating a sample within an insulated chamber to precise, often very high, temperatures to induce physical or chemical changes. Common applications include hardening metals, firing ceramics, or performing scientific analysis.
The box furnace is the workhorse of batch thermal processing. Its value lies not in complexity, but in its robust simplicity, offering precise and uniform heating for a vast range of materials and applications where continuous throughput is not the primary requirement.
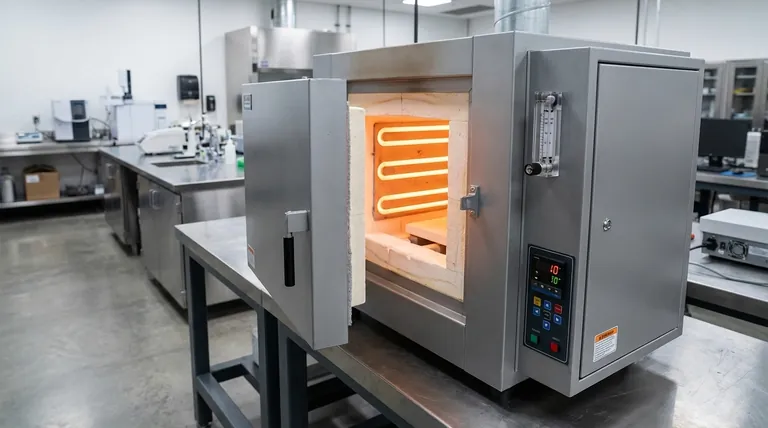

The Fundamental Design of a Box Furnace
A box furnace’s effectiveness comes from its straightforward and reliable design, which consists of a few core components working in unison. Understanding this anatomy clarifies its capabilities and limitations.
The Insulated Chamber
The core of the furnace is a chamber, typically cube- or box-shaped, lined with high-performance insulation. This is often made from refractory firebrick or ceramic fiber.
This insulation is critical for two reasons: it contains the extreme heat to protect the user and the surrounding environment, and it minimizes heat loss, which improves energy efficiency and temperature stability.
The Heating Elements
Heating is achieved via electric resistance elements. These are strategically placed along the walls of the chamber, and sometimes in the door or hearth, to provide even heat distribution.
Common element materials include Kanthal (iron-chromium-aluminum alloy) for temperatures up to around 1200°C, silicon carbide (SiC) for up to 1600°C, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) for even higher temperatures, sometimes exceeding 1800°C.
The Front-Loading Door
The defining feature is its single front-facing door. This door, also heavily insulated, swings open or lifts vertically to allow an operator to manually place and remove materials.
This design makes it ideal for batch work, where one set of parts is processed, the cycle ends, the furnace cools, and a new batch is loaded.
The Control System
Modern box furnaces are governed by a sophisticated control system. A thermocouple, a temperature-sensing probe, sits inside the chamber and relays data to a digital controller.
This controller, typically a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, precisely modulates the power sent to the heating elements to follow a programmed temperature profile, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
Key Applications and Processes
The box furnace's versatility makes it indispensable across numerous industries and research fields. It is not just a heater, but a tool for material transformation.
Heat Treating Metals
This is a primary application. Processes like annealing (softening metal for workability), hardening (strengthening steel), and tempering (reducing brittleness after hardening) all rely on the precise temperature cycles of a box furnace.
Sintering and Firing
In powder metallurgy and ceramics, finely ground powders are compressed and then heated in a box furnace. This process, called sintering, bonds the particles together to form a solid, dense object without melting it.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
In analytical chemistry labs, a sample is placed in a box furnace and heated to a high temperature to completely burn off all organic matter. The remaining inorganic material, or ash, is then weighed to determine the composition of the original sample.
Material Testing and Research
Engineers and scientists use box furnaces to test how new alloys, composites, or coatings behave under extreme thermal stress. This helps determine their durability, melting points, and other critical properties for applications in aerospace, automotive, and energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly capable, the box furnace is not the universal solution for all heating needs. Its strengths in one area create limitations in another.
Advantage: Versatility and Simplicity
A single box furnace can be programmed to run hundreds of different processes, from a low-temperature bake-out to a high-temperature ceramic firing. Their simple design also makes them highly reliable and easy to maintain.
Advantage: Excellent Batch Uniformity
Because the parts remain stationary in a sealed, stable environment, a well-designed box furnace provides exceptional temperature uniformity across the entire batch. This is critical for processes where every part must have identical properties.
Limitation: Batch Processing Throughput
The manual, one-batch-at-a-time workflow is its biggest constraint. The time spent waiting for the furnace to cool, unloading, and reloading makes it unsuitable for high-volume, continuous production lines.
Limitation: Basic Atmosphere Control
Standard box furnaces operate in an air atmosphere. While some can be modified with ports to introduce an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, they are not hermetically sealed. For processes requiring a high-purity vacuum or a reactive gas atmosphere, a specialized vacuum or tube furnace is a far better choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace requires matching its fundamental design to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is versatile lab research or small-batch production: The box furnace is an ideal, cost-effective solution due to its simplicity and process flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous manufacturing: You should investigate a conveyor belt, roller hearth, or tunnel furnace designed for automated production lines.
- If your primary focus is processing with a highly pure or specific atmosphere: A dedicated tube furnace or vacuum furnace will provide the superior environmental control your process requires.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select the right thermal processing tool for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch thermal processing (heating, firing, testing) |
| Key Applications | Heat treating metals, sintering ceramics, ashing, material research |
| Typical Temp Range | Up to 1800°C, depending on heating elements |
| Key Advantage | Excellent temperature uniformity and process versatility |
| Main Limitation | Lower throughput compared to continuous furnaces |
Ready to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your lab?
Whether you need a versatile box furnace for heat treating, sintering, or material testing, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your specific needs. Our range of high-temperature furnaces ensures precise control and reliable performance for your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















