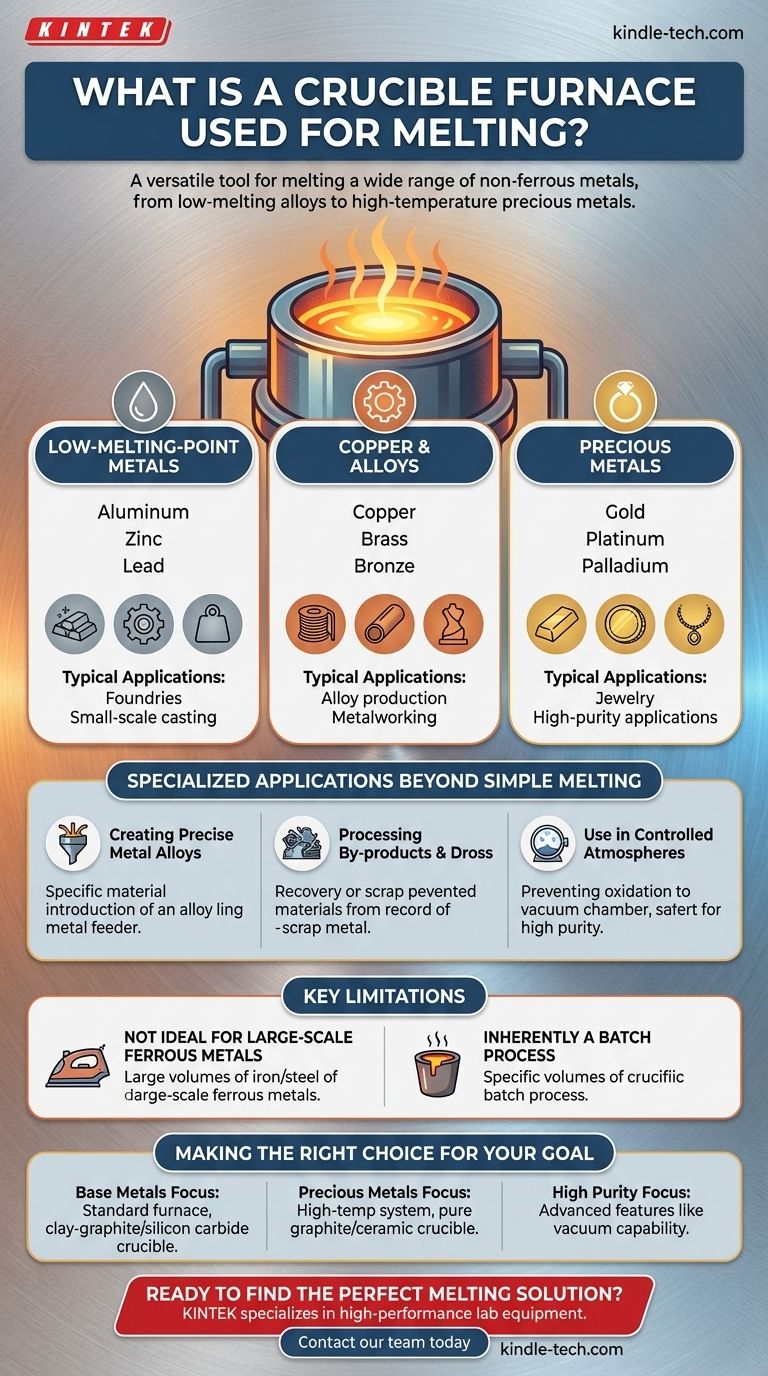
In short, a crucible furnace is used to melt a wide range of non-ferrous metals. Its applications span from common, low-melting-point metals like aluminum, zinc, and lead to high-temperature precious metals such as gold, platinum, and palladium, as well as copper-based alloys like brass and bronze.
The versatility of a crucible furnace comes not from a single design, but from its core concept: a high-temperature vessel (the crucible) is used to contain the material. The specific metal you can melt is determined by the crucible's material and the furnace's maximum temperature capability.
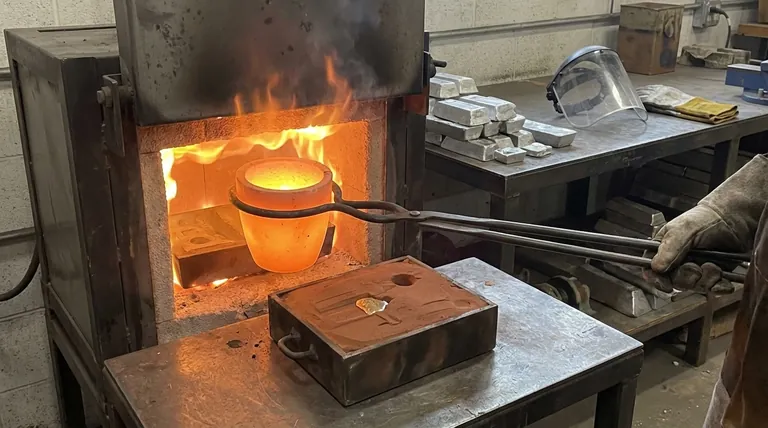

The Primary Role: Melting Non-Ferrous Metals
A crucible furnace is a foundational tool in metallurgy, primarily for metals that do not contain a significant amount of iron. The applications can be broadly categorized by the metal's melting point and value.
Low-Melting-Point Base Metals
The most common use for crucible furnaces is melting base metals that have relatively low melting points. This makes them ideal for foundries and small-scale casting operations.
Metals in this category include aluminum, zinc, and lead. The process is efficient and straightforward for these materials.
Copper and Its Alloys
Crucible furnaces are essential for producing and working with copper and its widely used alloys.
This includes melting pure copper as well as creating brass (a copper-zinc alloy) and bronze (typically a copper-tin alloy).
High-Temperature Precious Metals
For applications requiring extreme heat resistance, specialized crucible furnaces are employed to melt precious metals.
These systems use crucibles made from materials like graphite carbon or clay that can withstand the intense temperatures needed for gold, platinum, and palladium.
Specialized Applications Beyond Simple Melting
The function of a crucible furnace often extends beyond simply turning solid metal into liquid. Advanced systems are designed for more precise metallurgical tasks.
Creating Precise Metal Alloys
Many furnaces are equipped with alloy feeders, allowing operators to introduce specific materials into the molten base metal. This is critical for creating alloys with exact chemical compositions and desired physical properties.
Processing By-products and Dross
In the interest of efficiency and material recovery, crucible furnaces are also used to process by-products from other metallurgical operations. This includes melting dross, the metallic waste that forms on the surface of molten metal, to reclaim valuable material.
Use in Controlled Atmospheres
For high-purity applications, the crucible is sometimes installed within the chamber of a vacuum furnace. This prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen and other atmospheric gases, ensuring the final product is free from oxidation and impurities.
Understanding the Key Limitation: Scale and Material Type
While versatile, crucible furnaces are not the solution for every melting task. Their primary limitation is tied to batch size and material type.
Not Ideal for Large-Scale Ferrous Metals
Crucible furnaces are rarely the primary choice for melting large volumes of ferrous metals like iron and steel.
Industrial steel production relies on different technologies, such as Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) or Basic Oxygen Furnaces (BOF), which are designed for massive, continuous, or semi-continuous throughput.
Inherently a Batch Process
By design, a crucible can only hold a specific volume of material. This makes it a batch-processing tool, which is perfect for foundries, labs, and jewelers but inefficient for producing thousands of tons of metal per day.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible furnace system depends entirely on the material you intend to work with and your final objective.
- If your primary focus is casting base metals like aluminum or zinc: A standard furnace with a clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible is an efficient and direct solution.
- If your primary focus is working with precious metals like gold or platinum: You must select a high-temperature furnace system equipped with a pure graphite or ceramic crucible capable of handling extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is material purity or creating specialized alloys: Your system requires advanced features like vacuum capability and automated, precise feeding mechanisms.
Ultimately, the crucible furnace is a highly adaptable tool, defined by the specific crucible and heating technology it employs for the metallurgical task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Metal Category | Common Examples | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Melting-Point Metals | Aluminum, Zinc, Lead | Foundries, Small-scale casting |
| Copper & Alloys | Copper, Brass, Bronze | Alloy production, Metalworking |
| Precious Metals | Gold, Platinum, Palladium | Jewelry, High-purity applications |
Ready to find the perfect melting solution for your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including crucible furnaces designed for melting everything from aluminum to precious metals. Our experts can help you select the right system for your specific material and purity requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of high-purity ceramic crucibles in rare earth steel research? Ensure Accurate Data Results
- What is the protective function of high-purity ceramic crucibles? Secure the Chemical Integrity of Your SA508 Alloys
- Why must aluminum alloys be heated in alumina crucibles? Ensure Pure Results in Molten Corrosion Experiments
- Why are Pt-Rh crucibles used for aluminoborosilicate glass? Ensure Maximum Purity at 1450°C
- What is the crucible in an induction furnace? A Passive Container for Direct Metal Melting
- Why are alumina crucibles or baskets essential for Boudouard reaction studies? Ensure Pure Data & Chemical Inertness
- Why are graphite crucibles selected as melting vessels for AlMgZn cross-over alloys? Essential Benefits & Purity Tips
- What is the function of a high-precision precursor crucible in ruthenium CVD? Master Uniform Thin Film Deposition



















