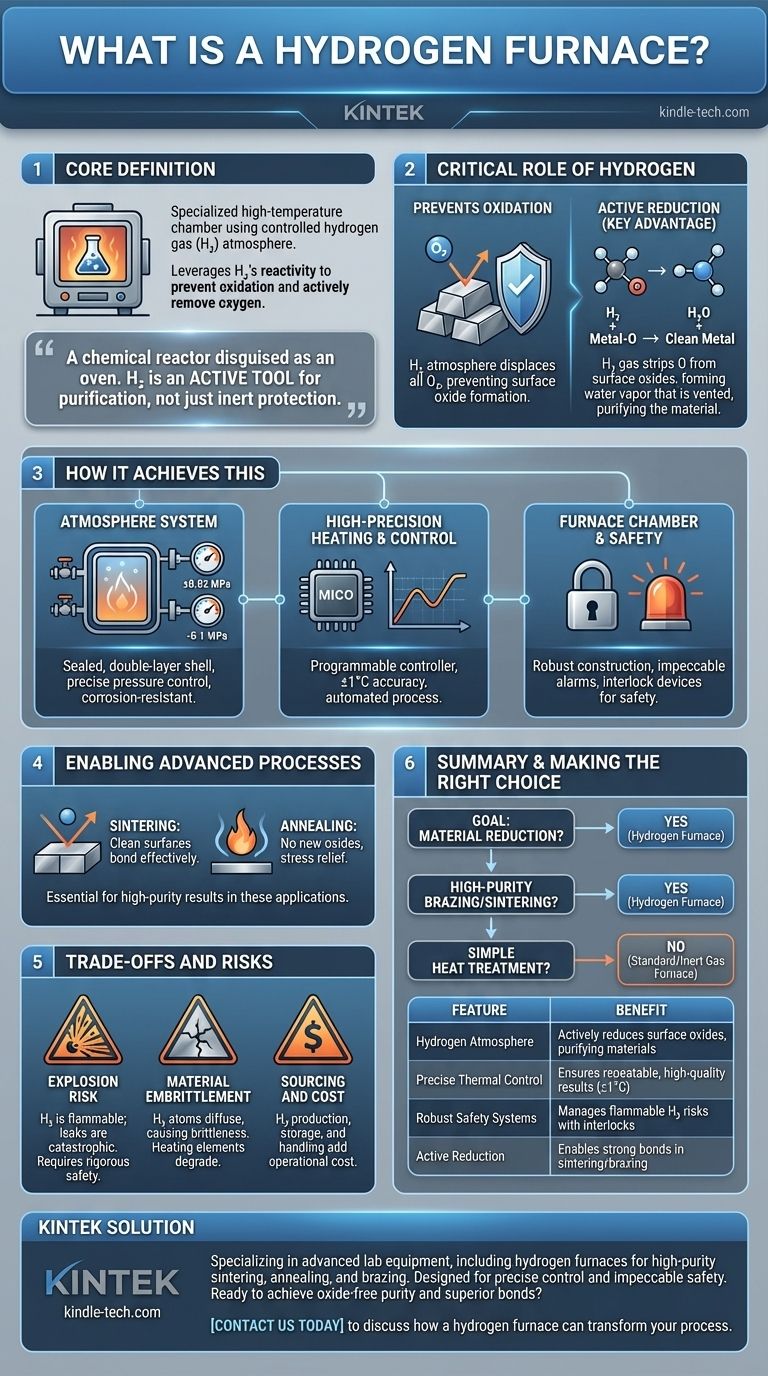
At its core, a hydrogen furnace is a specialized high-temperature chamber that uses a controlled hydrogen gas atmosphere instead of air. Its primary purpose is not just to heat materials, but to leverage the chemical reactivity of hydrogen to prevent oxidation and actively remove oxygen from surfaces, a process known as reduction. This enables unique material processing outcomes that are impossible in a standard furnace.
A hydrogen furnace is fundamentally a chemical reactor disguised as an oven. While other furnaces use inert gases to simply prevent reactions, a hydrogen furnace uses reactive hydrogen gas as an active tool to purify and modify materials at extreme temperatures.

How a Hydrogen Furnace Achieves This
A hydrogen furnace integrates several critical systems to safely manage its reactive environment and achieve precise thermal control. These systems work in concert to create a highly specific processing atmosphere.
The Hydrogen Atmosphere System
The defining feature is the system that manages the hydrogen gas. It consists of a double-layer, sealed furnace shell that can be air- and water-cooled.
This allows the system to maintain a precise internal pressure, either slightly positive (up to 0.02 MPa) to prevent air from leaking in or negative (vacuum pressures up to -0.1 MPa) for purging cycles.
All piping and valves are made from corrosion-resistant stainless steel to ensure a leak-tight seal, which is critical for both safety and process purity.
High-Precision Heating and Control
These furnaces are built for exacting thermal processes. Heating is managed by a programmable controller that can execute complex temperature profiles with extreme precision, often within ±1°C.
An industrial microcomputer automates the entire process, controlling temperature, process time, gas flow rates, and valve actions. This ensures repeatability and minimizes the need for manual intervention in a hazardous environment.
The Furnace Chamber and Safety
The furnace body itself is robustly constructed with a main chamber, cover, and base. The system is equipped with extensive safety features, including impeccable alarm functions and safety interlock devices.
These systems constantly monitor gas pressure, water flow, and temperature, automatically initiating a shutdown or safe state if any parameter deviates from its setpoint.
The Critical Role of Hydrogen
Using hydrogen instead of an inert gas like argon or nitrogen is a deliberate choice for its powerful chemical properties. This is what separates a hydrogen furnace from other atmosphere furnaces.
Preventing Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals will rapidly react with any available oxygen, forming oxides on their surface. A pure hydrogen atmosphere displaces all oxygen, completely preventing this from occurring.
Active Reduction
This is the key advantage. Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent, meaning it actively attracts and bonds with oxygen atoms.
When heated, hydrogen gas (H₂) will strip oxygen atoms from metal oxides on a material's surface, forming water vapor (H₂O) that is then vented from the chamber. This actively cleans and purifies the material.
Enabling Advanced Processes
This reducing environment is essential for processes like sintering and annealing.
In sintering, the perfectly clean surfaces of metal powders bond together more effectively. In annealing, the reduction process ensures no new oxides form as the material's internal stresses are relieved.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The powerful capabilities of a hydrogen furnace come with significant challenges and risks that must be managed. It is not a universally applicable tool.
The Risk of Explosion
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Any leak in the furnace system can create a catastrophic safety hazard.
This is why hydrogen furnaces require specialized facilities, rigorous safety protocols, leak detection systems, and automated interlocks.
Material Embrittlement
While hydrogen purifies many materials, it can also harm them. At high temperatures, small hydrogen atoms can diffuse into the crystal structure of certain metals, a phenomenon called hydrogen embrittlement.
This can make the material brittle and prone to fracture. The heating elements (resistors) themselves can become brittle over time, reducing their service life.
Sourcing and Cost
Hydrogen is more difficult and expensive to produce, store, and handle in the required high-purity grades compared to inert gases like nitrogen or argon. This adds significant operational complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding to use a hydrogen furnace depends entirely on whether your material processing goal is purely thermal or also chemical.
- If your primary focus is material reduction: A hydrogen furnace is the correct tool, specifically designed for processes like converting metal oxides back into pure metals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity brazing or sintering: A hydrogen furnace is ideal for creating perfectly clean, oxide-free surfaces that result in the strongest possible bonds.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment without surface chemistry concerns: A standard air furnace or an inert gas furnace is a much safer, simpler, and more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, a hydrogen furnace should be chosen when the chemical benefits of its reducing atmosphere are essential to achieving your final material properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Atmosphere | Creates a reactive, oxygen-free environment | Actively reduces surface oxides, purifying materials |
| Precise Thermal Control | Executes complex temperature profiles (±1°C) | Ensures repeatable, high-quality results |
| Robust Safety Systems | Monitors gas, pressure, and temperature with interlocks | Manages the risks of using flammable hydrogen gas |
| Active Reduction | Hydrogen strips oxygen, forming water vapor | Enables strong bonds in sintering and brazing |
Ready to achieve oxide-free purity and superior material bonds?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including hydrogen furnaces for high-purity sintering, annealing, and brazing. Our solutions are designed for laboratories that demand precise atmosphere control and impeccable safety.
Contact us today to discuss how a hydrogen furnace can transform your material processing and meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an inert oven? A Guide to Oxidation-Free Thermal Processing
- How does a hydrogen furnace work? Master High-Purity, Oxide-Free Heat Treatment
- What role does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace play in Al0.5CoCrFeNi HEAs? Optimize Phase & Microstructure
- What role do high-vacuum or atmosphere furnaces play in the annealing of metals? Enhance Material Performance & Purity
- What is protective atmosphere heat treatment? Prevent Oxidation and Decarburization for Superior Metal Parts
- How does a high-temperature annealing furnace influence the performance of Pt3Mn catalysts? Master Atomic Order
- What are the typical air-to-gas ratios for endothermic generators? Optimize Natural Gas and Propane Settings
- What role does a high-purity argon gas blanket play in high-temperature corrosion testing? Ensure Precise Data Accuracy



















