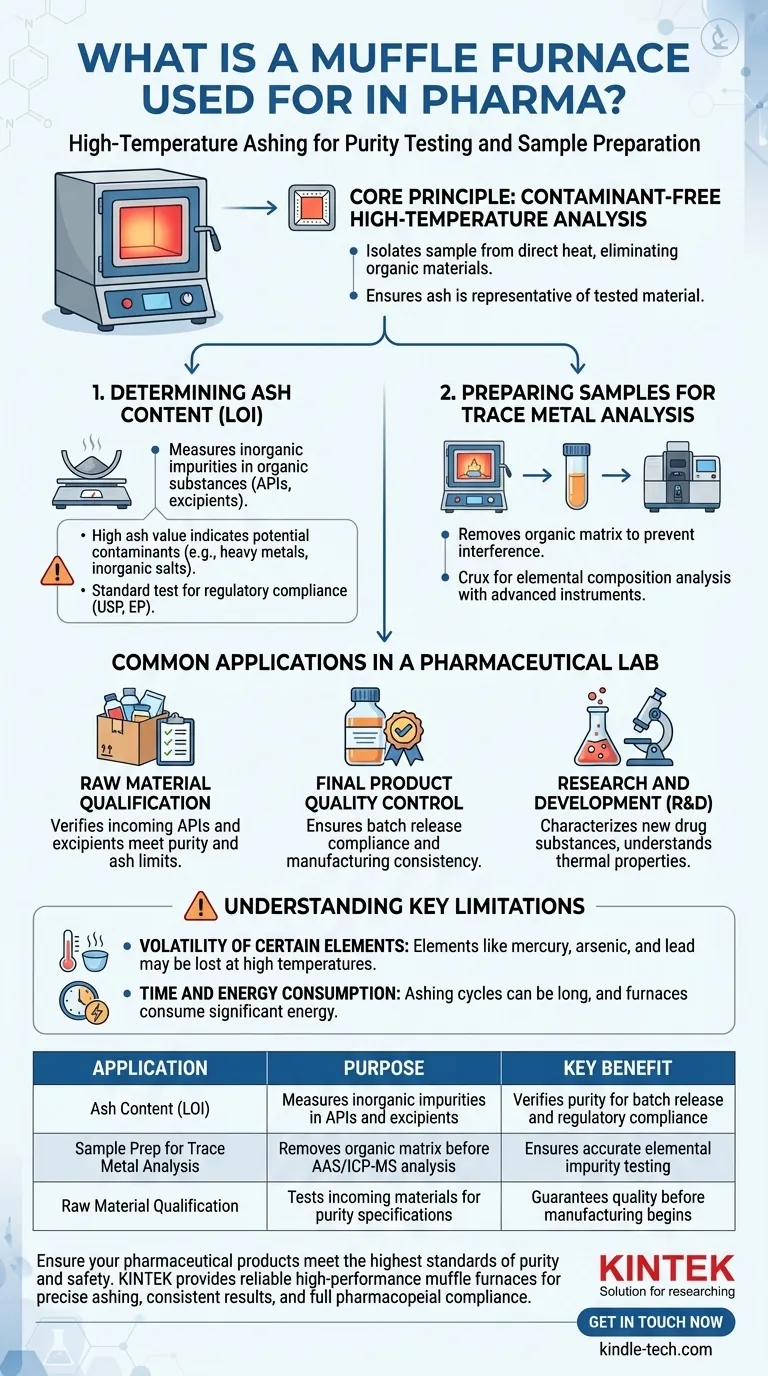
In the pharmaceutical industry, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for critical quality control and sample preparation tasks. Its primary function is to perform ashing, a process that involves heating a sample to extreme temperatures to burn off all organic and volatile materials. This procedure leaves behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue, which is essential for testing the purity and composition of pharmaceutical ingredients and finished products.
The core challenge in pharmaceuticals is verifying the absolute purity of a substance. A muffle furnace is the definitive tool for one of the most fundamental purity tests: measuring the inorganic residue (ash) to confirm a sample meets the strict quality and regulatory standards mandated by pharmacopeias.

The Core Principle: Why High-Temperature Analysis is Critical
A muffle furnace provides a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment, which is fundamental to several key analytical processes in a pharmaceutical laboratory.
Determining Ash Content (Loss on Ignition)
The most common application is determining the ash content of a sample, a procedure often referred to as Loss on Ignition (LOI). This test measures the amount of inorganic impurities in an organic substance, such as an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) or an excipient.
A high ash value can indicate the presence of contaminants like heavy metals or inorganic salts, which could compromise the drug's safety and efficacy. This is a standard test required by regulatory bodies and detailed in official pharmacopeias (e.g., USP, EP).
Preparing Samples for Trace Metal Analysis
Before a sample can be analyzed for specific trace metals using advanced instruments like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP-MS), the organic "matrix" of the drug must be removed.
The muffle furnace is used to completely digest or ash the sample, eliminating the organic compounds that would otherwise interfere with the analysis. This leaves a clean, inorganic residue that can be dissolved and accurately measured for its elemental composition.
Ensuring a Contaminant-Free Process
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's design. The sample is placed inside a separate ceramic chamber, or muffle, which is heated externally.
This design is crucial because it isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements. This prevents any potential contamination from the furnace itself, ensuring that the resulting ash is representative of only the material being tested.
Common Applications in a Pharmaceutical Lab
The muffle furnace is a workhorse instrument used across the pharmaceutical product lifecycle.
Raw Material Qualification
Before raw materials are accepted into a manufacturing facility, they undergo rigorous testing. The muffle furnace is used to verify that incoming APIs and excipients meet their specified purity and ash content limits.
Final Product Quality Control
As part of batch release testing, the final drug product is tested to ensure it meets all quality specifications. Ash content is a critical parameter that confirms the purity and consistency of the manufacturing process.
Research and Development (R&D)
In R&D, scientists use muffle furnaces to characterize new drug substances and formulations. The furnace helps in understanding the thermal properties of materials and in preparing samples for detailed compositional analysis.
Understanding the Key Limitations
While essential, a muffle furnace is not without its limitations, which a technical expert must consider.
Volatility of Certain Elements
The high temperatures used in ashing (often 500-1000°C) can cause certain inorganic compounds to volatilize and be lost. Elements like mercury, arsenic, and lead, as well as some halides and sulfides, can be partially or fully driven off, leading to an underestimation of the total inorganic content if not handled with a specific protocol.
Time and Energy Consumption
Ashing procedures are not rapid. A typical cycle of heating, holding at temperature, and cooling can take several hours to complete. This, combined with the high temperatures, makes muffle furnaces significant consumers of energy.
Not a Standalone Analytical Tool
A muffle furnace performs a bulk measurement (total ash) or a preparatory step. It does not identify the specific elements within the ash. For that, it must be used in conjunction with more sophisticated analytical instruments like ICP-MS or AAS.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The specific use of a muffle furnace depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Use the furnace to perform the sulfated ash or loss on ignition tests exactly as described in the relevant pharmacopeial monograph for batch release.
- If your primary focus is elemental impurity analysis: Use the furnace as the first step to digest the organic sample matrix before dissolving the residue for analysis with an instrument like an ICP-MS.
- If your primary focus is research and material science: Use the furnace to investigate the thermal stability of new compounds or to synthesize novel inorganic materials in a controlled, high-temperature environment.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a gatekeeper of purity, providing the unambiguous data required to ensure pharmaceutical safety, quality, and efficacy.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ash Content (LOI) | Measures inorganic impurities in APIs and excipients | Verifies purity for batch release and regulatory compliance |
| Sample Prep for Trace Metal Analysis | Removes organic matrix before AAS/ICP-MS analysis | Ensures accurate elemental impurity testing |
| Raw Material Qualification | Tests incoming materials for purity specifications | Guarantees quality before manufacturing begins |
Ensure your pharmaceutical products meet the highest standards of purity and safety.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including high-performance muffle furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of pharmaceutical quality control. Our solutions help you achieve precise ashing, consistent results, and full compliance with pharmacopeial methods.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace for your lab's needs. Let KINTEK be your partner in quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the operation temperature of the muffle furnace? A Guide to Internal and Ambient Ranges
- What is the use of muffle furnace in laboratory? Essential for High-Temp Analysis & Materials Processing
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- What is a natural sintering? Uncover the Geological Process That Forms Ore Deposits
- What is the high temperature of a muffle furnace? From 1100°C to 1700°C+ for Your Lab Needs



















