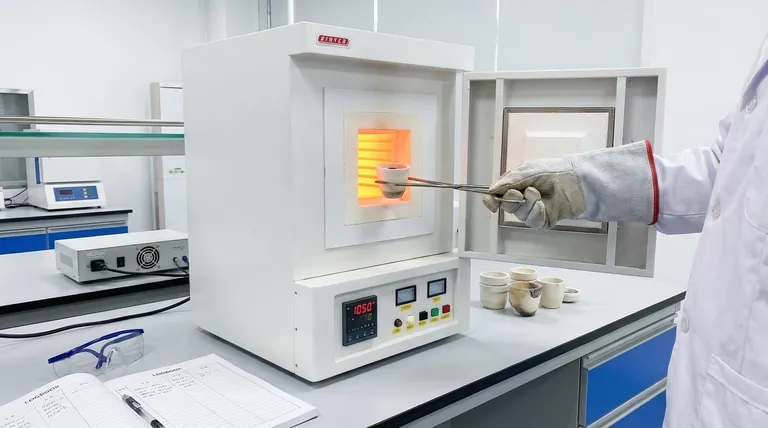
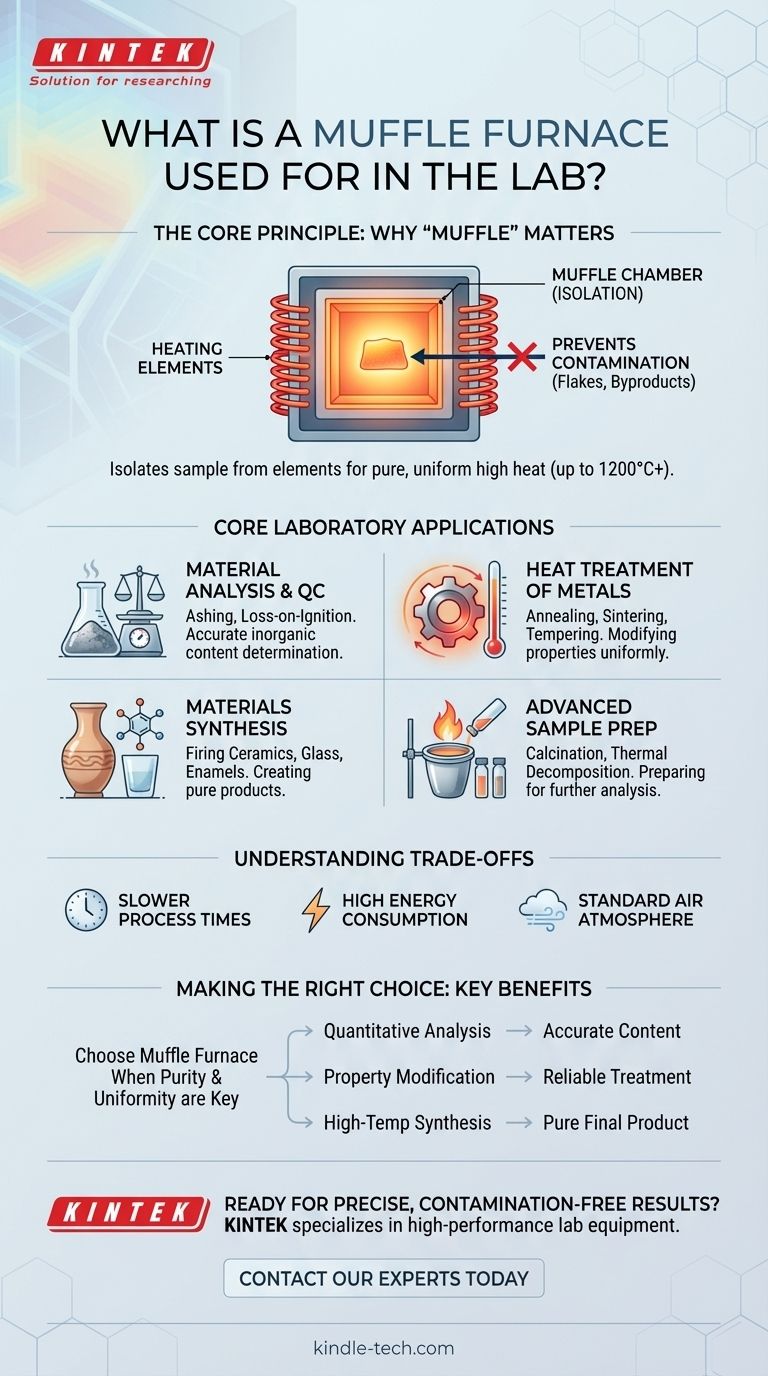
In a laboratory setting, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for processes that demand a precisely controlled, contamination-free environment. Its applications range from determining the ash content of a sample and heat-treating metals to sintering advanced ceramics and conducting materials research at temperatures often exceeding 1000°C.
The core value of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to do so without contaminating the sample. The internal chamber, or "muffle," isolates the material from the heating elements, ensuring the heat applied is pure and the results are untainted.

The Principle: Why "Muffle" Matters
The defining feature of this furnace is the "muffle" itself—an insulating chamber that physically separates the sample from the heating elements and any potential contaminants. This design principle is what makes it indispensable for specific scientific and industrial tasks.
The Purpose of Isolation
The muffle is typically made of a high-temperature ceramic material. It shields the sample from direct contact with the electric heating elements, preventing any flakes or impurities from the elements from falling into the material.
Preventing Chemical Contamination
Unlike heating with a direct flame, a muffle furnace uses radiant electrical heat. This eliminates the introduction of combustion byproducts, ensuring that any changes observed in the sample are due solely to the effects of temperature.
Achieving Uniform, High Temperatures
These furnaces are engineered to provide extremely uniform and stable temperatures, often up to 1200°C and beyond. This precision is critical for heat-treating metals or performing quantitative chemical analyses where temperature consistency directly impacts the outcome.
Core Laboratory Applications
A muffle furnace is not a general-purpose oven. It is a specialized tool selected for tasks that require its unique combination of high heat and a clean environment.
Material Analysis and Quality Control
This is one of the most common uses. The furnace is used to determine the non-combustible or non-volatile content of a material through processes like ashing and loss-on-ignition. It is essential for quality control in fields from environmental analysis to drug inspections.
Heat Treatment of Metals and Alloys
In metallurgy, a muffle furnace provides the controlled thermal environment needed to alter the physical properties of metals. Key processes include annealing (softening), quenching (hardening), tempering (reducing brittleness), and sintering powdered metals into a solid mass.
Synthesis of Ceramics, Glass, and Enamels
The creation of advanced ceramics, technical glass, and enamel coatings requires high-temperature firing in a clean environment to achieve the desired molecular structure and physical properties. The furnace provides the ideal conditions for these delicate processes.
Advanced Sample Preparation
Muffle furnaces are used for the thermal decomposition or pretreatment of various samples. This includes calcination to remove water and carbon dioxide, ashing medical samples for analysis, and preparing samples for water quality or environmental testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not always the right tool. Understanding its operational limitations is key to using it effectively.
Slower Process Times
The insulated muffle that protects the sample also means the furnace has significant thermal mass. It takes a considerable amount of time to heat up to the target temperature and even longer to cool down, making it unsuitable for rapid-cycle processes.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or more requires a substantial amount of electrical energy. This makes it a more expensive tool to operate compared to lower-temperature ovens.
Standard Atmosphere is Air
A basic muffle furnace operates in a normal air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert or specific gas environment to prevent oxidation, a more specialized and expensive vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select this tool when the purity of the heating environment is as important as the temperature itself.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: A muffle furnace is the standard instrument for accurately determining the ash or inorganic content of a sample.
- If your primary focus is modifying the properties of metals or ceramics: The furnace's uniform, high-temperature environment is essential for reliable annealing, sintering, and hardening.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material synthesis: Its contamination-free chamber ensures the purity of the final product, from special alloys to technical glass.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize a controlled and uncontaminated environment for high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Application | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition | Accurate determination of inorganic content |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Tempering, Sintering | Alters metal/ceramic properties uniformly |
| Materials Synthesis | Firing ceramics, glass, enamels | Creates pure products in a clean environment |
| Sample Preparation | Calcination, Thermal Decomposition | Prepares samples for further analysis |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free results in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including reliable muffle furnaces designed for critical applications like ashing, heat treatment, and materials synthesis. Our solutions ensure the uniform high temperatures and clean environment your research demands.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature setting of a muffle furnace? Select the Right Model for Your Process
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the condition of a muffle furnace? Ensuring Clean, Controlled Heat for Your Lab
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- Can a muffle furnace be used for pyrolysis? How to adapt it for oxygen-free thermal decomposition



















