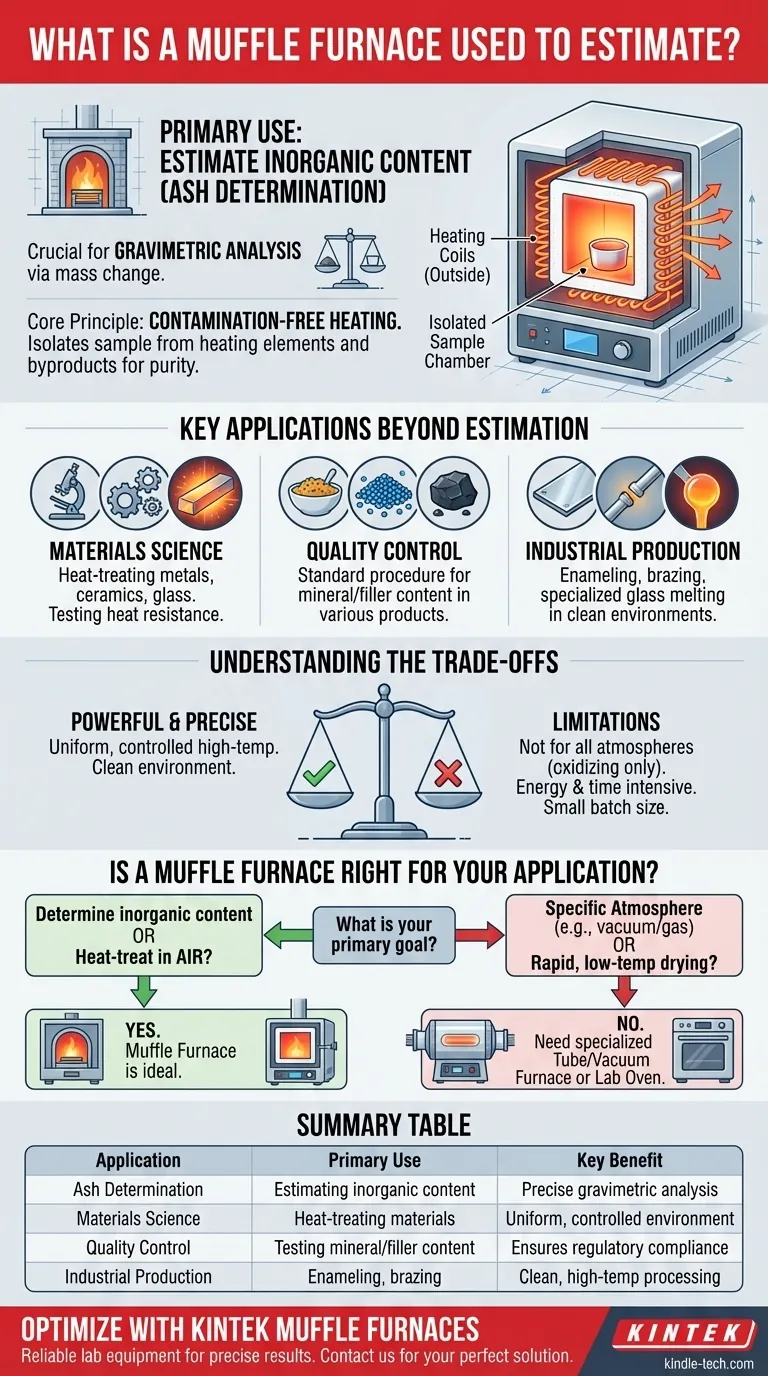
In a laboratory setting, a muffle furnace is primarily used to estimate the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample. This process, known as ashing or ash determination, is a critical function in gravimetric analysis, where changes in mass are used to precisely quantify a material's composition. The furnace burns away all organic matter at high temperatures, leaving only the inorganic ash behind for weighing and analysis.
While a muffle furnace is a key tool for estimation, its fundamental purpose is much broader. It is designed to provide a highly controlled, high-temperature environment that is completely isolated from heating elements and combustion byproducts, ensuring the purity of the sample being processed. This principle of clean heating makes it an indispensable tool for analyzing and treating materials.
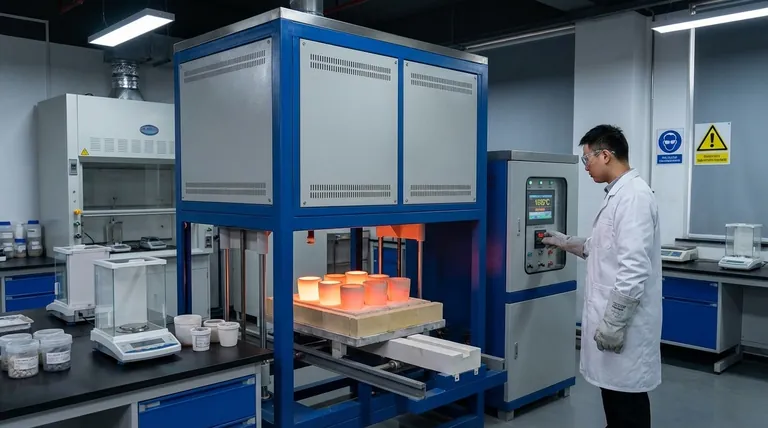

The Core Principle: Contamination-Free Heating
At its heart, a muffle furnace solves one critical problem: how to heat a material to very high temperatures without contaminating it.
What "Muffle" Means
The term "muffle" refers to the core design feature—a separated chamber that encloses the material being heated.
This chamber isolates the sample from the actual heat source and any byproducts of combustion. In historical furnaces, this meant keeping smoke and fly ash away from the sample.
Modern Electric Design
Today, most muffle furnaces are electric. High-temperature heating coils surround the muffle chamber, heating it through radiation and convection.
The chamber itself is made of high-purity insulating material, which prevents heat from escaping and, crucially, stops the heating elements from directly interacting with or contaminating the sample.
Key Applications Beyond Estimation
The ability to provide pure, uniform, and precise heat makes the muffle furnace a universal tool in both scientific and industrial settings.
Materials Science and Research
Scientists use muffle furnaces to develop and test new materials. This includes creating technical ceramics, testing the heat resistance of alloys, or performing heat-treatment processes like annealing and tempering to alter a metal's physical properties.
Quality Control and Testing
Ashing is a standard quality control procedure in many industries. For example, it is used to determine the mineral content in food, the filler content in plastics, or the non-combustible material in coal. This data is vital for ensuring a product meets regulatory or manufacturing specifications.
Industrial Production
On a larger scale, muffle furnaces are used for manufacturing processes that require clean, high-temperature environments. This includes creating durable enamel coatings, brazing or soldering complex components, and melting glass for specialized applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized piece of equipment with specific limitations that are important to understand.
Not for All Atmospheres
A standard muffle furnace operates by heating the sample in the presence of air (an oxidizing atmosphere). This is ideal for ashing but unsuitable for materials that would be damaged by oxygen at high temperatures.
Processes requiring a vacuum or a specific inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) need a more specialized tube furnace or vacuum furnace.
Energy Consumption and Heat-Up Time
Reaching temperatures of 1000°C or higher requires a significant amount of energy. While modern units are designed for efficiency, they are power-intensive devices.
They also require time to safely heat up to the target temperature and, just as importantly, to cool down. This cycle time must be factored into any laboratory or production workflow.
Sample Volume Limitations
Muffle furnaces are generally designed for batch processing of relatively small samples. They are not suitable for continuous-flow operations or for processing very large volumes of material, which would require a different type of industrial oven or kiln.
Is a Muffle Furnace Right for Your Application?
To determine if this tool fits your goal, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is determining inorganic content: A muffle furnace is the standard and essential tool for ashing samples as part of gravimetric analysis.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating materials in air: It is an ideal choice for altering the properties of metals, ceramics, or glass due to its uniform and precisely controlled high-temperature environment.
- If your primary focus requires a specific atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or vacuum): A standard muffle furnace is insufficient; you must investigate a specialized tube or vacuum furnace designed for atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-temperature drying: A muffle furnace is overkill; a simple laboratory oven is a more efficient and appropriate tool for this task.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace provides the precise and pure high-temperature environment required for revealing the fundamental properties of a material.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ash Determination | Estimating inorganic content in samples | Precise gravimetric analysis via mass change |
| Materials Science | Heat-treating metals, ceramics, and glass | Uniform, controlled high-temperature environment |
| Quality Control | Testing mineral content in food, plastics, coal | Ensures product meets regulatory specifications |
| Industrial Production | Enameling, brazing, glass melting | Clean, high-temperature processing without contamination |
Optimize your lab's analytical capabilities with KINTEK's muffle furnaces. Whether you're performing precise ash determination, heat-treating materials, or ensuring quality control, our equipment delivers the contamination-free, high-temperature environment you need for accurate results. Serving laboratories in research, quality control, and industrial production, KINTEK specializes in reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your needs. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your application and enhance your analytical workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve High-Temperature Processing with Purity
- What is the difference between sintering and firing? A Guide to Thermal Process Terminology
- What is the difference between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What is the difference between sintering and vitrification? Key Thermal Process Distinctions
- What are the advantages and limitations of heat treatment? Tailor Material Properties for Peak Performance



















