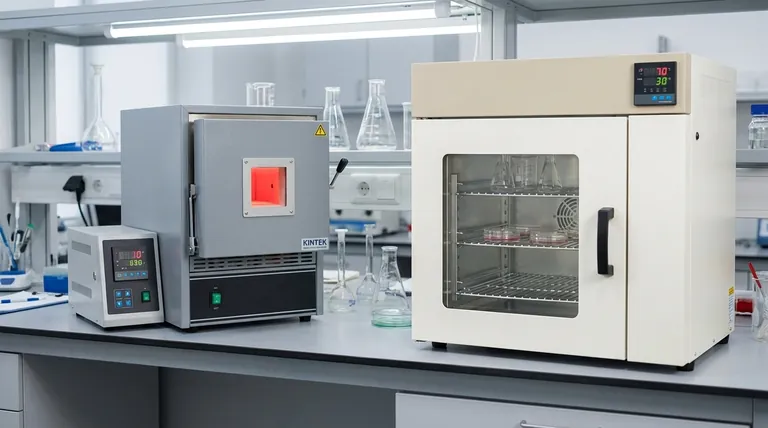
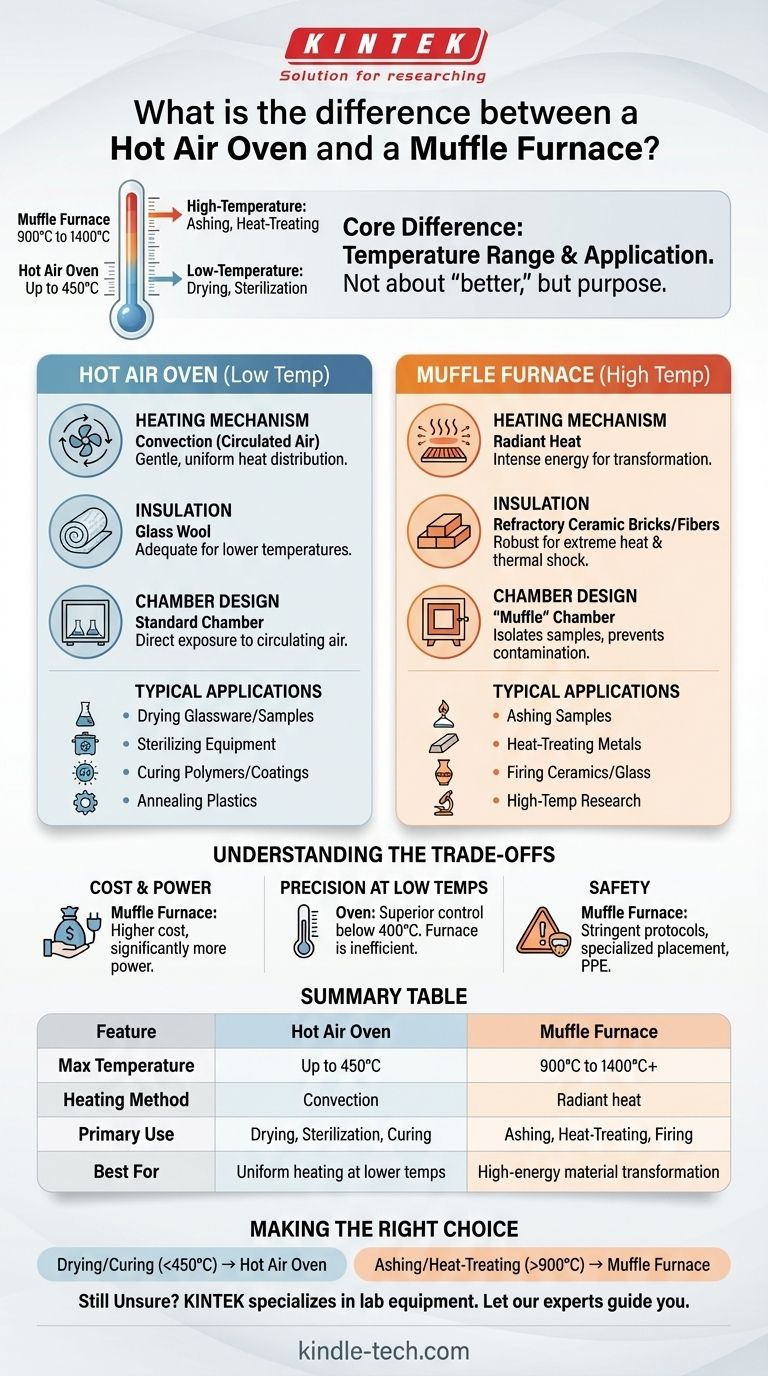
At its core, the difference between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace is their operational temperature range and the applications this enables. A hot air oven is a low-temperature device, typically operating up to 450°C, designed for tasks like drying and sterilization. A muffle furnace is a high-temperature system, reaching 900°C to 1400°C, used for processes like ashing and heat-treating metals.
The choice between an oven and a furnace is not about which is "better," but which is designed for the specific thermal process you need to perform. Ovens use circulated air for gentle, uniform heating, while furnaces use intense radiant heat for material transformation.

Beyond Temperature: Core Design Differences
While the temperature gap is the most obvious distinction, it is a direct result of fundamental differences in how these two instruments are designed and how they transfer heat.
Heating Mechanism: Convection vs. Radiation
A hot air oven works primarily through convection. A fan circulates air past a heating element and throughout the chamber, ensuring a gentle and highly uniform temperature distribution. This is ideal for processes that require consistent heat across the entire surface of a sample.
A muffle furnace, by contrast, relies on intense radiant heat. Its heating elements surround an insulating chamber (the "muffle"), which radiates heat at extremely high temperatures onto the sample. This method is designed for delivering the raw energy needed to alter a material's chemical or physical state.
Insulation and Construction
The materials used reflect the vast difference in heat. An oven is typically insulated with materials like glass wool, which is perfectly adequate for its temperature range.
A furnace requires far more robust insulation to contain extreme temperatures safely and efficiently. It is constructed with heavy-duty refractory ceramic bricks and fibers capable of withstanding thermal shock and constant high-heat exposure.
Chamber Design: The "Muffle"
The term "muffle" is key. It refers to the inner chamber of the furnace, which isolates the samples from the heating elements. This separation prevents contamination, for instance from combustion byproducts, which is critical in analytical processes like determining the ash content of a sample.
Choosing the Right Tool: Ovens vs. Furnaces in Practice
Understanding the design differences makes it clear why each tool is suited for very different tasks. Using one for the other's purpose is not only inefficient but often impossible.
Typical Applications for a Hot Air Oven
Ovens are the workhorses for general laboratory and industrial heating where precision and uniformity at lower temperatures are essential. Common uses include:
- Drying glassware or chemical samples
- Sterilizing medical or laboratory equipment
- Curing polymers, coatings, and epoxies
- Annealing plastics to relieve internal stresses
Typical Applications for a Muffle Furnace
Furnaces are specialized tools for high-energy thermal processes that transform materials. Common uses include:
- Ashing samples (burning off all organic matter) to determine inorganic content
- Heat-treating metals to alter their hardness and durability (e.g., hardening, tempering)
- Firing ceramics and melting glass
- Conducting high-temperature materials science research
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument can lead to failed processes, damaged equipment, and significant safety risks.
The Cost of High Heat
A muffle furnace is significantly more expensive to purchase and operate. Its construction is more complex, and its power consumption is dramatically higher than that of an oven to achieve and maintain extreme temperatures.
Precision at Lower Temperatures
You cannot simply "turn down" a furnace for a low-temperature task. Ovens provide far superior temperature control and uniformity below 400°C. Using a furnace for drying glassware would be inefficient, imprecise, and a waste of energy.
Safety and Infrastructure
The safety protocols for a muffle furnace are far more stringent. Due to the extreme external temperatures and potential fumes, they require specialized placement, ventilation, and personal protective equipment (PPE) that are not necessary for a standard hot air oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based entirely on the temperature and type of process your application requires.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing below 450°C: A hot air oven is the correct, most efficient, and most precise tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing, heat-treating metals, or transforming materials above 900°C: A muffle furnace is the only suitable choice to achieve the necessary temperatures.
Ultimately, selecting the right equipment begins with a clear understanding of your specific thermal requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 450°C | 900°C to 1400°C+ |
| Heating Method | Convection (circulated air) | Radiant heat |
| Primary Use | Drying, Sterilization, Curing | Ashing, Heat-Treating, Firing |
| Best For | Uniform heating at lower temps | High-energy material transformation |
Still Unsure Which Equipment You Need?
Selecting the right tool is critical for your lab's efficiency, safety, and results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert advice and high-quality thermal processing solutions.
Let our experts help you make the perfect choice for your specific application. We can guide you to the ideal equipment—whether it's a precise hot air oven for gentle heating or a powerful muffle furnace for high-temperature processes.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure you get the right tool for the job.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of calcination? Unlock Material Transformation for Industrial Processes
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- How do you perform calcination? Master Precise Thermal Treatment for Your Materials
- What is the purpose of a muffle? To Ensure Pure, Contamination-Free Heating in Your Lab
- What is the burning temperature of a furnace? From 200°C to 3000°C, It Depends on Your Needs



















