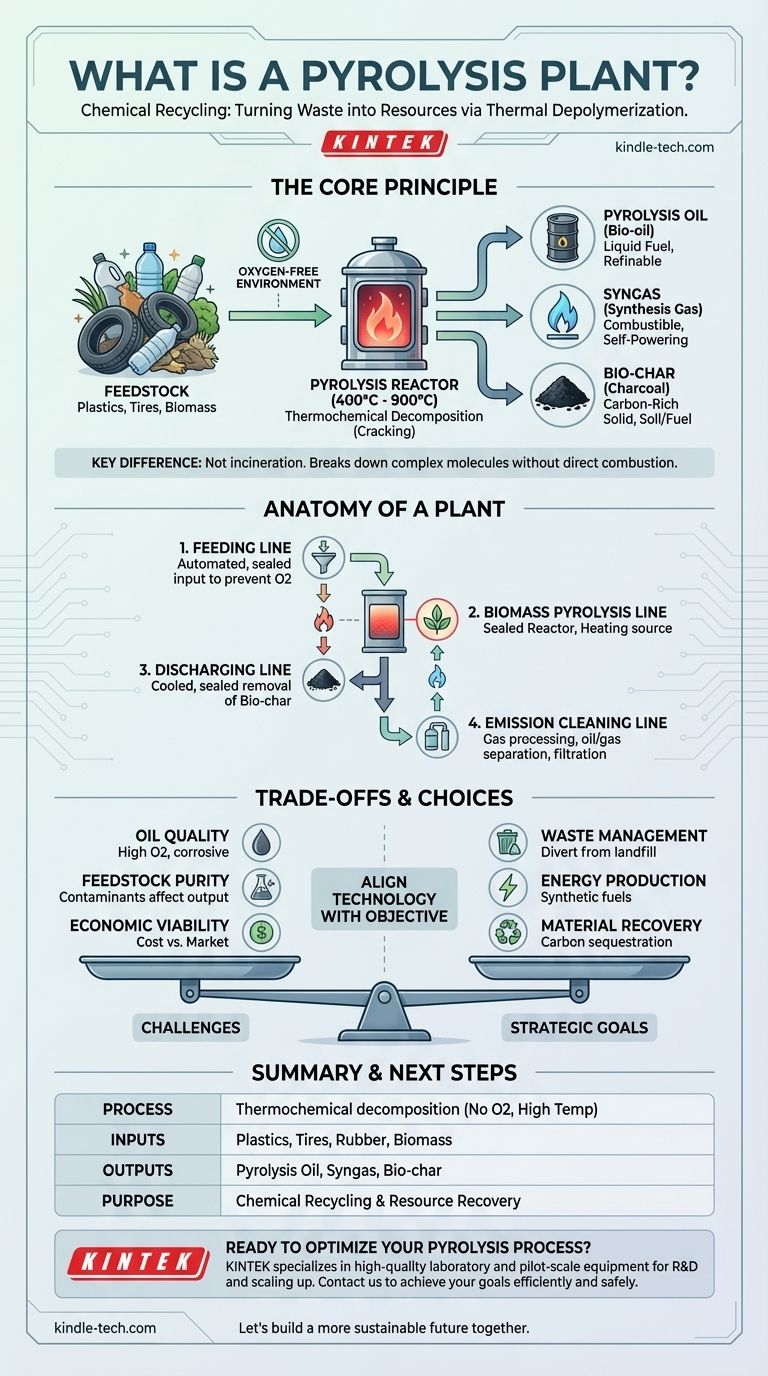
At its core, a pyrolysis plant is a facility designed for chemical recycling. It uses a high-temperature process in an oxygen-free environment to break down complex waste materials—like plastics, tires, or biomass—into simpler, valuable substances such as synthetic oil, gas, and a carbon-rich solid called bio-char. This process, known as thermal depolymerization or 'cracking', transforms waste from a liability into a resource without direct combustion.
The central purpose of a pyrolysis plant is not to burn waste, but to chemically decompose it. It offers a method to reclaim value from materials that are otherwise destined for a landfill, converting them into fuel and other industrial feedstocks.

The Core Principle: How Pyrolysis Works
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition process. Understanding its core components reveals how it differs fundamentally from simple incineration.
The Absence of Oxygen is Key
The entire process occurs within a sealed reactor devoid of oxygen. This is the critical distinction between pyrolysis and burning. Without oxygen, the waste material does not combust; instead, the intense heat breaks the chemical bonds of its large molecules, reforming them into smaller, more stable molecules.
The Reactor and High Temperatures
Feedstock is heated to extreme temperatures, typically between 400°C and 900°C. This heat provides the energy needed to "crack" the complex hydrocarbons found in plastics, rubber, and biomass into simpler, more useful forms. The plant's control systems carefully manage this temperature to optimize the output.
The Key Inputs (Feedstock)
While a plant can be designed for specific inputs, the most common feedstocks are post-consumer waste streams. These include plastics, scrap tires, rubber, wood waste, and other forms of biomass. The composition of the input material directly influences the quality and proportion of the final products.
The Valuable Outputs
The process separates the feedstock into three primary products:
- Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil): A liquid fuel similar in some ways to crude oil, which can be refined for use in engines, boilers, or furnaces.
- Syngas (Synthesis Gas): A mixture of combustible gases. This is often captured and used to power the pyrolysis plant itself, creating a more energy-efficient, self-sustaining operation.
- Bio-char (Charcoal): A stable, solid material rich in carbon. Depending on the feedstock, this can be used as a soil amendment, for filtration (activated carbon), or as a solid fuel.
Anatomy of a Pyrolysis Plant
A typical plant is a sophisticated system composed of several integrated lines to ensure safe, continuous, and efficient operation.
The Feeding Line
This automated system introduces the raw waste material into the sealed pyrolysis reactor. Proper design is crucial to prevent oxygen from entering the system and to handle a consistent flow of feedstock.
The Biomass Pyrolysis Line
This is the heart of the facility, containing the sealed reactor where the material is heated. The design of the reactor varies based on the scale and type of feedstock being processed.
The Discharging Line
Once the reaction is complete, this system safely cools and removes the solid bio-char from the reactor. Advanced systems use sealed cooling conveyors to prevent dust and emissions.
The Emission Cleaning Line
This is a critical environmental and safety component. It processes the hot gases, separating the condensable pyrolysis oil from the non-condensable syngas. It also includes systems to scrub and filter any potential pollutants before any excess gas is safely flared or released.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, pyrolysis technology is not a perfect solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
The Quality of Pyrolysis Oil
The oil produced is not a direct replacement for petroleum products. It often has a high oxygen content, which can make it corrosive, thermally unstable, and immiscible with conventional fossil fuels. This means it frequently requires significant secondary processing and upgrading before it can be used as a high-grade fuel.
Feedstock Purity Matters
The efficiency of the process and the quality of the outputs are highly dependent on the purity and consistency of the feedstock. Contaminants in the waste stream can disrupt the chemical reactions or introduce undesirable elements into the final products, reducing their value.
Economic Viability
The financial success of a pyrolysis plant depends on a delicate balance. Key factors include the cost of acquiring and preparing the feedstock, the plant's operational energy costs, and the fluctuating market prices for the oil, gas, and char it produces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating pyrolysis requires aligning the technology's capabilities with a specific objective.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is an effective method for diverting high-volume waste streams like plastics and tires from landfills, significantly reducing their environmental footprint.
- If your primary focus is energy production: The technology is a viable source of synthetic fuels, but you must account for the necessary costs and infrastructure to upgrade the raw pyrolysis oil into a stable, usable product.
- If your primary focus is material recovery: Bio-char is a valuable product with a growing market in agriculture and industry, representing a way to sequester carbon in a stable, useful form.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis plant represents a sophisticated tool for chemical recycling, turning problematic waste into potential resources when its process and products are properly understood.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermochemical decomposition in an oxygen-free environment (400°C - 900°C) |
| Main Inputs (Feedstock) | Plastics, tires, rubber, biomass, wood waste |
| Primary Outputs | Pyrolysis Oil, Syngas, Bio-char |
| Primary Purpose | Chemical recycling and resource recovery, not incineration |
Ready to turn your waste stream into a revenue stream?
A pyrolysis plant is a significant investment in sustainability and resource recovery. The right equipment is critical to your project's success, from feedstock handling to final product quality.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality laboratory and pilot-scale equipment for testing and optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you are in R&D or scaling up your operation, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve your goals efficiently and safely.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your pyrolysis project from concept to reality. Let's build a more sustainable future together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds














