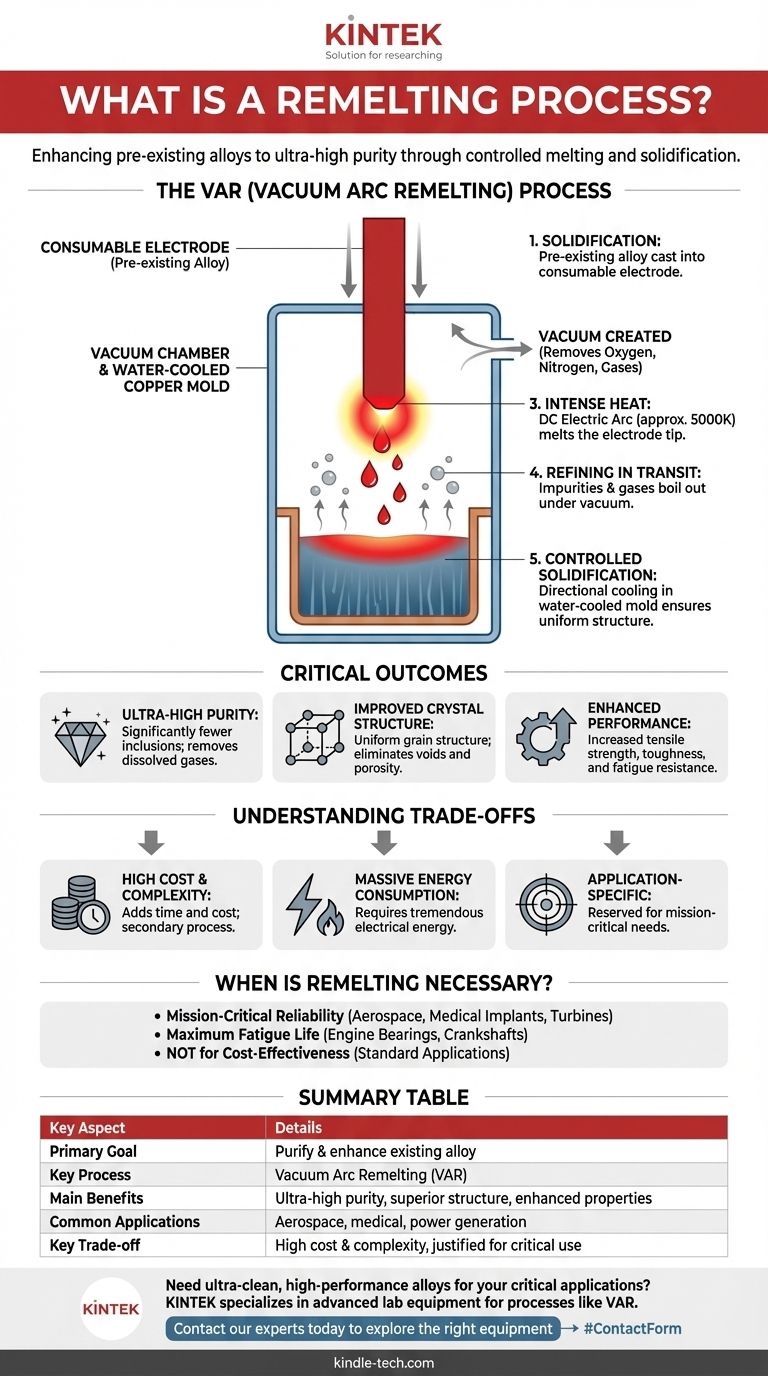
At its core, a remelting process is a secondary metallurgical technique used to purify and enhance a pre-existing metal alloy. Rather than creating a metal from raw ore, it takes a solid, already-formed alloy and melts it again under highly controlled conditions to remove impurities, eliminate defects, and refine its internal crystal structure for superior performance.
The central purpose of remelting is not to create a new material, but to elevate an existing one. By re-melting an alloy in a vacuum, processes like Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) systematically strip away impurities and control solidification to produce an exceptionally clean and robust final product.
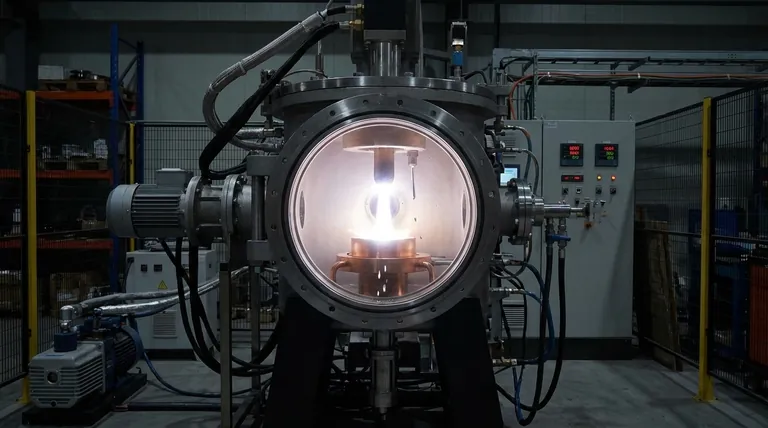
How a Remelting Process Works: The VAR Example
To understand the mechanics, we can analyze the most common method: Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR). This process is a clear illustration of how controlled energy and environment achieve material refinement.
Step 1: The Consumable Electrode
The process begins with the material to be refined, which has been cast into a solid bar or cylinder. This bar is called a consumable electrode, as it will be entirely consumed (melted) during the operation.
Step 2: The Controlled Environment
The electrode is placed inside a sealed, water-cooled copper mold. Crucially, all the air is then pumped out to create a vacuum. This vacuum is essential for removing atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which are common sources of impurities and defects in high-performance alloys.
Step 3: Applying Intense, Focused Heat
A powerful Direct Current (DC) electric arc is struck between the bottom of the electrode and a small amount of starter material in the mold. This arc generates incredibly high temperatures, often approaching 5000K, causing the tip of the electrode to melt rapidly.
Step 4: Refining in Transit
As the electrode melts, droplets of liquid metal detach and fall through the vacuum into the mold below. This brief journey is a critical refining stage. The combination of intense heat and vacuum causes unwanted gaseous impurities and elements with high vapor pressure to boil out of the molten metal, effectively cleaning it in mid-air.
Step 5: Controlled Solidification
The purified molten metal collects in the water-cooled copper mold. The constant cooling from the mold walls causes the metal to solidify in a highly controlled, directional manner. This prevents the random crystallization that can introduce defects and ensures a dense, uniform internal structure in the final ingot.
The Critical Outcomes of Remelting
This carefully controlled process is not merely for show; it produces tangible improvements in the final material that are unattainable with standard melting techniques.
Achieving Ultra-High Purity
The vacuum environment is exceptionally effective at removing dissolved gases like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. This results in an "ultraclean" alloy with significantly fewer non-metallic inclusions, which are often the starting points for material failure.
Improving Crystal Structure
The controlled, directional solidification in the water-cooled mold produces a more uniform and refined grain structure. This eliminates internal voids, porosity, and inconsistencies (segregation) that can weaken the material.
Enhancing Mechanical Performance
The combined effect of high purity and a superior crystal structure is a dramatic enhancement of the alloy's properties. This includes increased tensile strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance, making the material more reliable under extreme stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, remelting processes like VAR are specialized and come with inherent trade-offs.
High Cost and Complexity
VAR is a secondary process performed on an already-made alloy. This adds significant time, complexity, and cost to the manufacturing cycle, making the final material much more expensive.
Massive Energy Consumption
Sustaining a high-temperature electric arc in a vacuum requires a tremendous amount of electrical energy. This contributes to the high operational cost and environmental footprint of the process.
Application-Specific Necessity
This level of refinement is overkill for the vast majority of metal applications. It is reserved for industries where performance and reliability are absolutely non-negotiable, and the high cost can be justified.
When is a Remelting Process Necessary?
Deciding whether to specify a remelted material comes down to the demands of the final application.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical reliability: For aerospace components, medical implants, or power generation turbines where failure could be catastrophic, the enhanced purity and structure are essential.
- If your primary focus is maximum fatigue life: Applications involving cyclical loading, such as engine bearings or high-performance crankshafts, benefit immensely from the removal of micro-impurities that initiate fatigue cracks.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general use: For standard structural, automotive, or consumer product applications, traditional melting methods are perfectly adequate and far more economical.
Ultimately, choosing a remelting process is a strategic decision to invest in material integrity for applications where performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Purify and enhance an existing metal alloy, not create a new one. |
| Key Process | Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) under controlled conditions. |
| Main Benefits | Ultra-high purity, superior crystal structure, enhanced mechanical properties. |
| Common Applications | Aerospace components, medical implants, power generation turbines. |
| Key Trade-off | High cost and complexity, justified for mission-critical applications. |
Need ultra-clean, high-performance alloys for your critical applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced lab equipment and consumables that make processes like Vacuum Arc Remelting possible. Whether you are in R&D or production, our solutions support the creation of materials with superior purity, strength, and reliability.
Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs. Contact our experts today to explore the right equipment for your material science challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What is var in metals? A Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting for Superior Alloys
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity
- What is the VAR melting process? The Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting



















