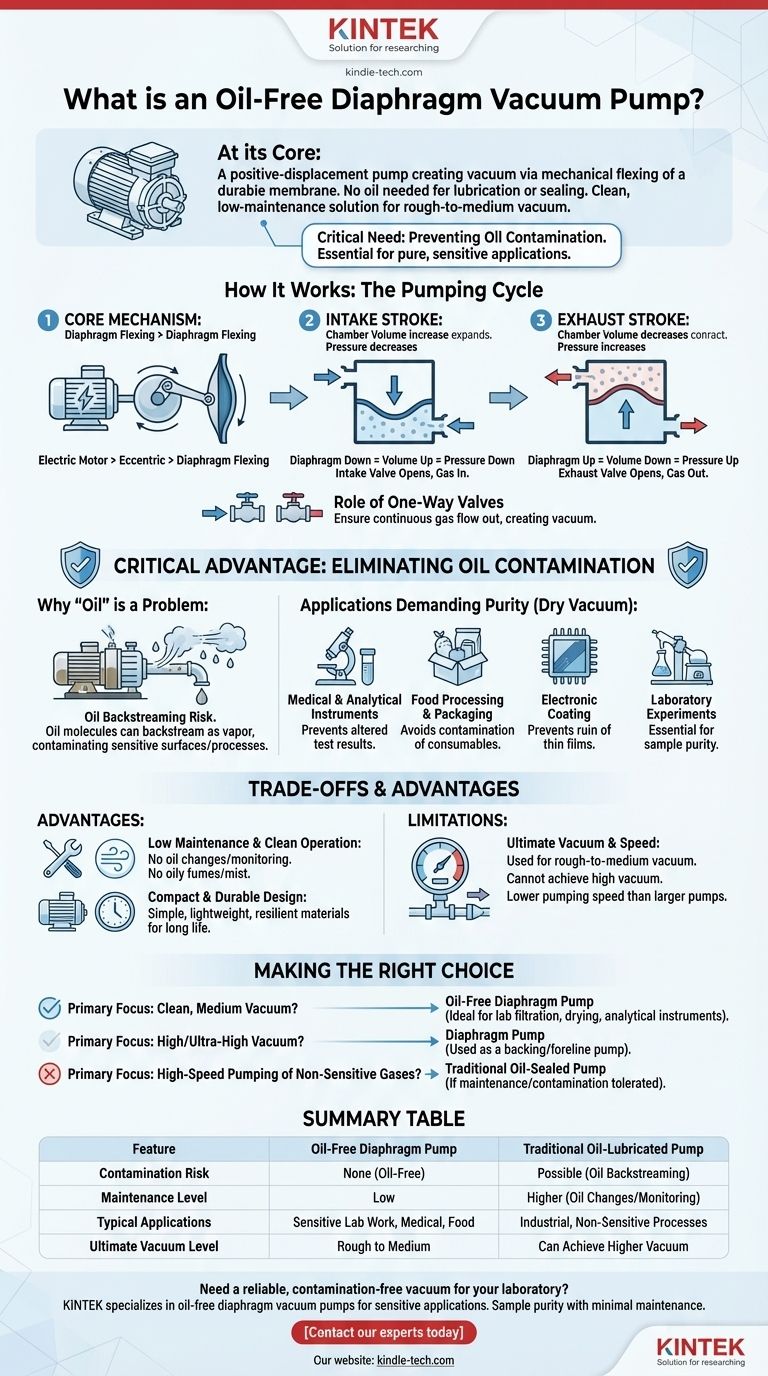
At its core, an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump is a positive-displacement pump that creates a vacuum using the mechanical flexing of a durable, flexible membrane. Unlike many other pump types, it requires no oil for lubrication or sealing. This design choice makes it a clean, low-maintenance solution for generating a rough-to-medium vacuum.
The decision to use an oil-free diaphragm pump is almost always driven by one critical need: preventing oil contamination. It is the go-to choice for sensitive applications where maintaining a pure, oil-free environment is not just a preference, but a requirement.

How a Diaphragm Pump Creates a Vacuum
The pump's operation is based on a simple, reliable mechanical principle that mimics a piston but uses a flexible diaphragm instead.
The Core Mechanism: Diaphragm and Eccentric
An electric motor turns an eccentric shaft. This eccentric is connected to the diaphragm via a connecting rod. As the shaft rotates, it pushes the connecting rod up and down, causing the diaphragm to flex or oscillate within a sealed pump head.
The Pumping Cycle: Intake Stroke
When the diaphragm moves down, the volume of the chamber above it increases. This expansion reduces the pressure inside the chamber, causing the intake valve to open and draw gas in from the connected system.
The Pumping Cycle: Exhaust Stroke
As the eccentric continues its rotation, it pushes the diaphragm up. This action decreases the chamber volume, compressing the trapped gas. The increased pressure forces the exhaust valve to open, expelling the gas from the pump.
The Role of One-Way Valves
This entire process depends on a set of simple one-way valves. The intake valve only allows gas to enter the chamber, and the exhaust valve only allows gas to leave. This coordinated action ensures a continuous flow of gas out of the system, thereby creating a vacuum.
The Critical Advantage: Eliminating Oil Contamination
The term "oil-free" is the most important feature of this pump and the primary reason for its existence.
Why "Oil" is a Problem
Many traditional vacuum pumps, like rotary vane pumps, rely on oil for both lubrication and to create a seal within the pumping mechanism. A significant drawback is that oil molecules can "backstream" into the vacuum system as vapor, contaminating sensitive surfaces or processes.
Applications Demanding Purity
For many scientific and industrial fields, this contamination is unacceptable. An oil-free diaphragm pump ensures a clean vacuum (often called a "dry" vacuum) essential for:
- Medical and Analytical Instruments: Where oil could alter test results.
- Food Processing and Packaging: To prevent contamination of consumables.
- Electronic Coating: Where thin films can be ruined by hydrocarbon deposits.
- Laboratory Experiments: Such as rotary evaporation or vacuum filtration, where sample purity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While eliminating oil is the primary benefit, it's important to understand the full context of a diaphragm pump's capabilities.
Advantage: Low Maintenance and Clean Operation
With no oil to monitor, change, or refill, diaphragm pumps require significantly less maintenance than their oil-sealed counterparts. They also produce no oily fumes or mist, leading to a cleaner work environment and eliminating the need for expensive exhaust filters.
Advantage: Compact and Durable Design
The simple mechanical design often results in a compact and lightweight device. The diaphragms are typically made from highly resilient materials, giving them a long operational life.
Limitation: Ultimate Vacuum and Pumping Speed
Diaphragm pumps are generally used for creating rough to medium vacuums. They cannot achieve the extremely low pressures (high vacuum) of pumps like turbomolecular or diffusion pumps. Their pumping speed, or the volume of gas they can remove per unit of time, may also be lower than larger, oil-sealed industrial pumps.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a vacuum pump requires matching the technology to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is a clean, medium vacuum: An oil-free diaphragm pump is the ideal choice for applications like lab filtration, sample drying, or operating analytical instruments.
- If your primary focus is achieving high or ultra-high vacuum: A diaphragm pump is not sufficient on its own but is often used as a "backing" or "foreline" pump to create the initial rough vacuum for a high-vacuum pump.
- If your primary focus is high-speed pumping of non-sensitive gases: A traditional oil-sealed rotary vane pump might offer higher performance for the cost, as long as you can tolerate the maintenance and potential for oil contamination.
By understanding that its core purpose is to provide a clean vacuum, you can confidently determine if an oil-free diaphragm pump is the right tool for your task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Oil-Free Diaphragm Pump | Traditional Oil-Lubricated Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Contamination Risk | None (Oil-Free) | Possible (Oil Backstreaming) |
| Maintenance Level | Low | Higher (Oil Changes/Monitoring) |
| Typical Applications | Sensitive Lab Work, Medical, Food Processing | Industrial, Non-Sensitive Processes |
| Ultimate Vacuum Level | Rough to Medium | Can Achieve Higher Vacuum |
Need a reliable, contamination-free vacuum for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps designed for sensitive applications like filtration, evaporation, and analytical instrumentation. Our pumps ensure sample purity with minimal maintenance. Contact our experts today to find the perfect vacuum solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the working of oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps differ from conventional pumps? A Guide to Clean vs. Deep Vacuum
- How should an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump be maintained? A Proactive Guide to Maximize Pump Lifespan
- What is the main characteristic of oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps? Guaranteeing a Contamination-Free Vacuum
- What are the advantages of using oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps? Achieve Clean, Low-Maintenance Vacuum
- What factors should be considered when selecting an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump? A Guide to Optimal Performance & Longevity



















