In short, calcination is a high-temperature heating process used to transform or purify solid materials. It is always conducted below the material's melting point and in an environment with little to no available air, which forces the material to thermally decompose and release volatile substances like water or carbon dioxide.
The essential purpose of calcination is not merely to heat something, but to use controlled heat to strip away specific unwanted components, fundamentally changing the chemical or physical structure of a solid without melting it.

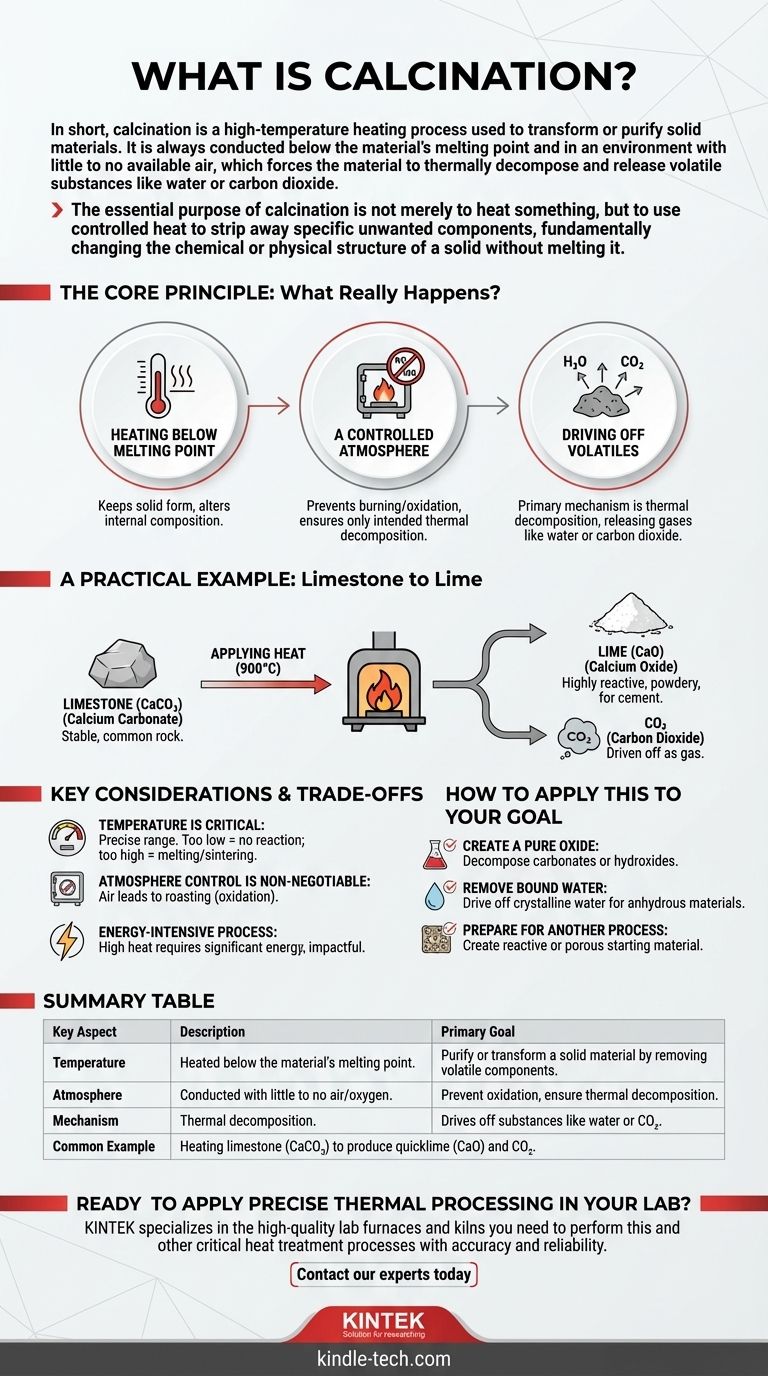
The Core Principle: What Really Happens During Calcination?
To understand calcination, it’s crucial to look beyond the simple act of heating. The process is defined by three specific conditions that work together to achieve a precise outcome.
Heating Below the Melting Point
The goal is to induce chemical or physical changes within the solid material itself. By keeping the temperature below its melting point, the material's overall solid form is maintained while its internal composition is altered.
A Controlled Atmosphere
Calcination is performed in the absence or a very limited supply of air (oxygen). This is a critical distinction. It prevents the material from burning or oxidizing, ensuring that the only reaction taking place is the intended thermal decomposition.
Driving Off Volatiles
The primary mechanism is thermal decomposition. The applied heat provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds, forcing the material to release volatile fractions. These are typically substances that can become a gas, such as water (H₂O) or carbon dioxide (CO₂).
A Practical Example: From Limestone to Lime
The most common and easily understood example of calcination is its role in producing lime for the cement industry.
The Starting Material: Limestone
The process begins with limestone, which is chemically known as calcium carbonate (CaCO₃). It is a stable, common rock.
The Process: Applying Heat
The limestone is heated in a large kiln to temperatures around 900°C (1650°F). This high heat breaks down the calcium carbonate.
The End Products: Lime and CO₂
The calcination process drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂) as a gas, leaving behind a highly reactive, powdery substance known as calcium oxide (CaO), or quicklime. This resulting lime is a fundamental ingredient in cement and other industrial applications.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
While powerful, calcination is a process that requires precision. Misunderstanding its core requirements can lead to failed or inefficient outcomes.
Temperature is Critical
The process operates within a specific temperature window. If the temperature is too low, the decomposition reaction will not occur. If it's too high, the material could melt or sinter (fuse into a solid mass), which may be undesirable for the final application.
Atmosphere Control is Non-Negotiable
Allowing uncontrolled air into the kiln would change the process entirely. For example, heating a metal sulfide in the presence of air is called roasting, an oxidation process with a completely different outcome from calcination.
It's an Energy-Intensive Process
Heating vast quantities of material to such high temperatures requires a significant amount of energy. This makes calcination a costly and environmentally impactful step in any industrial workflow.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding when and why to use calcination is key to leveraging it effectively in materials science, chemistry, and engineering.
- If your primary focus is creating a pure oxide: Calcination is the definitive method for decomposing carbonates (like limestone) or hydroxides to produce their corresponding oxides.
- If your primary focus is removing bound water: The process is used to drive off crystalline water from hydrated minerals, creating an anhydrous (water-free) version of the material.
- If your primary focus is preparing a material for another process: Calcination is often a crucial preparatory step to create a more reactive or porous starting material for subsequent chemical reactions.
Ultimately, calcination is a precise industrial tool for using controlled heat to fundamentally purify and transform solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Purify or transform a solid material by removing volatile components. |
| Temperature | Heated below the material's melting point. |
| Atmosphere | Conducted with little to no air/oxygen to prevent oxidation. |
| Mechanism | Thermal decomposition drives off substances like water or CO₂. |
| Common Example | Heating limestone (CaCO₃) to produce quicklime (CaO) and CO₂. |
Ready to apply precise thermal processing in your lab?
Calcination is a fundamental step for creating pure oxides, removing water, and preparing reactive materials. KINTEK specializes in the high-quality lab furnaces and kilns you need to perform this and other critical heat treatment processes with accuracy and reliability.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect calcination solution for your laboratory's specific materials and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is microwave pyrolysis? Unlock Faster, More Efficient Waste-to-Value Conversion
- What role does a high-temperature rotary kiln play in the production of cement clinker? Mastering Sintering Efficiency
- What is the composition of wood pyrolysis gas? A Guide to Syngas Production & Control
- What is biochar processing? Mastering Slow Pyrolysis for Soil Enhancement & Carbon Sequestration
- Why is the rotary kiln inclined? To Control Material Flow and Reaction Time
- What are the products of catalytic pyrolysis? Unlock High-Value Biofuels & Chemicals
- What are the conditions for calcination reactions? Mastering Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What is the production of biochar through pyrolysis? Optimize for Soil Health & Carbon Sequestration



















