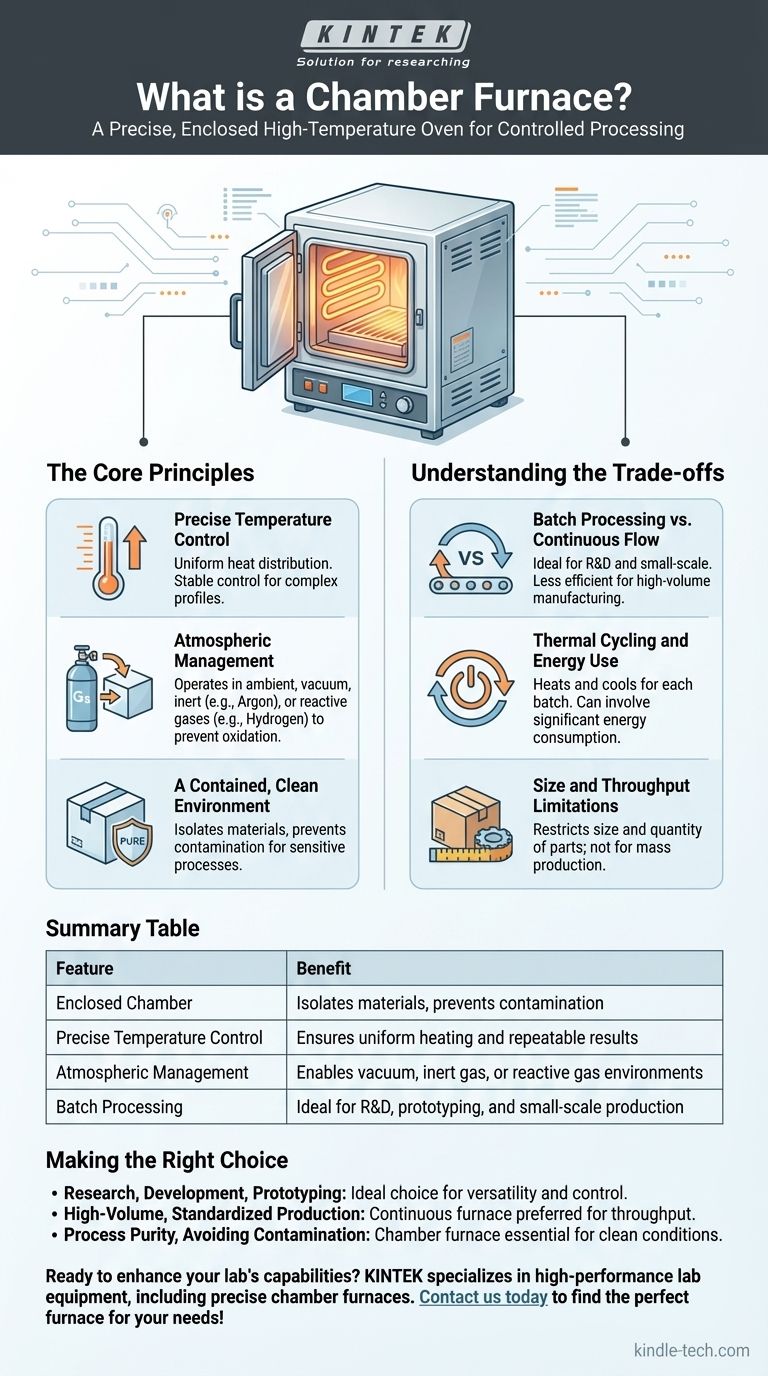
In essence, a chamber furnace is a high-temperature oven with a fully enclosed, box-shaped chamber designed for processing materials in a tightly controlled environment. Often called a "box furnace," its primary function is to execute precise thermal processes like annealing, sintering, or heat treatment by managing temperature and atmospheric conditions with high uniformity and stability.
A chamber furnace's true value is not just its ability to generate heat, but its power to create a pure, contained, and highly repeatable processing environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for research, development, and small-scale manufacturing where material quality and process integrity are paramount.

The Core Principles of a Chamber Furnace
A chamber furnace operates on a few key principles that distinguish it from other heating equipment. It is fundamentally a batch-processing tool designed for maximum control over a single, enclosed volume.
Precise Temperature Control
The hallmark of a quality chamber furnace is its ability to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the interior. This is critical for ensuring that an entire part or batch of materials receives the exact same thermal treatment.
These systems are engineered for stable control and rapid heating rates, allowing users to execute specific temperature profiles required for complex processes.
Atmospheric Management
Unlike a simple oven, a chamber furnace allows for deliberate management of the internal atmosphere. This can range from operating in ambient air to introducing specific gases.
Many models, particularly vacuum chamber furnaces, can pull a vacuum to remove contaminants and then introduce inert gases like argon or nitrogen, or reactive gases like hydrogen or oxygen. This atmospheric control is crucial for preventing oxidation and achieving specific material reactions.
A Contained, Clean Environment
The enclosed "box" design serves to isolate the workload from the outside environment. This prevents contamination and ensures the purity of the process, which is vital in fields like dental prosthetics or electronics manufacturing.
The sealed nature of the chamber is what makes precise atmospheric and vacuum control possible.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the chamber furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its inherent design limitations is key to using it effectively.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
A chamber furnace is a batch processing tool. You load the material, seal the chamber, run the heating cycle, cool it down, and then unload it.
This is ideal for research, prototyping, or low-volume production. However, for high-volume manufacturing, a continuous furnace (like a conveyor or tunnel furnace) that processes parts without interruption is far more efficient.
Thermal Cycling and Energy Use
Because the entire chamber must be heated and cooled for each batch, there can be significant energy consumption and time spent on non-productive thermal cycling.
While modern designs are very energy-efficient, this start-and-stop nature contrasts with continuous furnaces that are held at a stable operating temperature for long periods.
Size and Throughput Limitations
The physical volume of the chamber inherently limits the size and quantity of the parts that can be processed at one time. This design is not well-suited for very large components or mass production scenarios where throughput is the primary metric.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your objective. The chamber furnace excels in applications where precision outweighs sheer volume.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or prototyping: A chamber furnace is the ideal choice due to its versatility and precise control over temperature and atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace design will likely offer better throughput and operational efficiency for your manufacturing line.
- If your primary focus is process purity and avoiding contamination: The sealed environment of a chamber furnace provides the clean, controlled conditions necessary for sensitive materials.
Ultimately, a chamber furnace is a foundational tool for anyone who needs to reliably and accurately transform materials through heat.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Enclosed Chamber | Isolates materials, prevents contamination |
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures uniform heating and repeatable results |
| Atmospheric Management | Enables vacuum, inert gas, or reactive gas environments |
| Batch Processing | Ideal for R&D, prototyping, and small-scale production |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a reliable chamber furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including chamber furnaces designed for precise thermal processing. Whether you're in research, development, or small-scale manufacturing, our solutions ensure material integrity and process repeatability. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















